Question Number 97554 by 1549442205 last updated on 08/Jun/20

$$\mathrm{Find}\:\mathrm{all}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{triples}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{positive}\:\mathrm{integers}\:\left(\mathrm{x};\mathrm{y};\mathrm{z}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{so}\:\mathrm{that}\:\frac{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{y}\sqrt{\mathrm{2020}}}{\mathrm{y}−\mathrm{z}\sqrt{\mathrm{2020}}}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{rational}\:\mathrm{number} \\ $$$$\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{be}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{prime}\:\mathrm{number}. \\ $$
Commented by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 09/Jun/20
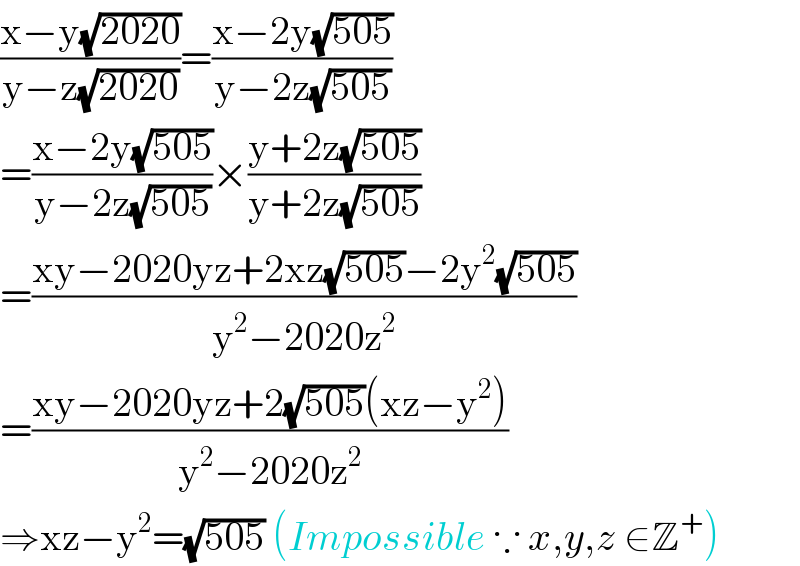
$$\frac{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{y}\sqrt{\mathrm{2020}}}{\mathrm{y}−\mathrm{z}\sqrt{\mathrm{2020}}}=\frac{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2y}\sqrt{\mathrm{505}}}{\mathrm{y}−\mathrm{2z}\sqrt{\mathrm{505}}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2y}\sqrt{\mathrm{505}}}{\mathrm{y}−\mathrm{2z}\sqrt{\mathrm{505}}}×\frac{\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{2z}\sqrt{\mathrm{505}}}{\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{2z}\sqrt{\mathrm{505}}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{xy}−\mathrm{2020yz}+\mathrm{2xz}\sqrt{\mathrm{505}}−\mathrm{2y}^{\mathrm{2}} \sqrt{\mathrm{505}}}{\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2020z}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{xy}−\mathrm{2020yz}+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{505}}\left(\mathrm{xz}−\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}{\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2020z}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{xz}−\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} =\sqrt{\mathrm{505}}\:\left({Impossible}\:\because\:{x},{y},{z}\:\in\mathbb{Z}^{+} \right) \\ $$
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 08/Jun/20

$$\mathrm{or}\:{xz}−{y}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 08/Jun/20

$$\mathcal{T}{hank}\:{you}\:{sir}! \\ $$
Commented by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 09/Jun/20

$$\:\:\:\:{If}\:{xz}−{y}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:{y}^{\mathrm{2}} ={xz} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} +{z}^{\mathrm{2}} ={x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{xz}+{z}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$=\left({x}+{z}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −{xz}=\left({x}+{z}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\left({x}+{y}+{z}\right)\left({x}−{y}+{z}\right)\:\in\mathbb{P} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:{x}+{y}+{z}=\mathrm{1}\wedge\:{x}−{y}+{z}\:\in\mathbb{P} \\ $$$$\left({But}\:{x}+{y}+{z}\neq\mathrm{1}\:{for}\:{x},{y},{z}\in\mathbb{Z}^{+} \right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{or} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:{x}−{y}+{z}=\mathrm{1}\wedge\:{x}+{y}+{z}\:\in\mathbb{P} \\ $$$${x}−{y}+{z}=\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{x}={y}\wedge{z}=\mathrm{1}\:\mid\:{y}={z}\wedge{x}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\:{Let}\:{x}={y}={k}\:\Rightarrow{x}+{y}+{z}=\mathrm{2}{k}+\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\:\:\left({Similarly}\:{y}={z}={k}\Rightarrow{x}+{y}+{z}=\mathrm{2}{k}+\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$… \\ $$$${x}={z}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$…. \\ $$
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 09/Jun/20
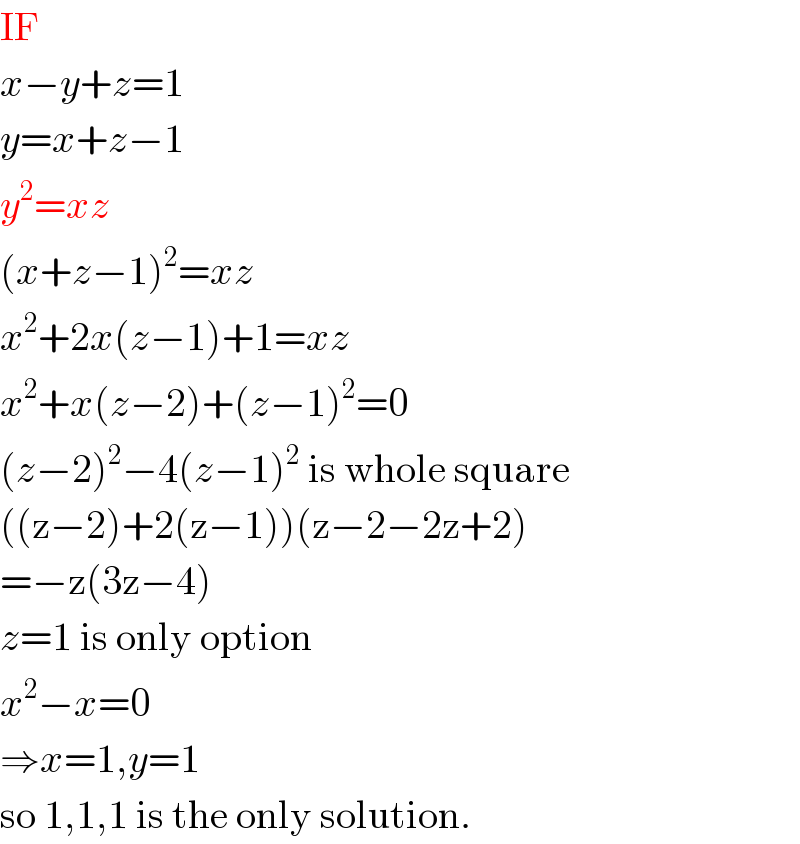
$$\mathrm{IF} \\ $$$${x}−{y}+{z}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${y}={x}+{z}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${y}^{\mathrm{2}} ={xz} \\ $$$$\left({x}+{z}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} ={xz} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}\left({z}−\mathrm{1}\right)+\mathrm{1}={xz} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}\left({z}−\mathrm{2}\right)+\left({z}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left({z}−\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}\left({z}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{whole}\:\mathrm{square} \\ $$$$\left(\left(\mathrm{z}−\mathrm{2}\right)+\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{z}−\mathrm{1}\right)\right)\left(\mathrm{z}−\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{2z}+\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$$=−\mathrm{z}\left(\mathrm{3z}−\mathrm{4}\right) \\ $$$${z}=\mathrm{1}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{only}\:\mathrm{option} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}=\mathrm{1},{y}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{so}\:\mathrm{1},\mathrm{1},\mathrm{1}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{only}\:\mathrm{solution}. \\ $$
Answered by 1549442205 last updated on 09/Jun/20
![Let ((x−y(√(2020)))/(y−z(√(2020))))=(m/n),where m,n∈Z,gcd(m;n)=1 ⇔nx−2ny(√(505))=my−2mz(√(505)) ⇔(2mz−2ny)(√(505)) =my−nx if 2mz−2ny≠0 then (√(505))=((my−nx)/(2mz−2ny))∈Q(set of rational numbers) This is a contradiction because (√(505)) be irrational number Hence,we need must have { ((2mz−2ny=0)),((my−nx=0)) :} it follows that (m/n)=(x/y)=(y/z) ⇒y^2 =xz.Now we denote gcd(x,z)=d⇒ { ((x=ad)),((z=bd)) :} (1) with a,b∈N and gcd(a,b)=1 ⇒y^2 =abd^2 ⇒a=u^2 ,b=v^2 (u,v∈N^∗ )⇒y=uvd.Replace into (1) we get x=u^2 d,z=v^2 d. From this we get x^2 +y^2 +z^2 =d^2 (u^4 +u^2 v^2 +v^4 ) =d^2 [(u^2 +v^2 )^2 −u^2 v^2 ]=d^2 (u^2 −uv+v^2 )(u^2 +uv+v^2 ) From the condition x^2 +y^2 +z^2 is a prime we infer that { ((d^2 =1)),((u^2 −uv+v^2 =1)) :}.Therefore, (u−v)^2 =1−uv≥0 ⇔ ^(u,v∈N^∗ ) u=v=1⇔x=y=z=1 Thus,(x;y;z)=(1;1;1) is unique triple satisfying requirement of the problem](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q97639.png)
$$\mathrm{Let}\:\frac{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{y}\sqrt{\mathrm{2020}}}{\mathrm{y}−\mathrm{z}\sqrt{\mathrm{2020}}}=\frac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{n}},\mathrm{where}\:\mathrm{m},\mathrm{n}\in\mathbb{Z},\mathrm{gcd}\left(\mathrm{m};\mathrm{n}\right)=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\mathrm{nx}−\mathrm{2ny}\sqrt{\mathrm{505}}=\mathrm{my}−\mathrm{2mz}\sqrt{\mathrm{505}} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\left(\mathrm{2mz}−\mathrm{2ny}\right)\sqrt{\mathrm{505}}\:=\mathrm{my}−\mathrm{nx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{if}\:\mathrm{2mz}−\mathrm{2ny}\neq\mathrm{0}\:\mathrm{then}\:\sqrt{\mathrm{505}}=\frac{\mathrm{my}−\mathrm{nx}}{\mathrm{2mz}−\mathrm{2ny}}\in\mathbb{Q}\left(\mathrm{set}\:\mathrm{of}\:\:\mathrm{rational}\:\mathrm{numbers}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{This}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{contradiction}\:\mathrm{because}\:\sqrt{\mathrm{505}}\:\mathrm{be}\:\mathrm{irrational}\:\mathrm{number} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Hence},\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{need}\:\mathrm{must}\:\mathrm{have}\:\begin{cases}{\mathrm{2mz}−\mathrm{2ny}=\mathrm{0}}\\{\mathrm{my}−\mathrm{nx}=\mathrm{0}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{follows}\:\mathrm{that}\:\frac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{n}}=\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{y}}=\frac{\mathrm{y}}{\mathrm{z}}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{xz}.\mathrm{Now}\:\mathrm{we}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{denote}\:\mathrm{gcd}\left(\mathrm{x},\mathrm{z}\right)=\mathrm{d}\Rightarrow\begin{cases}{\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{ad}}\\{\mathrm{z}=\mathrm{bd}}\end{cases}\:\:\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:\mathrm{with}\:\mathrm{a},\mathrm{b}\in\mathbb{N}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{gcd}\left(\mathrm{a},\mathrm{b}\right)=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{abd}^{\mathrm{2}} \Rightarrow\mathrm{a}=\mathrm{u}^{\mathrm{2}} ,\mathrm{b}=\mathrm{v}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{u},\mathrm{v}\in\mathbb{N}^{\ast} \right)\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{uvd}.\mathrm{Replace}\:\mathrm{into} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{get}\:\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{u}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{d},\mathrm{z}=\mathrm{v}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{d}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{From}\:\mathrm{this}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{get}\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{d}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{u}^{\mathrm{4}} +\mathrm{u}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{v}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{v}^{\mathrm{4}} \right) \\ $$$$=\mathrm{d}^{\mathrm{2}} \left[\left(\mathrm{u}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{v}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{u}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{v}^{\mathrm{2}} \right]=\mathrm{d}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{u}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{uv}+\mathrm{v}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\left(\mathrm{u}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{uv}+\mathrm{v}^{\mathrm{2}} \right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{From}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{condition}\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{z}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{prime}\:\mathrm{we} \\ $$$$\mathrm{infer}\:\mathrm{that}\:\:\begin{cases}{\mathrm{d}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{1}}\\{\mathrm{u}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{uv}+\mathrm{v}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{1}}\end{cases}.\mathrm{Therefore}, \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{u}−\mathrm{v}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{uv}\geqslant\mathrm{0}\:\overset{\mathrm{u},\mathrm{v}\in\mathbb{N}^{\ast} } {\Leftrightarrow\:\:\:}\mathrm{u}=\mathrm{v}=\mathrm{1}\Leftrightarrow\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{z}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Thus},\left(\mathrm{x};\mathrm{y};\mathrm{z}\right)=\left(\mathrm{1};\mathrm{1};\mathrm{1}\right)\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{unique}\:\mathrm{triple}\:\mathrm{satisfying} \\ $$$$\mathrm{requirement}\:\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{problem} \\ $$
