Question Number 184557 by a.lgnaoui last updated on 08/Jan/23

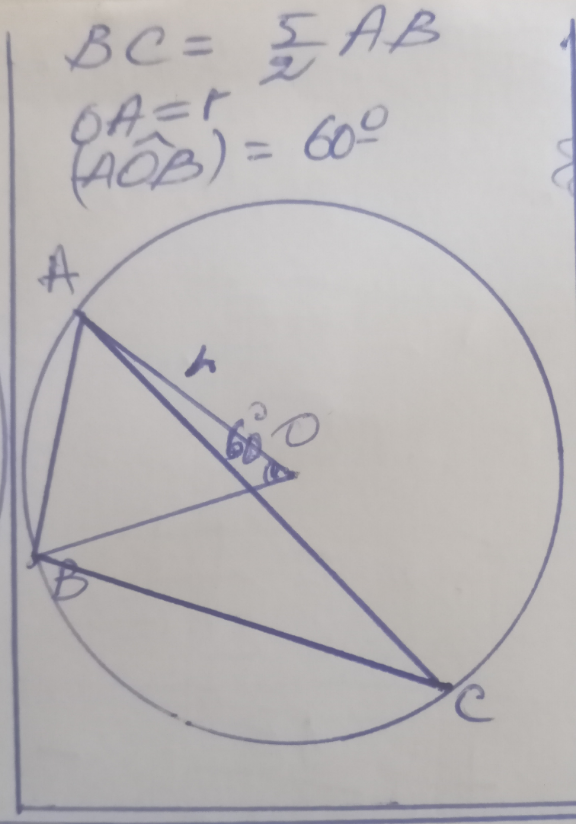
$${Determiner} \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}\bullet\mathrm{AB},\:\:\mathrm{BC}\:\:\mathrm{AC}\:\mathrm{en}\:\mathrm{fonction}\:\mathrm{de}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{r}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}\bullet\:\:\measuredangle\mathrm{CBA}\:;\:\:\measuredangle\mathrm{BAC}\:;{et}\:\measuredangle\mathrm{BCA} \\ $$
Commented by a.lgnaoui last updated on 08/Jan/23
Answered by a.lgnaoui last updated on 09/Jan/23
$$\: \\ $$$${Reponse} \\ $$$$−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−− \\ $$$$\measuredangle{AOB}=\mathrm{60}=\mathrm{2}\measuredangle{ACCB}\:\Rightarrow\measuredangle{ACB}=\mathrm{30} \\ $$$$\left({Propriete}\:{de}\:{angle}\:{au}\:{centre}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}\bullet{AB}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{2}{r}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{60}\right)\Rightarrow\boldsymbol{{AB}}=\boldsymbol{{r}}\left(\bigtriangleup{AOB}\:{Equilaterale}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:{AB}^{\mathrm{2}} ={AC}^{\mathrm{2}} +{BC}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{AC}×{BC}\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{30} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:{AB}=\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}{BC}\:\:\:\Rightarrow\:\boldsymbol{{BC}}=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}\boldsymbol{{r}}\: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{r}^{\mathrm{2}} ={AC}^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{25}}{r}^{\mathrm{2}} −\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{5}}{rAC}\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{30} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:{r}^{\mathrm{2}} ={AC}^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{25}}{r}^{\mathrm{2}} −\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{5}}{r}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\:×{AC} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:{AC}={x}\:\: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:−\frac{\mathrm{2}{r}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{5}}{x}−\frac{\mathrm{21}}{\mathrm{25}}{r}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\left({x}−\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\:+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{6}}\:}{\mathrm{5}}{r}\right)\left({x}−\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\:−\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{6}}\:\:}{\mathrm{5}}{r}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{AC}=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\:+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{6}}}{\mathrm{5}}\boldsymbol{{r}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}\bullet{calul}\:{des}\:{angles} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\measuredangle{BCA}=\frac{\mathrm{60}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{30} \\ $$$$\:\:\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\measuredangle{ABC}\right)}{\left(\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\:+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{6}}}{\mathrm{5}}\:\right){r}}=\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{30}}{{r}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{r}} \\ $$$$\:\:\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\measuredangle{ABC}\right)=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\:+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{6}}}{\mathrm{10}}=\mathrm{0},\mathrm{6631} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\measuredangle{ABC}=\mathrm{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\:+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{6}}}{\mathrm{10}}\right)\: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\measuredangle\boldsymbol{{ABC}}=\mathrm{41},\mathrm{53} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\measuredangle{BAC}=\left(\mathrm{180}−\mathrm{30}−\mathrm{41},\mathrm{53}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\measuredangle\boldsymbol{{BAC}}=\mathrm{108},\mathrm{47} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\: \\ $$
