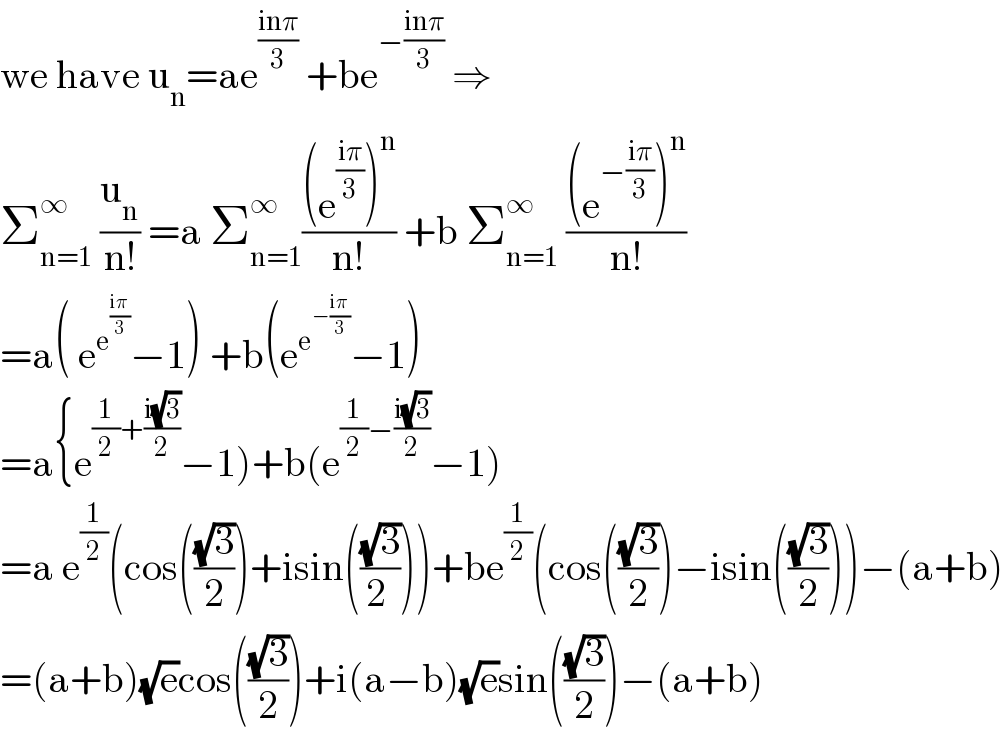Question Number 119754 by Bird last updated on 26/Oct/20
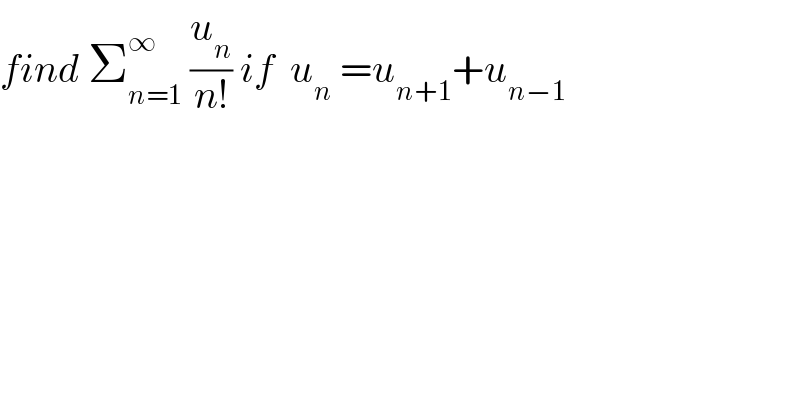
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 26/Oct/20
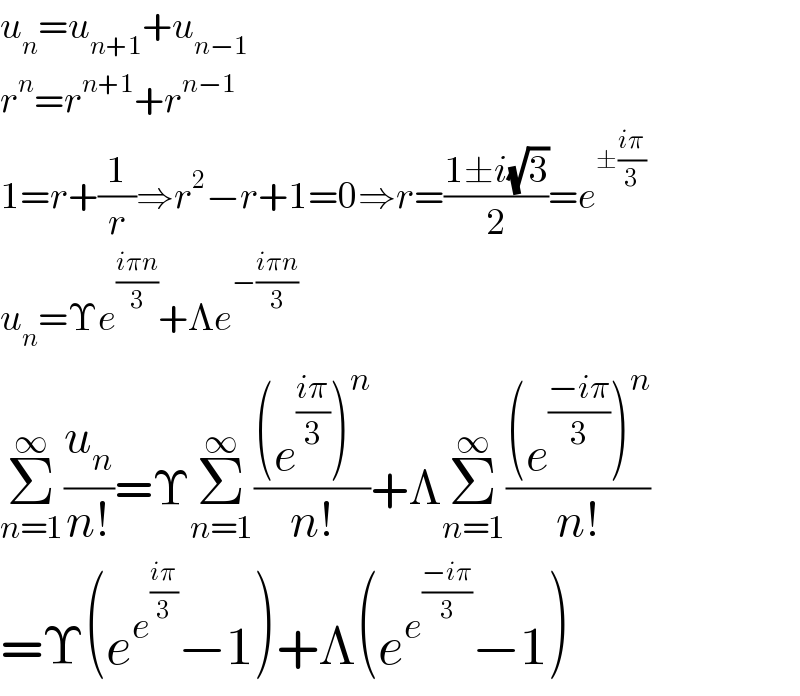
Commented by talminator2856791 last updated on 27/Oct/20
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 27/Oct/20
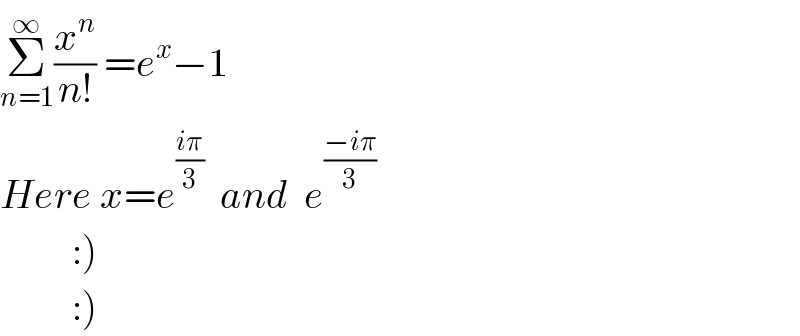
Answered by Olaf last updated on 26/Oct/20
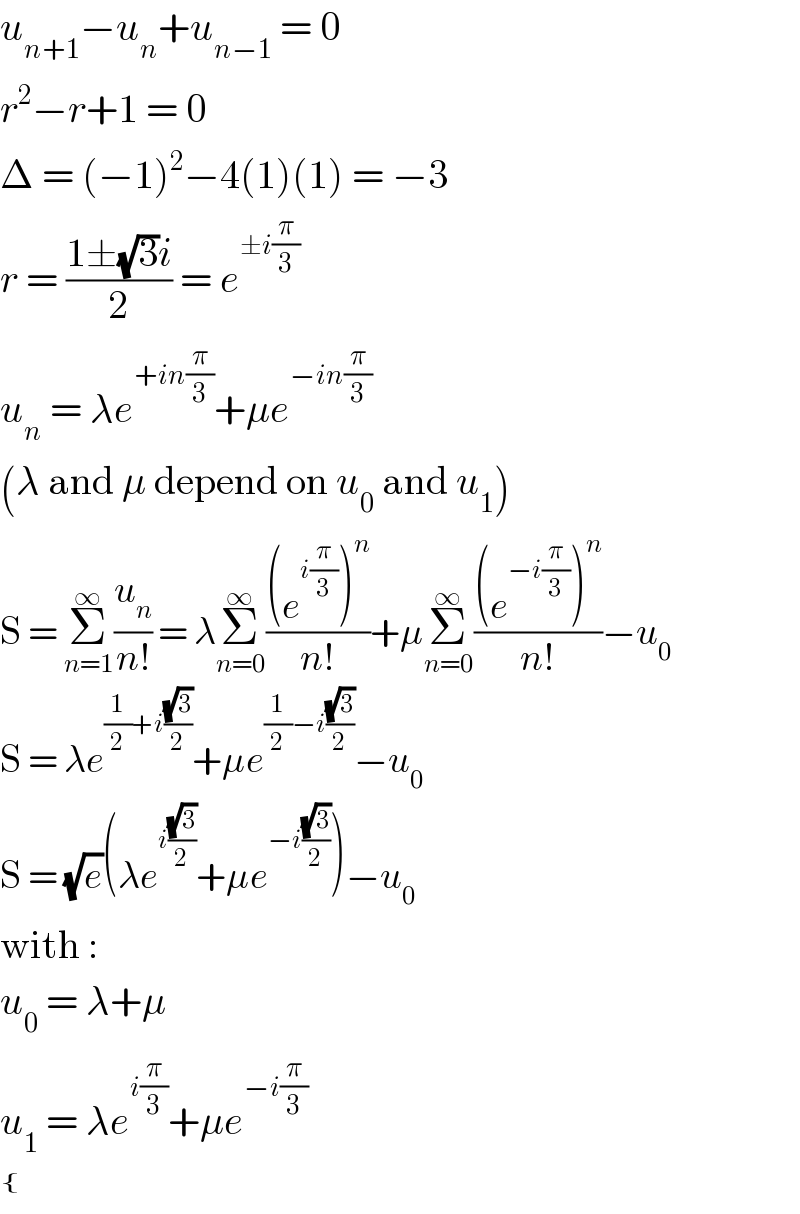
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 26/Oct/20
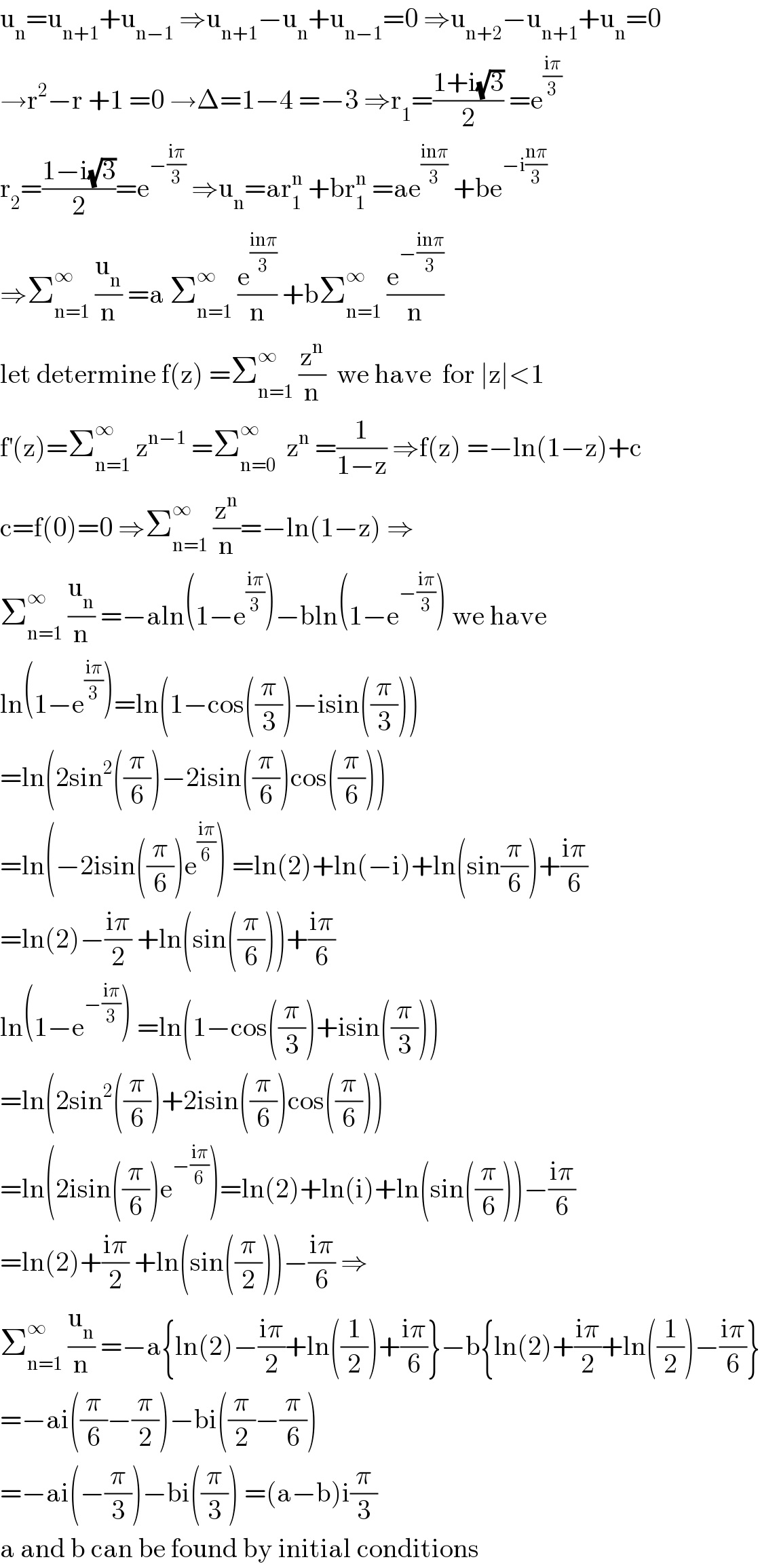
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 27/Oct/20
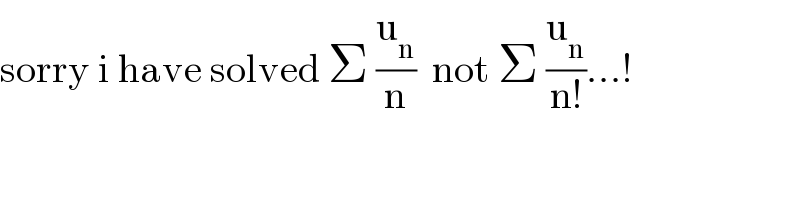
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 27/Oct/20