Question Number 95397 by ~blr237~ last updated on 25/May/20
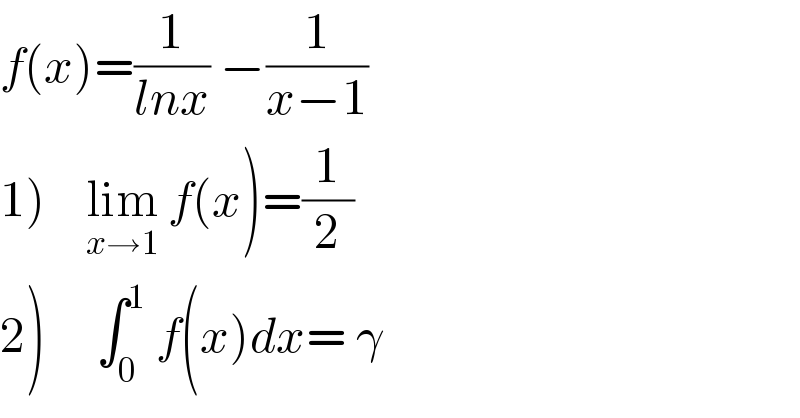
$${f}\left({x}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{lnx}}\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\: \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right)\:\:\:\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\: \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right)\:\:\:\:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:{f}\left({x}\right){dx}=\:\gamma\: \\ $$
Commented by Mikael_786 last updated on 25/May/20
![1. lim_(x→1) {(1/(lnx))−(1/(x−1))} lim_(x→1) {(1/(x−1))(((x−1)/(lnx))−1)}=lim_(x→1) {(1/(x−1))(∫_0 ^1 x^y dy−1)} lim_(x→1) {∫_0 ^1 (x^y /(x−1))dy−∫_0 ^1 (1/(x−1))dy} lim_(x→1) {∫_0 ^1 ((x^y −1)/(x−1))dy}=∫_0 ^1 {lim_(x→1) ((x^y −1)/(x−1))}dy =∫_0 ^1 ydy=[(y^2 /2)]_0 ^1 =(1/2)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q95519.png)
$$\mathrm{1}.\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {{lim}}\left\{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{lnx}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\right\} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {{lim}}\left\{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\left(\frac{{x}−\mathrm{1}}{{lnx}}−\mathrm{1}\right)\right\}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {{lim}}\:\left\{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\left(\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}{x}^{{y}} {dy}−\mathrm{1}\right)\right\} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {{lim}}\left\{\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\frac{{x}^{{y}} }{{x}−\mathrm{1}}{dy}−\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}{dy}\right\} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {{lim}}\left\{\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\:\frac{{x}^{{y}} −\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}{dy}\right\}=\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\:\left\{\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{1}} {{lim}}\:\frac{{x}^{{y}} −\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\right\}{dy} \\ $$$$=\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}{ydy}=\left[\frac{{y}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by Mikael_786 last updated on 25/May/20
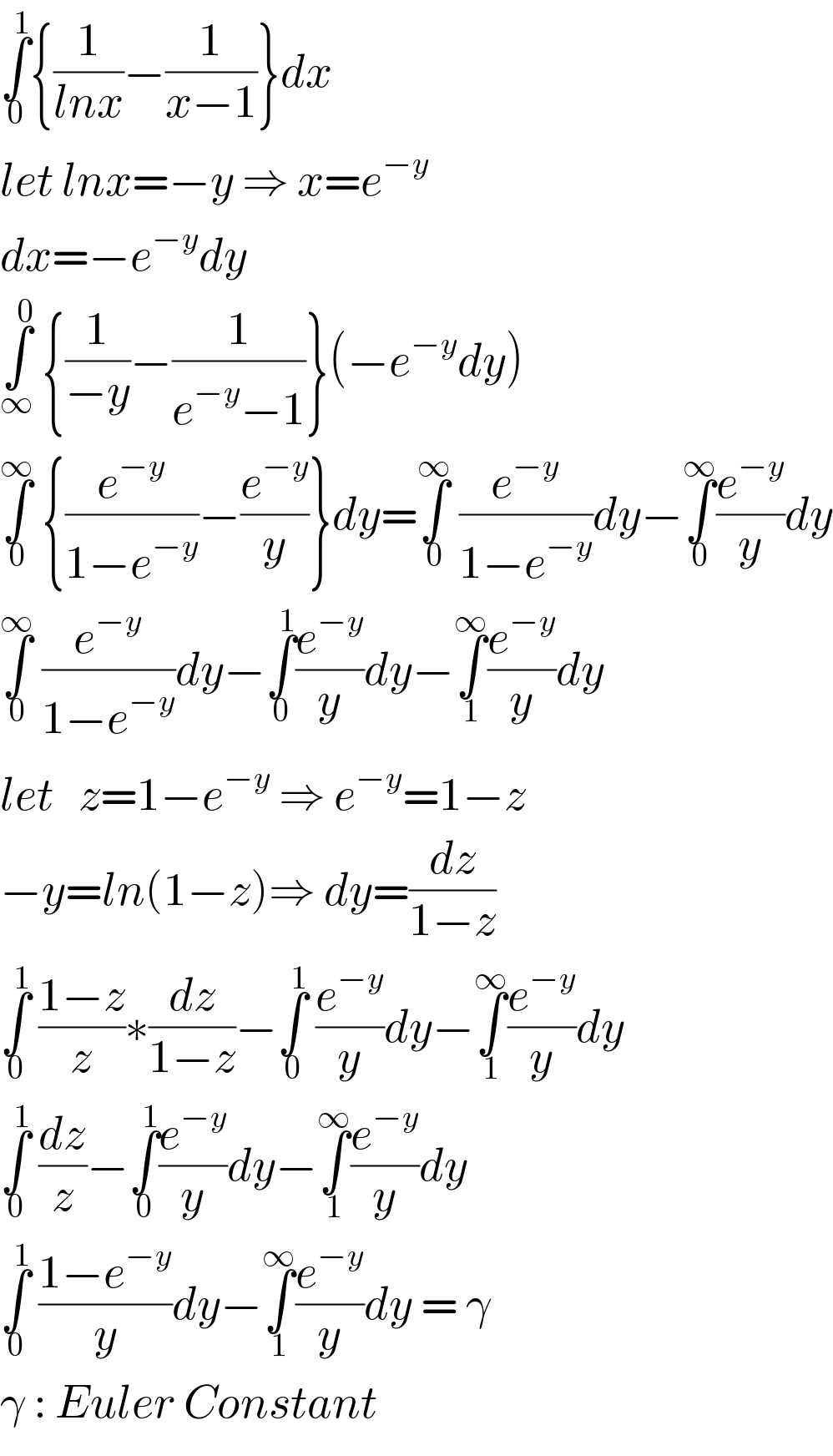
$$\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\left\{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{lnx}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\right\}{dx} \\ $$$${let}\:{lnx}=−{y}\:\Rightarrow\:{x}={e}^{−{y}} \\ $$$${dx}=−{e}^{−{y}} {dy} \\ $$$$\underset{\infty} {\overset{\mathrm{0}} {\int}}\:\left\{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{−{y}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{e}^{−{y}} −\mathrm{1}}\right\}\left(−{e}^{−{y}} {dy}\right) \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\int}}\:\left\{\frac{{e}^{−{y}} }{\mathrm{1}−{e}^{−{y}} }−\frac{{e}^{−{y}} }{{y}}\right\}{dy}=\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\int}}\:\frac{{e}^{−{y}} }{\mathrm{1}−{e}^{−{y}} }{dy}−\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\int}}\frac{{e}^{−{y}} }{{y}}{dy} \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\int}}\:\frac{{e}^{−{y}} }{\mathrm{1}−{e}^{−{y}} }{dy}−\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\frac{{e}^{−{y}} }{{y}}{dy}−\underset{\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\int}}\frac{{e}^{−{y}} }{{y}}{dy} \\ $$$${let}\:\:\:{z}=\mathrm{1}−{e}^{−{y}} \:\Rightarrow\:{e}^{−{y}} =\mathrm{1}−{z} \\ $$$$−{y}={ln}\left(\mathrm{1}−{z}\right)\Rightarrow\:{dy}=\frac{{dz}}{\mathrm{1}−{z}} \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}−{z}}{{z}}\ast\frac{{dz}}{\mathrm{1}−{z}}−\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\:\frac{{e}^{−{y}} }{{y}}{dy}−\underset{\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\int}}\frac{{e}^{−{y}} }{{y}}{dy} \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\:\frac{{dz}}{{z}}−\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\frac{{e}^{−{y}} }{{y}}{dy}−\underset{\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\int}}\frac{{e}^{−{y}} }{{y}}{dy} \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}} {\int}}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}−{e}^{−{y}} }{{y}}{dy}−\underset{\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\int}}\frac{{e}^{−{y}} }{{y}}{dy}\:=\:\gamma \\ $$$$\gamma\::\:{Euler}\:{Constant} \\ $$
