Question Number 122329 by mathocean1 last updated on 15/Nov/20
![find n ∈ N such that 5^(2n) +5^n ≡0[13]](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q122329.png)
$${find}\:{n}\:\in\:\mathbb{N}\:{such}\:{that} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}{n}} +\mathrm{5}^{{n}} \equiv\mathrm{0}\left[\mathrm{13}\right] \\ $$
Answered by 676597498 last updated on 15/Nov/20
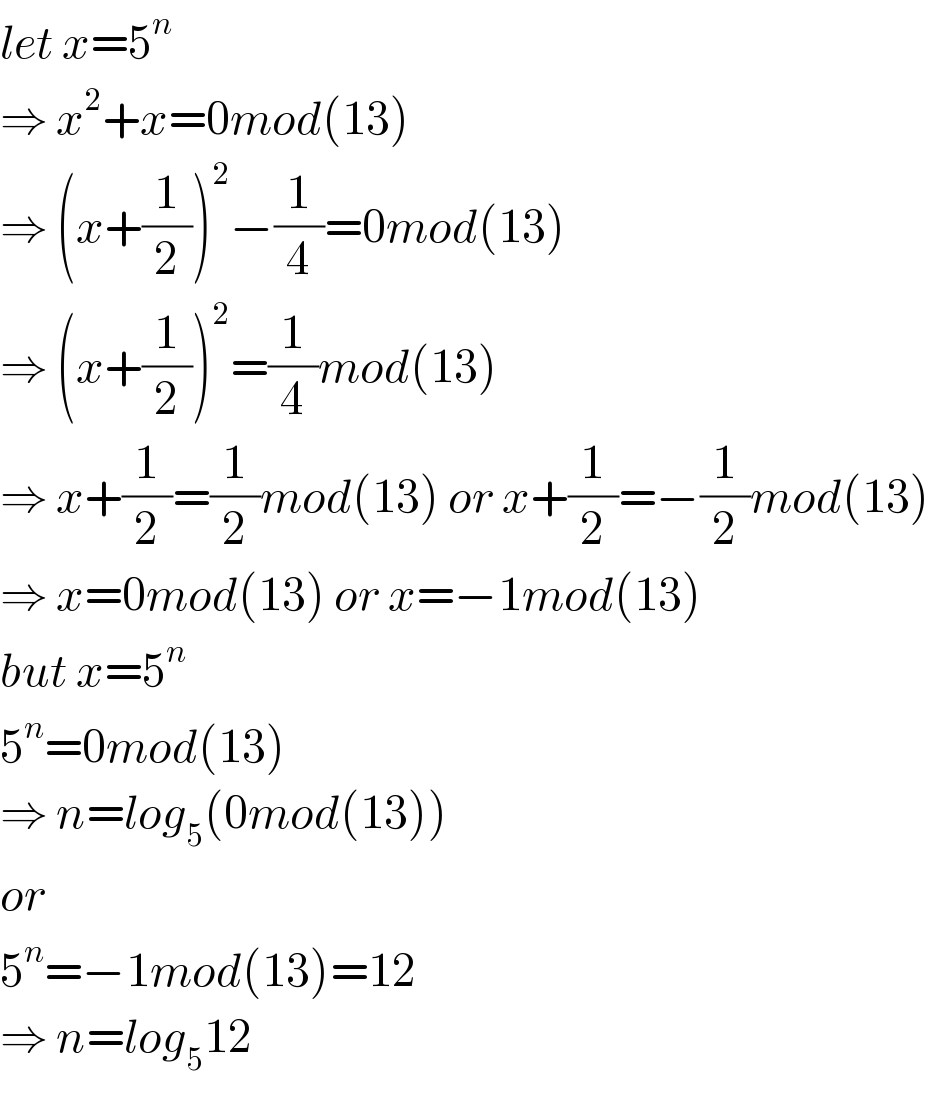
$${let}\:{x}=\mathrm{5}^{{n}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}=\mathrm{0}{mod}\left(\mathrm{13}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\left({x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}=\mathrm{0}{mod}\left(\mathrm{13}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\left({x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}{mod}\left(\mathrm{13}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{mod}\left(\mathrm{13}\right)\:{or}\:{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{mod}\left(\mathrm{13}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{x}=\mathrm{0}{mod}\left(\mathrm{13}\right)\:{or}\:{x}=−\mathrm{1}{mod}\left(\mathrm{13}\right) \\ $$$${but}\:{x}=\mathrm{5}^{{n}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}^{{n}} =\mathrm{0}{mod}\left(\mathrm{13}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{n}={log}_{\mathrm{5}} \left(\mathrm{0}{mod}\left(\mathrm{13}\right)\right) \\ $$$${or}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}^{{n}} =−\mathrm{1}{mod}\left(\mathrm{13}\right)=\mathrm{12} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{n}={log}_{\mathrm{5}} \mathrm{12} \\ $$
Commented by mindispower last updated on 16/Nov/20

$${x}\in\mathbb{N} \\ $$
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 15/Nov/20
![5^(2n) +5^n =13m; m∈N 5^n (5^n +1)=13m 5^n ≠13m [obviously] ⇒ 5^n =13m−1 trying the first few n we get n=4k+2](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q122339.png)
$$\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}{n}} +\mathrm{5}^{{n}} =\mathrm{13}{m};\:{m}\in\mathbb{N} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}^{{n}} \left(\mathrm{5}^{{n}} +\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{13}{m} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}^{{n}} \neq\mathrm{13}{m}\:\left[\mathrm{obviously}\right] \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{5}^{{n}} =\mathrm{13}{m}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{trying}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{first}\:\mathrm{few}\:{n}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{get} \\ $$$${n}=\mathrm{4}{k}+\mathrm{2} \\ $$
Answered by floor(10²Eta[1]) last updated on 16/Nov/20

$$\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{n}} \left(\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{n}} +\mathrm{1}\right)\equiv\mathrm{0}\left(\mathrm{mod13}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{n}} \equiv\mathrm{0}\left(\mathrm{mod13}\right)\:\vee\:\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{n}} \equiv\mathrm{12}\left(\mathrm{mod}\:\mathrm{13}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{n}} \equiv\mathrm{12}\left(\mathrm{mod13}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{2}\Rightarrow\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{n}} =\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{2}} \equiv\mathrm{12}\left(\mathrm{mod13}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{2}} \equiv\mathrm{1}\left(\mathrm{mod13}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}^{\mathrm{a}} \equiv\mathrm{1}\left(\mathrm{mod13}\right)\Rightarrow\mathrm{a}\mid\varphi\left(\mathrm{13}\right)=\mathrm{12}\Rightarrow\mathrm{a}=\mathrm{4}\therefore\mathrm{a}=\mathrm{4k} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{4k}\Rightarrow\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{4k}+\mathrm{2},\:\forall\:\mathrm{k}\geqslant\mathrm{0} \\ $$
