Question Number 60791 by arcana last updated on 25/May/19

$$\int\frac{{e}^{{n}} }{{x}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{dx},\:\mathrm{n}\in\mathbb{N} \\ $$
Commented by Forkum Michael Choungong last updated on 25/May/19
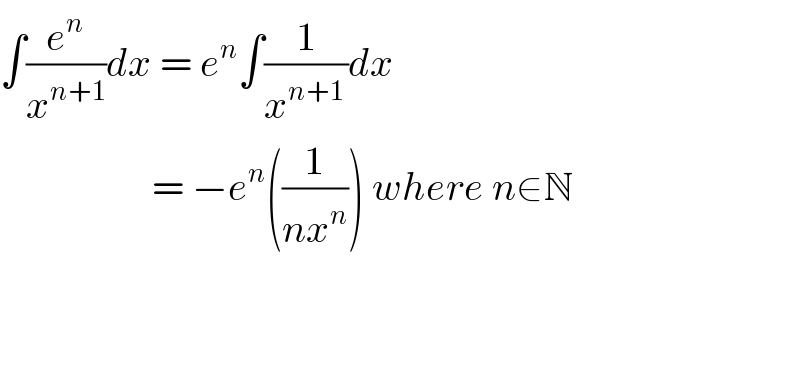
$$\int\frac{{e}^{{n}} }{{x}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{dx}\:=\:{e}^{{n}} \int\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}\:} }{dx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\:−{e}^{{n}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{nx}^{{n}} }\right)\:{where}\:{n}\in\mathbb{N} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by arcana last updated on 25/May/19

$$\mathrm{thanks} \\ $$
Answered by MJS last updated on 25/May/19
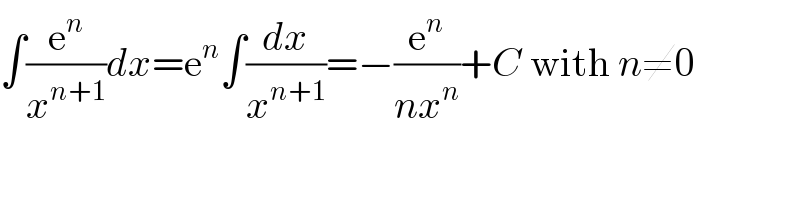
$$\int\frac{\mathrm{e}^{{n}} }{{x}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{dx}=\mathrm{e}^{{n}} \int\frac{{dx}}{{x}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }=−\frac{\mathrm{e}^{{n}} }{{nx}^{{n}} }+{C}\:\mathrm{with}\:{n}\neq\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by arcana last updated on 25/May/19

$$\mathrm{thanks} \\ $$
