Question Number 103860 by mathmax by abdo last updated on 17/Jul/20
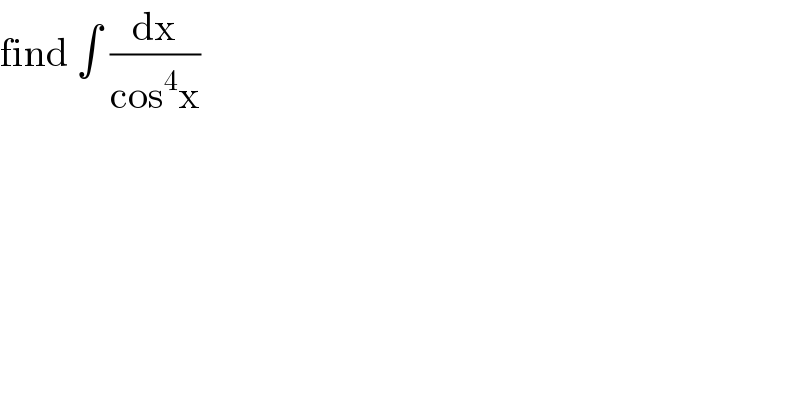
$$\mathrm{find}\:\int\:\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{4}} \mathrm{x}} \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 17/Jul/20
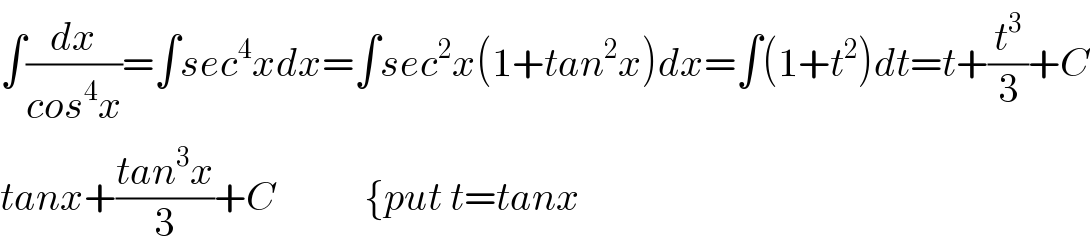
$$\int\frac{{dx}}{{cos}^{\mathrm{4}} {x}}=\int{sec}^{\mathrm{4}} {xdx}=\int{sec}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}\left(\mathrm{1}+{tan}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}\right){dx}=\int\left(\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \right){dt}={t}+\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}}+{C} \\ $$$${tanx}+\frac{{tan}^{\mathrm{3}} {x}}{\mathrm{3}}+{C}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\left\{{put}\:{t}={tanx}\right. \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 17/Jul/20
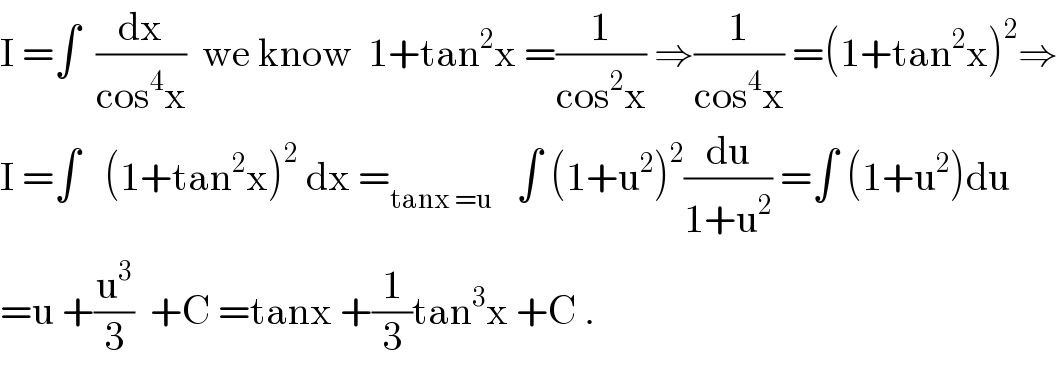
$$\mathrm{I}\:=\int\:\:\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{4}} \mathrm{x}}\:\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{know}\:\:\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{tan}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}}\:\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{4}} \mathrm{x}}\:=\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{tan}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:=\int\:\:\:\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{tan}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{dx}\:=_{\mathrm{tanx}\:=\mathrm{u}} \:\:\:\int\:\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{u}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\int\:\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{u}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\mathrm{du} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{u}\:+\frac{\mathrm{u}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}}\:\:+\mathrm{C}\:=\mathrm{tanx}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{tan}^{\mathrm{3}} \mathrm{x}\:+\mathrm{C}\:. \\ $$
