Question Number 167054 by shikaridwan last updated on 05/Mar/22
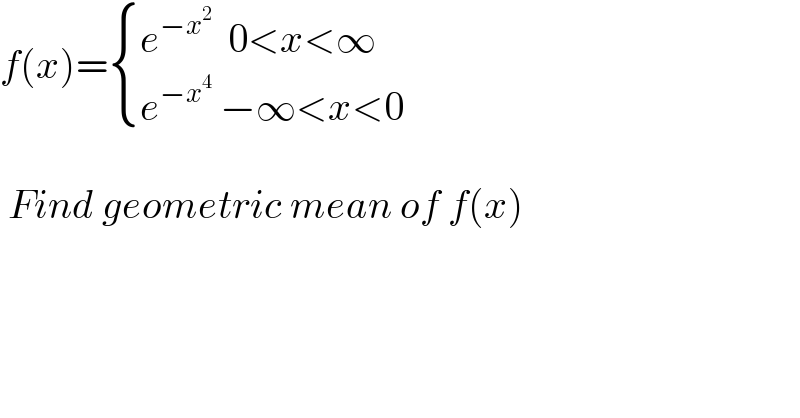
$${f}\left({x}\right)=\begin{cases}{{e}^{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \:\:\mathrm{0}<{x}<\infty}\\{{e}^{−{x}^{\mathrm{4}} } \:−\infty<{x}<\mathrm{0}\:\:\:\:}\end{cases} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\:{Find}\:{geometric}\:{mean}\:{of}\:{f}\left({x}\right) \\ $$
Answered by aleks041103 last updated on 05/Mar/22
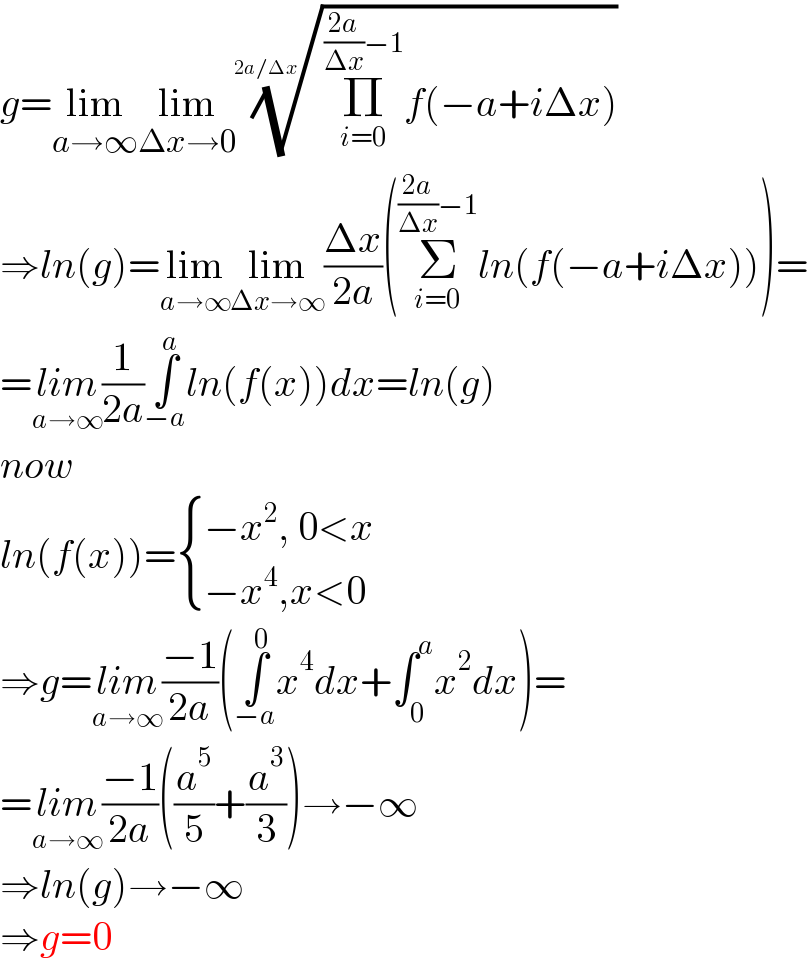
$${g}=\underset{{a}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\underset{\Delta{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\sqrt[{\mathrm{2}{a}/\Delta{x}}]{\underset{{i}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\frac{\mathrm{2}{a}}{\Delta{x}}−\mathrm{1}} {\prod}}{f}\left(−{a}+{i}\Delta{x}\right)} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{ln}\left({g}\right)=\underset{{a}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\underset{\Delta{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\Delta{x}}{\mathrm{2}{a}}\left(\underset{{i}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\frac{\mathrm{2}{a}}{\Delta{x}}−\mathrm{1}} {\sum}}{ln}\left({f}\left(−{a}+{i}\Delta{x}\right)\right)\right)= \\ $$$$=\underset{{a}\rightarrow\infty} {{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{a}}\underset{−{a}} {\overset{{a}} {\int}}{ln}\left({f}\left({x}\right)\right){dx}={ln}\left({g}\right) \\ $$$${now} \\ $$$${ln}\left({f}\left({x}\right)\right)=\begin{cases}{−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} ,\:\mathrm{0}<{x}}\\{−{x}^{\mathrm{4}} ,{x}<\mathrm{0}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{g}=\underset{{a}\rightarrow\infty} {{lim}}\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{a}}\left(\underset{−{a}} {\overset{\mathrm{0}} {\int}}{x}^{\mathrm{4}} {dx}+\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{a}} {x}^{\mathrm{2}} {dx}\right)= \\ $$$$=\underset{{a}\rightarrow\infty} {{lim}}\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{a}}\left(\frac{{a}^{\mathrm{5}} }{\mathrm{5}}+\frac{{a}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}}\right)\rightarrow−\infty \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{ln}\left({g}\right)\rightarrow−\infty \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{g}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
