Question Number 31056 by abdo imad last updated on 02/Mar/18
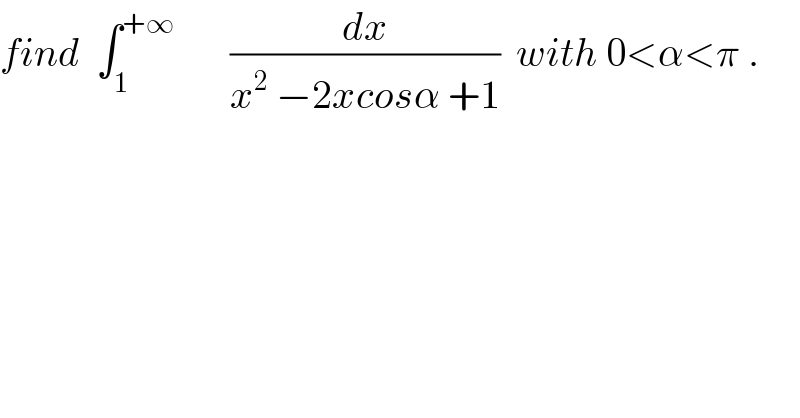
$${find}\:\:\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{+\infty} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{dx}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:−\mathrm{2}{xcos}\alpha\:+\mathrm{1}}\:\:{with}\:\mathrm{0}<\alpha<\pi\:. \\ $$
Commented by abdo imad last updated on 03/Mar/18
![I= ∫_1 ^(+∞) (dx/(x^2 −2xcosα +cos^2 α +sin^2 α)) =∫_1 ^(+∞) (dx/((x−cosα)^2 +sin^2 α)) the ch. x−cosα=sinα t give I= ∫_((1−cosα)/(sinα)) ^(+∞) ((sinαdt)/(sin^2 α(1+t^2 )))= (1/(sinα)) ∫_(tan((α/2))) ^(+∞) (dt/(1+t^2 )) I= (1/(sinα)) [ arctant]_(tan((α/2))) ^(+∞) =(1/(sinα))((π/2) −(α/2))⇒ I= ((π−α)/(2sinα)) .](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q31221.png)
$${I}=\:\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{+\infty} \:\:\frac{{dx}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:−\mathrm{2}{xcos}\alpha\:+{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \alpha\:+{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \alpha} \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{+\infty} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{dx}}{\left({x}−{cos}\alpha\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \:+{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \alpha}\:{the}\:{ch}.\:{x}−{cos}\alpha={sin}\alpha\:{t}\:{give} \\ $$$${I}=\:\int_{\frac{\mathrm{1}−{cos}\alpha}{{sin}\alpha}} ^{+\infty} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{sin}\alpha{dt}}{{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \alpha\left(\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{sin}\alpha}\:\int_{{tan}\left(\frac{\alpha}{\mathrm{2}}\right)} ^{+\infty} \:\:\frac{{dt}}{\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$${I}=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{sin}\alpha}\:\left[\:{arctant}\right]_{{tan}\left(\frac{\alpha}{\mathrm{2}}\right)} ^{+\infty} \:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{sin}\alpha}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\:−\frac{\alpha}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\Rightarrow \\ $$$${I}=\:\frac{\pi−\alpha}{\mathrm{2}{sin}\alpha}\:. \\ $$
