Question Number 113952 by bemath last updated on 16/Sep/20

$${find}\:{all}\:{asymptotes}\:{of}\:{function} \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)=\left(\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}{x}−\mathrm{5}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{3}}\right)^{{x}+\mathrm{5}} \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 16/Sep/20

$$\mathrm{forgot}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{squares}??? \\ $$
Commented by bemath last updated on 16/Sep/20

$${yes}\:{sir}.\:{sorry} \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 16/Sep/20

$$\mathrm{if}\:\mathrm{it}'\mathrm{s} \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)=\left(\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}{x}−\mathrm{5}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{3}}\right)^{{x}+\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{get}\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\pm\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}{f}\left({x}\right)\:=\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{horizontal}\:\mathrm{asymptote}\:{y}=\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{rest}\:\mathrm{I}'\mathrm{m}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{sure}\:\mathrm{as}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{still}\:\mathrm{get}\:\mathrm{some} \\ $$$$\mathrm{real}\:\mathrm{solutions}\:\mathrm{for}\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}{x}−\mathrm{5}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{3}}<\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 16/Sep/20

$$…\mathrm{there}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{vertical}\:\mathrm{asymptote}\:{x}=−\mathrm{5} \\ $$
Answered by 1549442205PVT last updated on 16/Sep/20

$$\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{find}\:\mathrm{horizontal}\:\mathrm{asymptote}: \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}=\underset{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{limf}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)}=\underset{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{3x}−\mathrm{8}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{3}}\right)^{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$$=\underset{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{3x}−\mathrm{8}}}\right)\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{3x}−\mathrm{8}}.\left(\frac{\left(\mathrm{3x}−\mathrm{8}\right)\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{5}\right)}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{3}}\right) \\ $$$$=\mathrm{e}^{\underset{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{3x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{7x}−\mathrm{40}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{3}}} =\mathrm{e}^{\underset{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{3}+\frac{\mathrm{4x}−\mathrm{49}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{3}}\right)} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{3}\:} \mathrm{since}\:\:\:\underset{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{3}+\frac{\mathrm{4x}−\mathrm{49}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{3}}\right)=\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Therefore}\:\mathrm{graph}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{function} \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)=\left(\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}{x}−\mathrm{5}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{3}}\right)^{{x}+\mathrm{5}} \mathrm{has}\:\mathrm{the} \\ $$$$\mathrm{horizontal}\:\mathrm{asymptote}\:\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$
Answered by bobhans last updated on 16/Sep/20

$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:{horizontal}\:{asymptotes}\: \\ $$$$\:{y}\:=\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\pm\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:{f}\left({x}\right)\:=\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\pm\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}{x}−\mathrm{5}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{3}}\right)^{{x}+\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:=\:{e}^{\underset{{x}\rightarrow\pm\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}{x}−\mathrm{5}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{3}}\:−\:\mathrm{1}\right).\left({x}+\mathrm{5}\right)} \\ $$$$\:\:\:=\:{e}^{\underset{{x}\rightarrow\pm\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{\left(\mathrm{3}{x}−\mathrm{8}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{5}\right)}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}+\mathrm{3}}\right)} \:=\:{e}^{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{2}\right){vertical}\:{asymptotes}\: \\ $$$$\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow{a}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\pm\infty\:.\:{we}\:{aplly}\:{formula} \\ $$$$\:{If}\:{f}\left({x}\right)\:=\:\left(\frac{{h}\left({x}\right)}{{g}\left({x}\right)}\right)^{{u}\left({x}\right)} ;\:{vertical}\:{asymptotes} \\ $$$${we}\:{get}\:{from}\:{h}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{0}\:,\:{in}\:{this}\:{case} \\ $$$${h}\left({x}\right)={x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}{x}−\mathrm{5}=\left({x}+\mathrm{5}\right)\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${so}\:{the}\:{vertical}\:{asymptotes}\:{is}\:{x}=−\mathrm{5}\:\wedge{x}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 16/Sep/20

$$\mathrm{but}\:{f}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{defined},\:\mathrm{so}\:\mathrm{there}'\mathrm{s}\:\mathrm{no}\:\mathrm{asymptote} \\ $$
Commented by bobhans last updated on 16/Sep/20

$${how}\:{about}\:{f}\left(−\mathrm{5}\right)\:{sir}?\: \\ $$$${oo}\:{f}\left(−\mathrm{5}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{0}^{\mathrm{0}} \:{sir}.\:{yes}\:{x}=−\mathrm{5}\:{is} \\ $$$${vertical}\:{asymptotes} \\ $$
Commented by bobhans last updated on 16/Sep/20

Commented by bobhans last updated on 16/Sep/20

$${i}\:{apply}\:{geogebra}.\:{this}\:{graph}\: \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 16/Sep/20

$${f}\left(−\mathrm{5}\right)=\left(\frac{\mathrm{0}}{\mathrm{17}}\right)^{\mathrm{0}} =\mathrm{0}^{\mathrm{0}} \:\mathrm{which}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{defined} \\ $$$$\mathrm{many}\:\mathrm{graphic}\:\mathrm{calculators}\:\mathrm{use}\:\mathrm{0}^{\mathrm{0}} =\mathrm{1}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{in} \\ $$$$\mathrm{this}\:\mathrm{case}\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow−\mathrm{5}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:{f}\left({x}\right)\:=\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{different}\:\mathrm{situation} \\ $$$$\mathrm{from}\:{f}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{would}\:\mathrm{also}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{say}\:{y}={x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{has}\:\mathrm{an}\:\mathrm{asymptote} \\ $$$${y}=\mathrm{0},\:\mathrm{would}\:\mathrm{we}? \\ $$
Commented by bemath last updated on 16/Sep/20
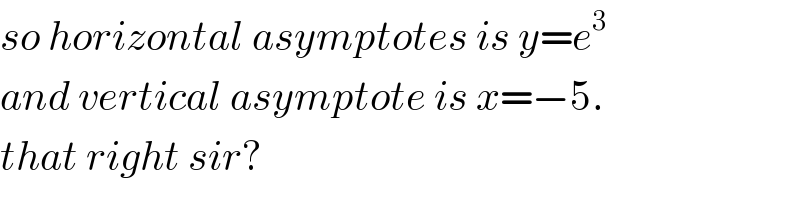
$${so}\:{horizontal}\:{asymptotes}\:{is}\:{y}={e}^{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$${and}\:{vertical}\:{asymptote}\:{is}\:{x}=−\mathrm{5}. \\ $$$${that}\:{right}\:{sir}? \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 16/Sep/20

$$\mathrm{yes}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{my}\:\mathrm{opinion}. \\ $$
Commented by bemath last updated on 16/Sep/20

$${thank}\:{you}\:{sir}.\:{i}\:{agree} \\ $$
