Question Number 36434 by prof Abdo imad last updated on 02/Jun/18

$${find}\:{g}\left({x}\right)\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{x}} \:\:\:\frac{{e}^{−{t}} }{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{dt}. \\ $$
Commented by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 02/Jun/18
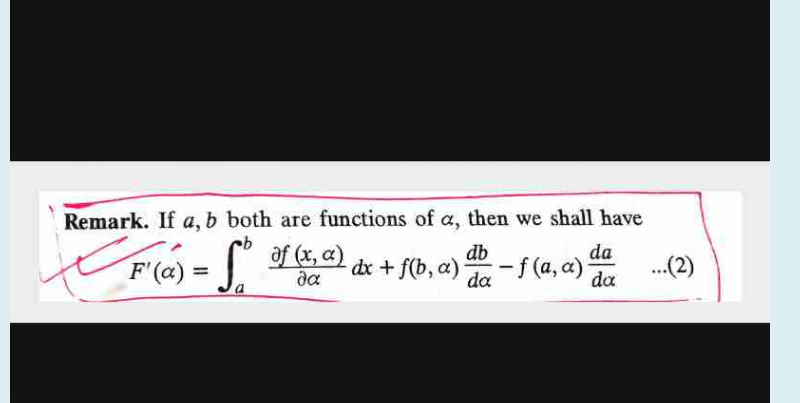
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 02/Jun/18

$$\frac{{dg}\left({x}\right)}{{dx}}=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{x}} \frac{\partial}{\partial{x}}\left(\frac{{e}^{−{t}} }{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \:}}\right){dt}+\frac{{dx}}{{dx}}×\frac{{e}^{−{x}} }{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}− \\ $$$$\frac{{dg}\left({x}\right)}{{dx}}=\frac{{e}^{−{x}} }{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}\: \\ $$
