Question Number 40052 by LXZ last updated on 15/Jul/18
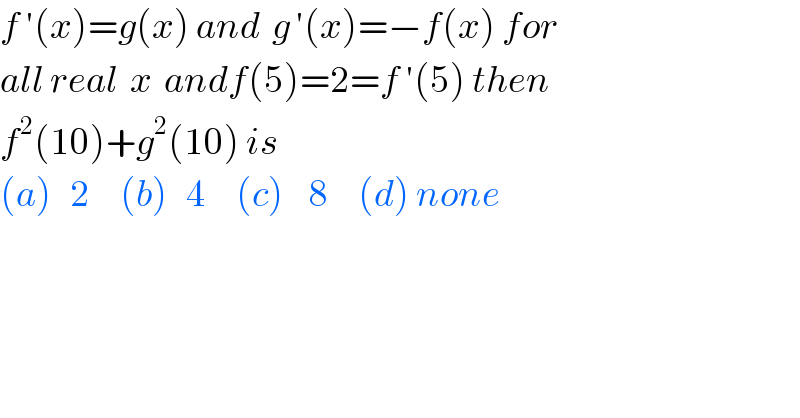
$${f}\:'\left({x}\right)={g}\left({x}\right)\:{and}\:\:{g}\:'\left({x}\right)=−{f}\left({x}\right)\:{for} \\ $$$${all}\:{real}\:\:{x}\:\:{andf}\left(\mathrm{5}\right)=\mathrm{2}={f}\:'\left(\mathrm{5}\right)\:{then} \\ $$$${f}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{10}\right)+{g}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{10}\right)\:{is} \\ $$$$\left({a}\right)\:\:\:\mathrm{2}\:\:\:\:\:\left({b}\right)\:\:\:\mathrm{4}\:\:\:\:\:\left({c}\right)\:\:\:\:\mathrm{8}\:\:\:\:\:\left({d}\right)\:{none} \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 15/Jul/18
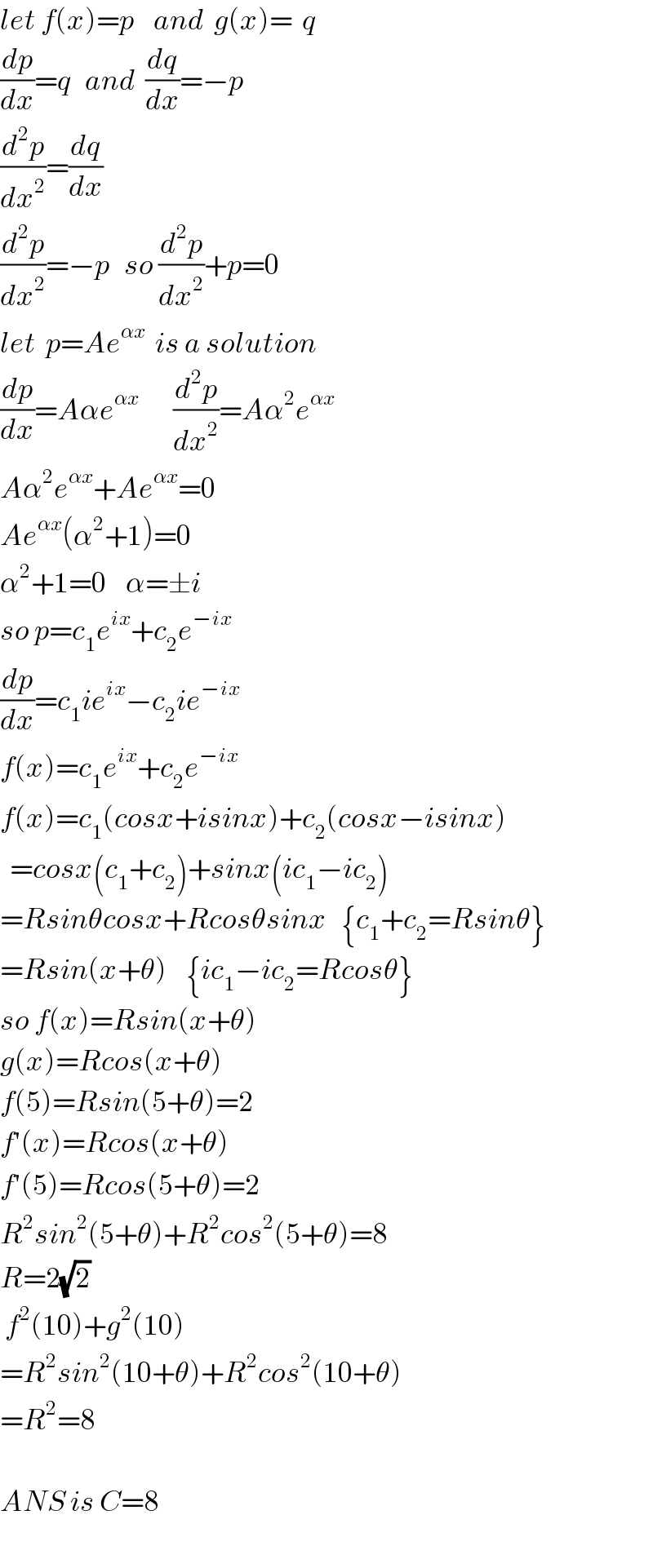
$${let}\:{f}\left({x}\right)={p}\:\:\:\:{and}\:\:{g}\left({x}\right)=\:\:{q} \\ $$$$\frac{{dp}}{{dx}}={q}\:\:\:{and}\:\:\frac{{dq}}{{dx}}=−{p} \\ $$$$\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {p}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{{dq}}{{dx}} \\ $$$$\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {p}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }=−{p}\:\:\:{so}\:\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {p}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }+{p}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${let}\:\:{p}={Ae}^{\alpha{x}} \:\:{is}\:{a}\:{solution} \\ $$$$\frac{{dp}}{{dx}}={A}\alpha{e}^{\alpha{x}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {p}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }={A}\alpha^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{\alpha{x}} \\ $$$${A}\alpha^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{\alpha{x}} +{Ae}^{\alpha{x}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${Ae}^{\alpha{x}} \left(\alpha^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\alpha^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0}\:\:\:\:\alpha=\pm{i} \\ $$$${so}\:{p}={c}_{\mathrm{1}} {e}^{{ix}} +{c}_{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−{ix}} \\ $$$$\frac{{dp}}{{dx}}={c}_{\mathrm{1}} {ie}^{{ix}} −{c}_{\mathrm{2}} {ie}^{−{ix}} \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)={c}_{\mathrm{1}} {e}^{{ix}} +{c}_{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−{ix}} \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)={c}_{\mathrm{1}} \left({cosx}+{isinx}\right)+{c}_{\mathrm{2}} \left({cosx}−{isinx}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:={cosx}\left({c}_{\mathrm{1}} +{c}_{\mathrm{2}} \right)+{sinx}\left({ic}_{\mathrm{1}} −{ic}_{\mathrm{2}} \right) \\ $$$$={Rsin}\theta{cosx}+{Rcos}\theta{sinx}\:\:\:\left\{{c}_{\mathrm{1}} +{c}_{\mathrm{2}} ={Rsin}\theta\right\} \\ $$$$={Rsin}\left({x}+\theta\right)\:\:\:\:\left\{{ic}_{\mathrm{1}} −{ic}_{\mathrm{2}} ={Rcos}\theta\right\} \\ $$$${so}\:{f}\left({x}\right)={Rsin}\left({x}+\theta\right) \\ $$$${g}\left({x}\right)={Rcos}\left({x}+\theta\right) \\ $$$${f}\left(\mathrm{5}\right)={Rsin}\left(\mathrm{5}+\theta\right)=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${f}'\left({x}\right)={Rcos}\left({x}+\theta\right) \\ $$$${f}'\left(\mathrm{5}\right)={Rcos}\left(\mathrm{5}+\theta\right)=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${R}^{\mathrm{2}} {sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{5}+\theta\right)+{R}^{\mathrm{2}} {cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{5}+\theta\right)=\mathrm{8} \\ $$$${R}=\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\: \\ $$$$\:{f}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{10}\right)+{g}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{10}\right) \\ $$$$={R}^{\mathrm{2}} {sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{10}+\theta\right)+{R}^{\mathrm{2}} {cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{10}+\theta\right) \\ $$$$={R}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{8} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${ANS}\:{is}\:{C}=\mathrm{8} \\ $$
Commented by LXZ last updated on 15/Jul/18

$${thanks}\:{sir} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by ajfour last updated on 16/Jul/18
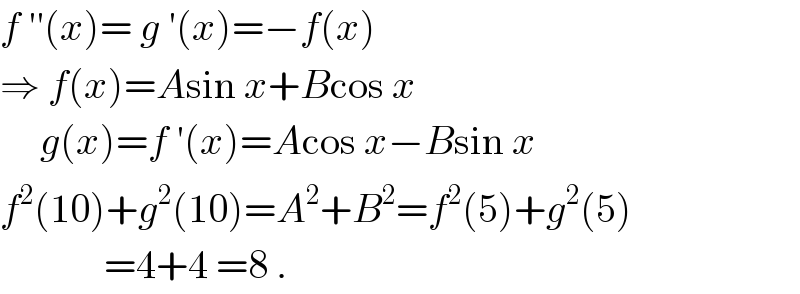
$${f}\:''\left({x}\right)=\:{g}\:'\left({x}\right)=−{f}\left({x}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{f}\left({x}\right)={A}\mathrm{sin}\:{x}+{B}\mathrm{cos}\:{x} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:{g}\left({x}\right)={f}\:'\left({x}\right)={A}\mathrm{cos}\:{x}−{B}\mathrm{sin}\:{x} \\ $$$${f}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{10}\right)+{g}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{10}\right)={A}^{\mathrm{2}} +{B}^{\mathrm{2}} ={f}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{5}\right)+{g}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{5}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{4}\:=\mathrm{8}\:. \\ $$
