Question Number 163828 by milandou last updated on 11/Jan/22

$$\int\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{{x}} \\ $$
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 11/Jan/22
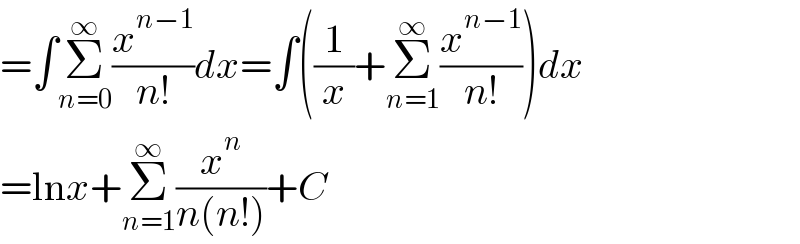
$$=\int\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{x}^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} }{{n}!}{dx}=\int\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}+\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{x}^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} }{{n}!}\right){dx} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{ln}{x}+\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{x}^{{n}} }{{n}\left({n}!\right)}+{C} \\ $$
Answered by essojean last updated on 20/Jan/22

$$\int\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{{x}}={Ei}\left({x}\right)+{c} \\ $$
