Question Number 33494 by mondodotto@gmail.com last updated on 17/Apr/18

$$\:\int\frac{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} }{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{sin}}^{\mathrm{2}} \boldsymbol{{x}}\:\:\:\:}\boldsymbol{{dx}} \\ $$
Commented by math khazana by abdo last updated on 18/Apr/18
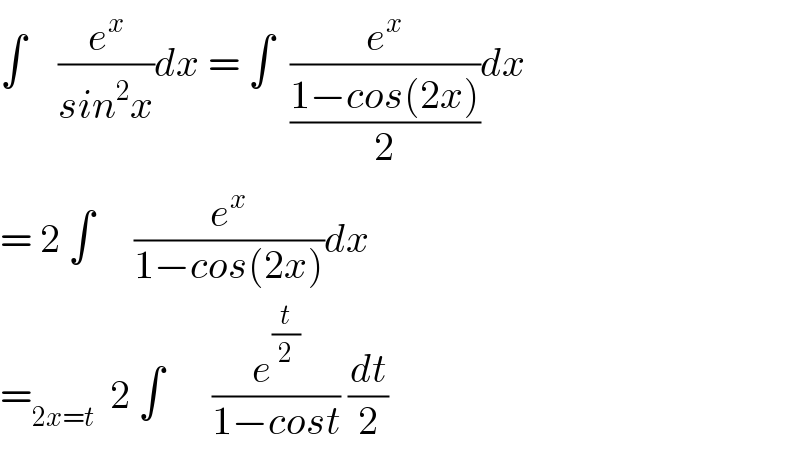
$$\int\:\:\:\:\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}{dx}\:=\:\int\:\:\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{\frac{\mathrm{1}−{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}}{dx} \\ $$$$=\:\mathrm{2}\:\int\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{\mathrm{1}−{cos}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)}{dx} \\ $$$$=_{\mathrm{2}{x}={t}} \:\:\mathrm{2}\:\int\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{e}^{\frac{{t}}{\mathrm{2}}} }{\mathrm{1}−{cost}}\:\frac{{dt}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by math khazana by abdo last updated on 18/Apr/18
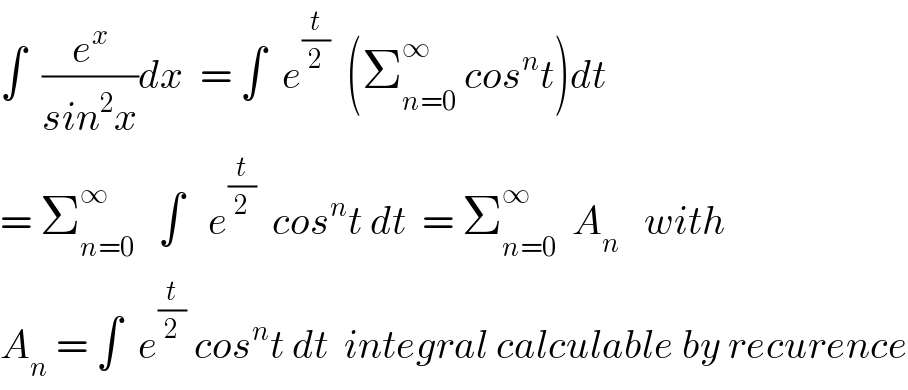
$$\int\:\:\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}{dx}\:\:=\:\int\:\:{e}^{\frac{{t}}{\mathrm{2}}} \:\:\left(\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:{cos}^{{n}} {t}\right){dt} \\ $$$$=\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\:\int\:\:\:{e}^{\frac{{t}}{\mathrm{2}}} \:\:{cos}^{{n}} {t}\:{dt}\:\:=\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:{A}_{{n}} \:\:\:{with} \\ $$$${A}_{{n}} \:=\:\int\:\:{e}^{\frac{{t}}{\mathrm{2}}} \:{cos}^{{n}} {t}\:{dt}\:\:{integral}\:{calculable}\:{by}\:{recurence} \\ $$
