Question Number 114922 by bemath last updated on 22/Sep/20
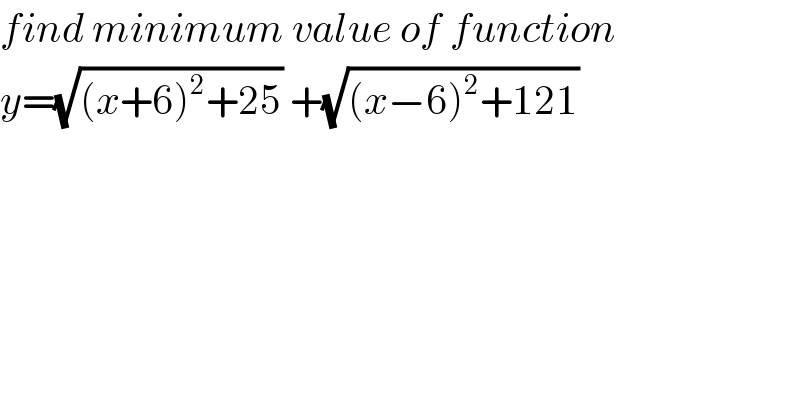
$${find}\:{minimum}\:{value}\:{of}\:{function} \\ $$$${y}=\sqrt{\left({x}+\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{25}}\:+\sqrt{\left({x}−\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{121}} \\ $$
Answered by john santu last updated on 22/Sep/20
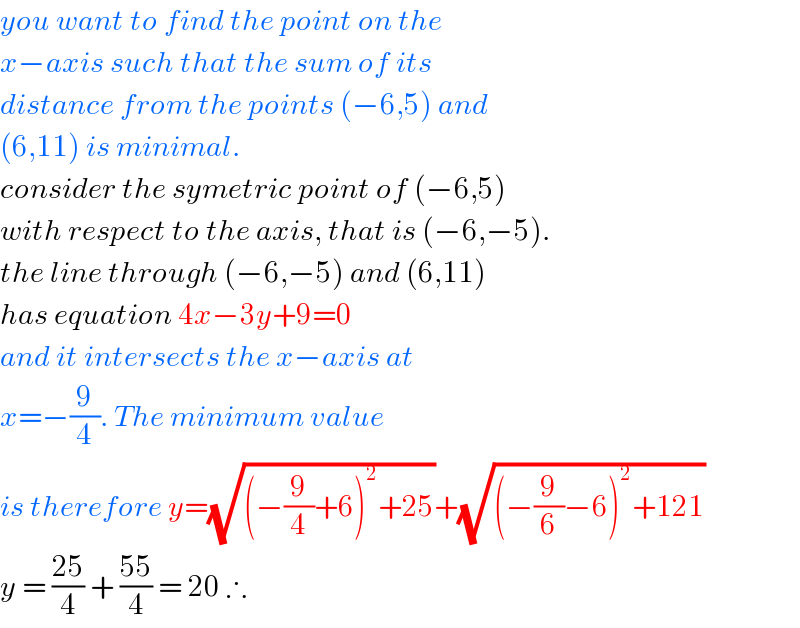
$${you}\:{want}\:{to}\:{find}\:{the}\:{point}\:{on}\:{the}\: \\ $$$${x}−{axis}\:{such}\:{that}\:{the}\:{sum}\:{of}\:{its}\: \\ $$$${distance}\:{from}\:{the}\:{points}\:\left(−\mathrm{6},\mathrm{5}\right)\:{and} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{6},\mathrm{11}\right)\:{is}\:{minimal}. \\ $$$${consider}\:{the}\:{symetric}\:{point}\:{of}\:\left(−\mathrm{6},\mathrm{5}\right) \\ $$$${with}\:{respect}\:{to}\:{the}\:{axis},\:{that}\:{is}\:\left(−\mathrm{6},−\mathrm{5}\right). \\ $$$${the}\:{line}\:{through}\:\left(−\mathrm{6},−\mathrm{5}\right)\:{and}\:\left(\mathrm{6},\mathrm{11}\right) \\ $$$${has}\:{equation}\:\mathrm{4}{x}−\mathrm{3}{y}+\mathrm{9}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${and}\:{it}\:{intersects}\:{the}\:{x}−{axis}\:{at}\: \\ $$$${x}=−\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{4}}.\:{The}\:{minimum}\:{value}\: \\ $$$${is}\:{therefore}\:{y}=\sqrt{\left(−\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{4}}+\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{25}}+\sqrt{\left(−\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{6}}−\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{121}} \\ $$$${y}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{25}}{\mathrm{4}}\:+\:\frac{\mathrm{55}}{\mathrm{4}}\:=\:\mathrm{20}\:\therefore \\ $$
Commented by bemath last updated on 22/Sep/20

$${gave}\:{kudos} \\ $$
Answered by bobhans last updated on 22/Sep/20
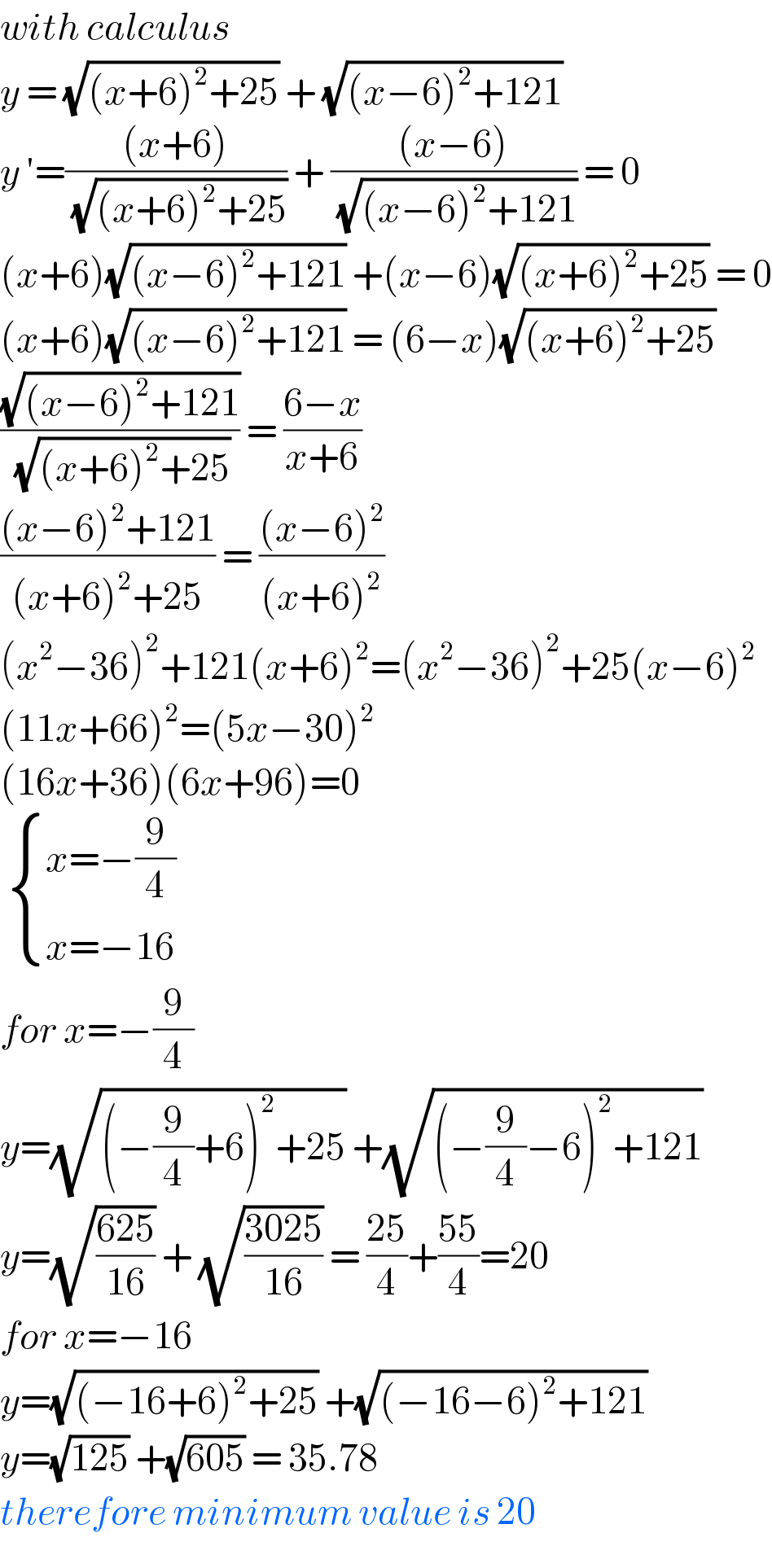
$${with}\:{calculus} \\ $$$${y}\:=\:\sqrt{\left({x}+\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{25}}\:+\:\sqrt{\left({x}−\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{121}} \\ $$$${y}\:'=\frac{\left({x}+\mathrm{6}\right)}{\:\sqrt{\left({x}+\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{25}}}\:+\:\frac{\left({x}−\mathrm{6}\right)}{\:\sqrt{\left({x}−\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{121}}}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left({x}+\mathrm{6}\right)\sqrt{\left({x}−\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{121}}\:+\left({x}−\mathrm{6}\right)\sqrt{\left({x}+\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{25}}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left({x}+\mathrm{6}\right)\sqrt{\left({x}−\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{121}}\:=\:\left(\mathrm{6}−{x}\right)\sqrt{\left({x}+\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{25}} \\ $$$$\frac{\sqrt{\left({x}−\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{121}}}{\:\sqrt{\left({x}+\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{25}}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{6}−{x}}{{x}+\mathrm{6}} \\ $$$$\frac{\left({x}−\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{121}}{\left({x}+\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{25}}\:=\:\frac{\left({x}−\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\left({x}+\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{36}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{121}\left({x}+\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{36}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{25}\left({x}−\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{11}{x}+\mathrm{66}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\left(\mathrm{5}{x}−\mathrm{30}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{16}{x}+\mathrm{36}\right)\left(\mathrm{6}{x}+\mathrm{96}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\begin{cases}{{x}=−\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{4}}}\\{{x}=−\mathrm{16}}\end{cases} \\ $$$${for}\:{x}=−\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$${y}=\sqrt{\left(−\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{4}}+\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{25}}\:+\sqrt{\left(−\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{4}}−\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{121}} \\ $$$${y}=\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{625}}{\mathrm{16}}}\:+\:\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{3025}}{\mathrm{16}}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{25}}{\mathrm{4}}+\frac{\mathrm{55}}{\mathrm{4}}=\mathrm{20} \\ $$$${for}\:{x}=−\mathrm{16} \\ $$$${y}=\sqrt{\left(−\mathrm{16}+\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{25}}\:+\sqrt{\left(−\mathrm{16}−\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{121}} \\ $$$${y}=\sqrt{\mathrm{125}}\:+\sqrt{\mathrm{605}}\:=\:\mathrm{35}.\mathrm{78} \\ $$$${therefore}\:{minimum}\:{value}\:{is}\:\mathrm{20} \\ $$
