Question Number 36799 by abdo.msup.com last updated on 05/Jun/18
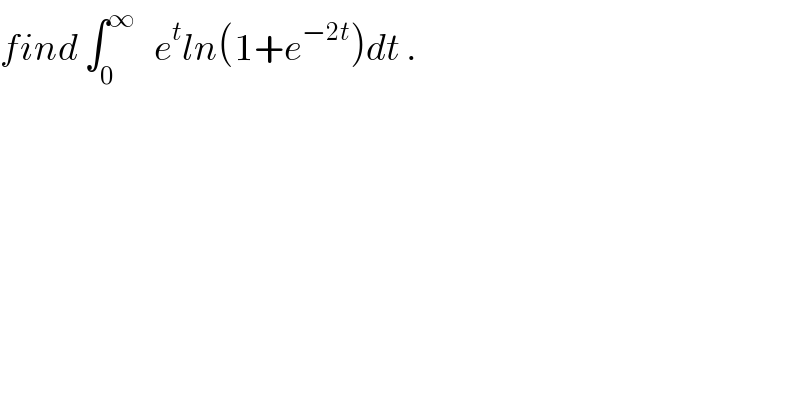
$${find}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\:{e}^{{t}} {ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} \right){dt}\:. \\ $$
Commented by math khazana by abdo last updated on 11/Jun/18
![let I = ∫_0 ^∞ e^t ln(1+e^(−2t) )dt by parts u^′ =e^t and v =ln(1+e^(−2t) ) ⇒ I = [ e^t ln(1+e^(−2t) )]_0 ^(+∞) −∫_0 ^∞ e^t ((−2 e^(−2t) )/(1+e^(−2t) ))dt =−ln(2) +2 ∫_0 ^∞ (e^(−t) /(1+e^(−2t) )) dt but ∫_0 ^∞ (e^(−t) /(1+e^(−2t) )) dt =_(e^t =x) ∫_1 ^(+∞) (1/(x(1+(1/x^2 )))) (dx/x) = ∫_1 ^(+∞) (dx/(x^2 +1)) =[arctanx]_1 ^(+∞) =(π/2) −(π/4) =(π/4) ⇒ ★I = −ln(2) +(π/2) ★](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q37242.png)
$${let}\:{I}\:=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\:{e}^{{t}} \:{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} \right){dt}\:{by}\:{parts} \\ $$$${u}^{'} ={e}^{{t}} \:\:{and}\:{v}\:={ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} \right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${I}\:=\:\left[\:{e}^{{t}} {ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} \right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{+\infty} \:−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:{e}^{{t}} \:\:\frac{−\mathrm{2}\:{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} }{\mathrm{1}+{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} }{dt} \\ $$$$=−{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:+\mathrm{2}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\:\frac{{e}^{−{t}} }{\mathrm{1}+{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} }\:{dt}\:{but} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\:\:\frac{{e}^{−{t}} }{\mathrm{1}+{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} }\:{dt}\:=_{{e}^{{t}} ={x}} \:\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{+\infty} \:\:\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)}\:\frac{{dx}}{{x}} \\ $$$$=\:\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{+\infty} \:\:\:\:\frac{{dx}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}}\:=\left[{arctanx}\right]_{\mathrm{1}} ^{+\infty} =\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\:−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\:=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\bigstar{I}\:=\:−{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:+\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\:\bigstar \\ $$
Answered by MJS last updated on 06/Jun/18
![∫e^t ln(1+e^(−2t) )dt= [((∫f′g=fg−∫fg′)),((f′=e^t ⇒ f=e^t )),((g=ln(1+e^(−2t) ) ⇒ g′=−((2e^(−2t) )/(1+e^(−2t) )))) ] =e^t ln(1+e^(−2t) )−2∫−(e^(−t) /(1+e^(−2t) ))dt= [u=−e^t → dt=−e^t du] =e^t ln(1+e^(−2t) )−2∫(u/(1+u^2 ))du= =e^t ln(1+e^(−2t) )−2arctan u= =e^t ln(1+e^(−2t) )−2arctan −e^t = =e^t ln(1+e^(−2t) )+2arctan e^t +C ∫_0 ^∞ e^t ln(1+e^(−2t) )dt=(π/2)−ln 2](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q36832.png)
$$\int\mathrm{e}^{{t}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} \right){dt}= \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\begin{bmatrix}{\int{f}'{g}={fg}−\int{fg}'}\\{{f}'=\mathrm{e}^{{t}} \:\Rightarrow\:{f}=\mathrm{e}^{{t}} }\\{{g}=\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} \right)\:\Rightarrow\:{g}'=−\frac{\mathrm{2e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} }{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} }}\end{bmatrix} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{e}^{{t}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} \right)−\mathrm{2}\int−\frac{\mathrm{e}^{−{t}} }{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} }{dt}= \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\left[{u}=−\mathrm{e}^{{t}} \:\rightarrow\:{dt}=−\mathrm{e}^{{t}} {du}\right] \\ $$$$=\mathrm{e}^{{t}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} \right)−\mathrm{2}\int\frac{{u}}{\mathrm{1}+{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }{du}= \\ $$$$=\mathrm{e}^{{t}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} \right)−\mathrm{2arctan}\:{u}= \\ $$$$=\mathrm{e}^{{t}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} \right)−\mathrm{2arctan}\:−\mathrm{e}^{{t}} = \\ $$$$=\mathrm{e}^{{t}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} \right)+\mathrm{2arctan}\:\mathrm{e}^{{t}} +{C} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\int}}\mathrm{e}^{{t}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} \right){dt}=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$
