Question Number 106391 by Ar Brandon last updated on 05/Aug/20
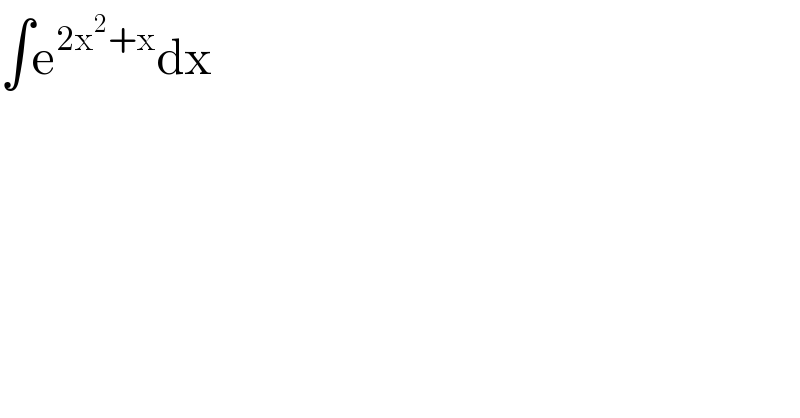
$$\int\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{dx} \\ $$
Answered by Sarah85 last updated on 05/Aug/20
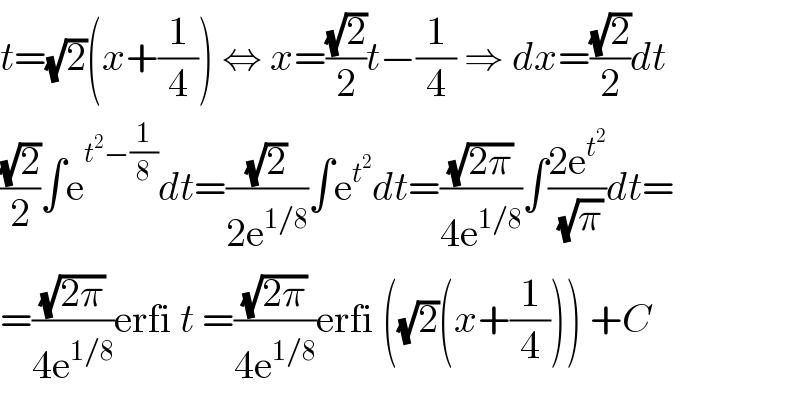
$${t}=\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\left({x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\right)\:\Leftrightarrow\:{x}=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{2}}{t}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\:\Rightarrow\:{dx}=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{2}}{dt} \\ $$$$\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\mathrm{e}^{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} −\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8}}} {dt}=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{2e}^{\mathrm{1}/\mathrm{8}} }\int\mathrm{e}^{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} } {dt}=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}\pi}}{\mathrm{4e}^{\mathrm{1}/\mathrm{8}} }\int\frac{\mathrm{2e}^{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} } }{\:\sqrt{\pi}}{dt}= \\ $$$$=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}\pi}}{\mathrm{4e}^{\mathrm{1}/\mathrm{8}} }\mathrm{erfi}\:{t}\:=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}\pi}}{\mathrm{4e}^{\mathrm{1}/\mathrm{8}} }\mathrm{erfi}\:\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\left({x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\right)\right)\:+{C} \\ $$
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 05/Aug/20
Thanks
