Question Number 64642 by mmkkmm000m last updated on 19/Jul/19
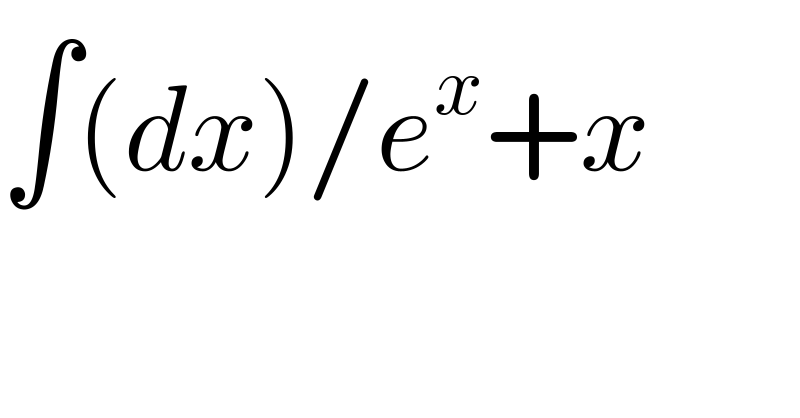
$$\int\left({dx}\right)/{e}^{{x}} +{x} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 20/Jul/19

$${let}\:{I}\:=\int\:\:\:\frac{{dx}}{{x}+{e}^{{x}} }\:\Rightarrow{I}\:=\int\:\:\:\frac{{e}^{−{x}} }{{xe}^{−{x}} \:+\mathrm{1}}{dx}\:\:\:{if}\:{we}\:{know}\:{that}\:\mid{x}\mid<\mathrm{1}\:{we}\:{get} \\ $$$${I}\:=\int\:{e}^{−{x}} \left(\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} \left({xe}^{−{x}} \right)^{{n}} \right)=\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} \:\int\:\:\:{x}^{{n}} {e}^{−\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right){x}} {dx} \\ $$$$=_{\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right){x}\:={t}} \:\:\:\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} \:\int\:\:\frac{{t}^{{n}} }{\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} }\:{e}^{−{t}} \:\frac{{dt}}{\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)} \\ $$$$=\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} }{\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }\:\int\:\:{t}^{{n}} \:{e}^{−{t}} {dt}\:=\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} }{\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }\:{A}_{{n}} \\ $$$${with}\:{A}_{{n}} =\int\:{t}^{{n}} \:{e}^{−{t}} \:{dt}\:\:{this}\:{sequence}\:{can}\:{be}\:{known}\:{if}\:{we}\:{have} \\ $$$${the}\:{limits}\:{of}\:{integral}… \\ $$$$ \\ $$
