Question Number 24042 by Tinkutara last updated on 11/Nov/17
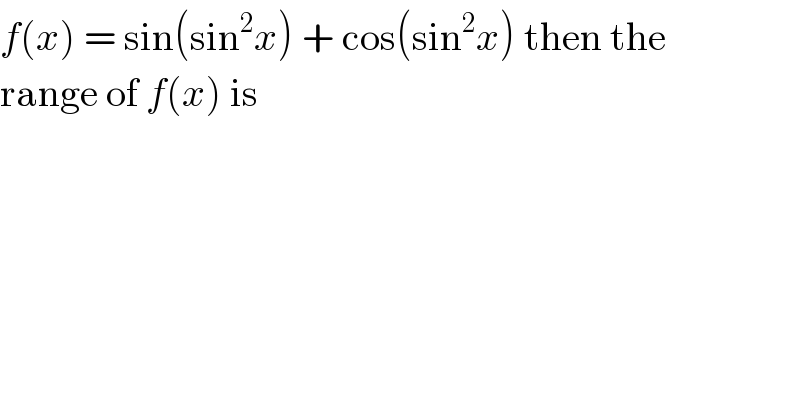
$${f}\left({x}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}\right)\:+\:\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}\right)\:\mathrm{then}\:\mathrm{the} \\ $$$$\mathrm{range}\:\mathrm{of}\:{f}\left({x}\right)\:\mathrm{is} \\ $$
Commented by mrW1 last updated on 11/Nov/17
![[1,(√2)] f(x)=sin (sin^2 x)+cos (sin^2 x) =(√2)[sin (sin^2 x)cos (π/4)+cos (sin^2 x)sin (π/4)] =(√2) sin (sin^2 x+(π/4)) sin (sin^2 x+(π/4))≥sin (π/4)=(1/( (√2))) sin (sin^2 x+(π/4))≤1 ⇒1≤f(x)≤(√2)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q24049.png)
$$\left[\mathrm{1},\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right] \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{x}\right)+\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{x}\right) \\ $$$$=\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\left[\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{x}\right)\mathrm{cos}\:\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}+\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{x}\right)\mathrm{sin}\:\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\right] \\ $$$$=\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\:\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{x}+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{x}+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\right)\geqslant\mathrm{sin}\:\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{x}+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\right)\leqslant\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{1}\leqslant{f}\left({x}\right)\leqslant\sqrt{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by Tinkutara last updated on 12/Nov/17
$$\mathrm{Thank}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{very}\:\mathrm{much}\:\mathrm{Sir}! \\ $$
Answered by chowdhuryashis last updated on 11/Nov/17
![[−2,2]](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q24046.png)
$$\left[−\mathrm{2},\mathrm{2}\right] \\ $$
Commented by Tinkutara last updated on 12/Nov/17

$$\mathrm{Wrong}. \\ $$
