Question Number 189053 by mathlove last updated on 11/Mar/23

$${find}\:{f}\left({x}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}:{f}\left(\frac{{x}+\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\right)={x}+\mathrm{3};\:{x}\neq\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}:{f}\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\right)={x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}\:;{x}\neq\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}:{f}\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)+{f}\left({x}−{y}\right)=\mathrm{2}{f}\left({x}\right){cosy}\:\forall{x},{y} \\ $$$${f}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)={f}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\right)=\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Answered by cortano12 last updated on 11/Mar/23

$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:\mathrm{f}\left(\frac{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{3}\:,\:\mathrm{x}\neq\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{let}\:\mathrm{u}=\frac{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{x}=\frac{\mathrm{u}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{u}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{u}\right)=\:\frac{\mathrm{u}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{u}−\mathrm{1}}\:+\mathrm{3}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{4u}−\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{u}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\:\therefore\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\:\frac{\mathrm{4}{x}−\mathrm{2}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}\:,\:{x}\:\neq\:\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Answered by aleks041103 last updated on 11/Mar/23
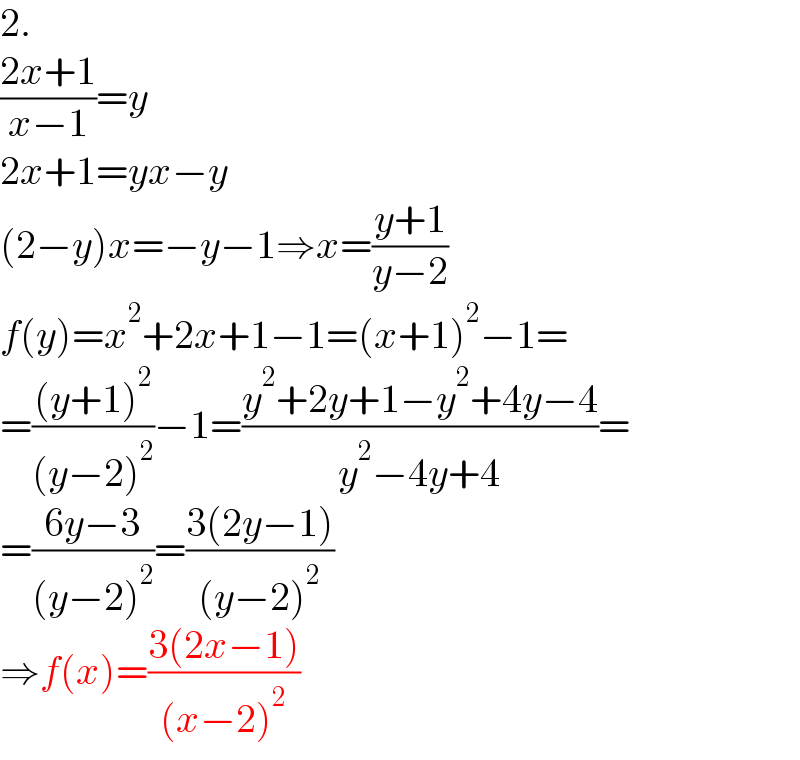
$$\mathrm{2}. \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{1}}={y} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}={yx}−{y} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{2}−{y}\right){x}=−{y}−\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow{x}=\frac{{y}+\mathrm{1}}{{y}−\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${f}\left({y}\right)={x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{1}=\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}= \\ $$$$=\frac{\left({y}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\left({y}−\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }−\mathrm{1}=\frac{{y}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{y}+\mathrm{1}−{y}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{4}{y}−\mathrm{4}}{{y}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}{y}+\mathrm{4}}= \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{6}{y}−\mathrm{3}}{\left({y}−\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{\mathrm{3}\left(\mathrm{2}{y}−\mathrm{1}\right)}{\left({y}−\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{f}\left({x}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{3}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)}{\left({x}−\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$
Answered by aleks041103 last updated on 11/Mar/23
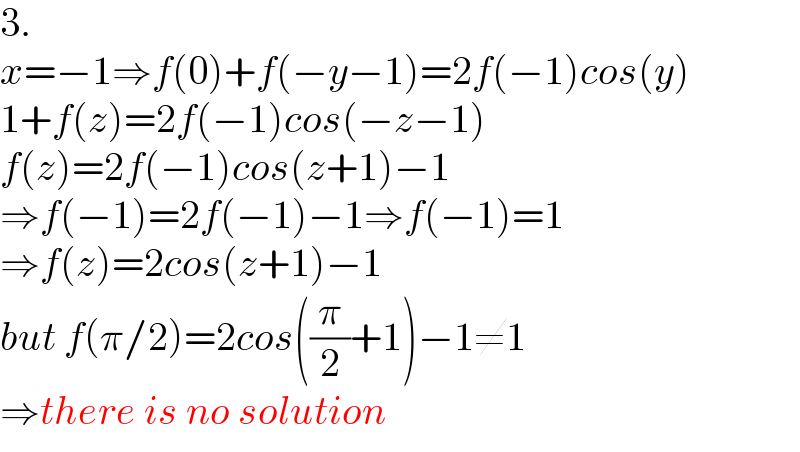
$$\mathrm{3}. \\ $$$${x}=−\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow{f}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)+{f}\left(−{y}−\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{2}{f}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right){cos}\left({y}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}+{f}\left({z}\right)=\mathrm{2}{f}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right){cos}\left(−{z}−\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$${f}\left({z}\right)=\mathrm{2}{f}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right){cos}\left({z}+\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{f}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{2}{f}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow{f}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{f}\left({z}\right)=\mathrm{2}{cos}\left({z}+\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${but}\:{f}\left(\pi/\mathrm{2}\right)=\mathrm{2}{cos}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{1}\neq\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{there}\:{is}\:{no}\:{solution} \\ $$
