Question Number 102639 by bobhans last updated on 10/Jul/20
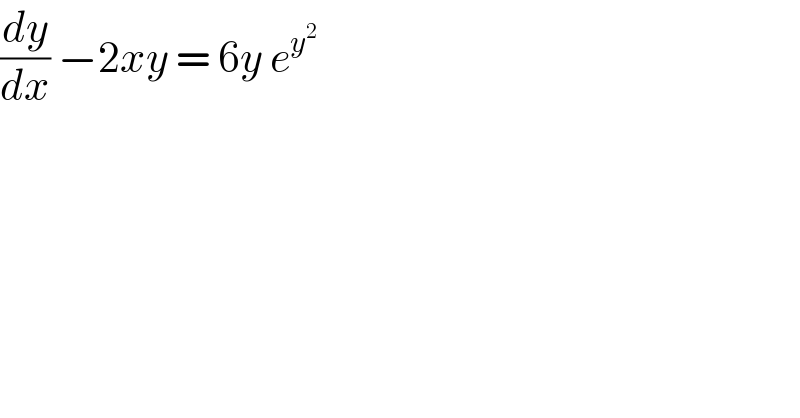
$$\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\:−\mathrm{2}{xy}\:=\:\mathrm{6}{y}\:{e}^{{y}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 10/Jul/20

$$\mathrm{Let}\:\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{vx}\:\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}=\mathrm{v}+\mathrm{x}\frac{\mathrm{dv}}{\mathrm{dx}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{v}+\mathrm{x}\frac{\mathrm{dv}}{\mathrm{dx}}−\mathrm{2vx}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{6vxe}^{\mathrm{v}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{x}\frac{\mathrm{dv}}{\mathrm{dx}}=\mathrm{v}\left(\mathrm{6xe}^{\mathrm{v}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } +\mathrm{2x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${Any}\:{idea}\:{to}\:{proceed}\:?\:{Am}\:{I}\:{on}\:{the}\:{right}\:{track}\:? \\ $$
