Question Number 123407 by bemath last updated on 25/Nov/20
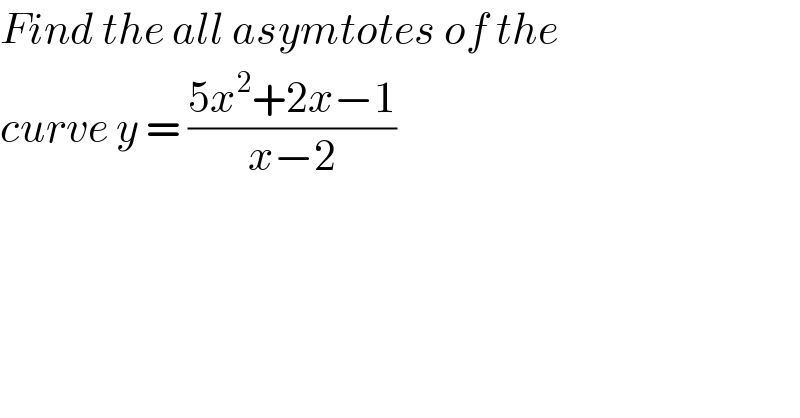
$${Find}\:{the}\:{all}\:{asymtotes}\:{of}\:{the} \\ $$$${curve}\:{y}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{5}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by EVIMENEBASSEY last updated on 25/Nov/20

$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${Find}\:{the}\:{all}\:{asymtotes}\:{of}\:{the} \\ $$$${curve}\:{y}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{5}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{solution} \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2}\right)=\mathrm{5x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2x}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{horizontal}\:\mathrm{asymtote}\:=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mathrm{no}\:\mathrm{horizontal}\:\mathrm{asymtote}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{but}\:\mathrm{letting}\:\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{mx}+\mathrm{c} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{mx}+\mathrm{c}\right)\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2}\right)=\mathrm{5x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2x}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{mx}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{mx}+\mathrm{xc}−\mathrm{2c}=\mathrm{5x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2x}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{c}=\mathrm{m}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{caddet} \\ $$
Commented by liberty last updated on 25/Nov/20

$$\left({i}\right)\:{vertical}\:{asymtotes}\::\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:{y}\:=\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{5}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{2}}\:=\:\infty \\ $$$$\:{we}\:{get}\:{vertical}\:{asymtotes}\:{x}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\left({ii}\right)\:{horizontal}\:{asymtotes}\::\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\pm\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}{y}\:=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\pm\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{5}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${clearly}\:{the}\:{limit}\:{does}\:{not}\:{exist}\:{so} \\ $$$${the}\:{curve}\:{no}\:{horizontal}\:{asymtotes} \\ $$$$\left({iii}\right)\:{we}\:{want}\:{find}\:{inclined}\:{asymtotes} \\ $$$${y}\:=\:{kx}\:+\:{b}\:{where}\:\begin{cases}{{k}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{{y}}{{x}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{5}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{x}}=\mathrm{5}}\\{{b}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left({y}−{kx}\right)=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{5}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{5}{x}\right)}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\:\Rightarrow{b}\:=\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{5}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{5}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{10}{x}}{{x}−\mathrm{2}}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{b}\:=\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{12}{x}−\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\mathrm{2}}\right)=\mathrm{12} \\ $$$${thus}\:{straight}\:{line}\:{y}\:=\:\mathrm{5}{x}+\mathrm{12}\:{is} \\ $$$${inclined}\:{asymtotes} \\ $$
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 25/Nov/20

$${y}=\frac{{p}\left({x}\right)}{{q}\left({x}\right)}\:\mathrm{with}\:{p},\:{q}\:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{polynomes}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{degree}\:\left({p}\right)\:\geqslant\mathrm{degree}\:\left({q}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{can}\:\mathrm{always}\:\mathrm{find}\:\mathrm{existing}\:\mathrm{asymptotic}\:\mathrm{lines} \\ $$$$\mathrm{or}\:\mathrm{curves}\:\mathrm{by}\:\mathrm{dividing}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{fraction} \\ $$$${y}=\frac{\mathrm{7}{x}+\mathrm{3}}{{x}−\mathrm{5}}=\mathrm{7}+\frac{\mathrm{38}}{{x}−\mathrm{5}}\:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{asymptotes}\:\begin{cases}{{x}=\mathrm{5}}\\{{y}=\mathrm{7}}\end{cases} \\ $$$${y}=\frac{\mathrm{7}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{3}}{{x}−\mathrm{5}}=\mathrm{7}{x}+\mathrm{35}+\frac{\mathrm{178}}{{x}−\mathrm{5}}\:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{asymptotes}\:\begin{cases}{{x}=\mathrm{5}}\\{{y}=\mathrm{7}{x}+\mathrm{35}}\end{cases} \\ $$$${y}=\frac{\mathrm{7}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{3}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5}}=\mathrm{7}{x}+\frac{\mathrm{35}{x}+\mathrm{3}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5}}\:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{asymptotes}\:\begin{cases}{{x}=\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}\\{{y}=\mathrm{7}{x}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\mathrm{asymptotic}\:\mathrm{curves}: \\ $$$${y}=\frac{\mathrm{7}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{3}}{{x}−\mathrm{5}}=\mathrm{7}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{35}{x}+\mathrm{175}+\frac{\mathrm{878}}{{x}−\mathrm{5}}\:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{asymptotes}\:\begin{cases}{{x}=\mathrm{5}}\\{{y}=\mathrm{7}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{35}{x}+\mathrm{175}}\end{cases} \\ $$$${y}=\frac{\mathrm{7}{x}^{\mathrm{4}} +\mathrm{3}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5}}=\mathrm{7}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{35}+\frac{\mathrm{178}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5}}\:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{asymptotes}\:\begin{cases}{{x}=\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}\\{{y}=\mathrm{7}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{35}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$… \\ $$
Commented by bemath last updated on 25/Nov/20

Commented by bemath last updated on 25/Nov/20
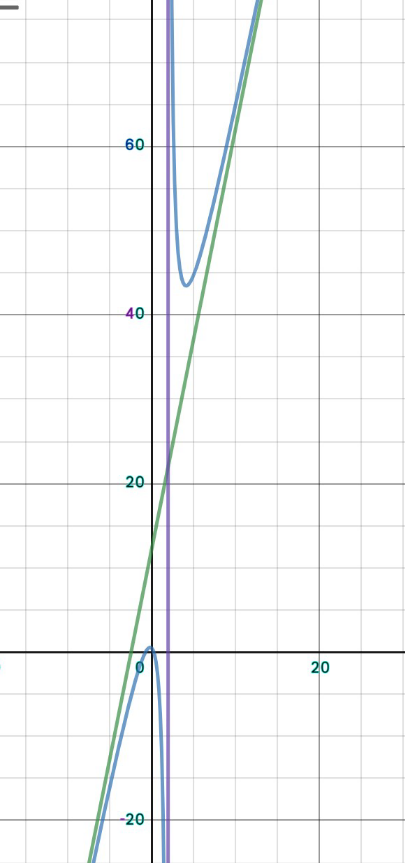
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 25/Nov/20
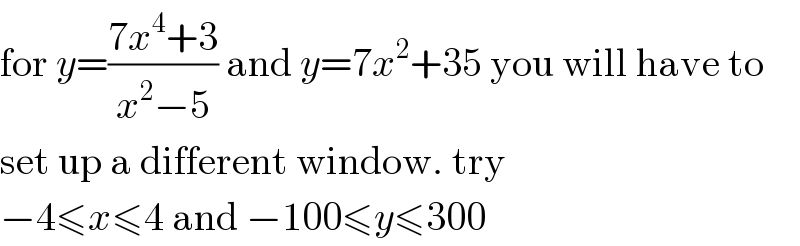
$$\mathrm{for}\:{y}=\frac{\mathrm{7}{x}^{\mathrm{4}} +\mathrm{3}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{5}}\:\mathrm{and}\:{y}=\mathrm{7}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{35}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{will}\:\mathrm{have}\:\mathrm{to} \\ $$$$\mathrm{set}\:\mathrm{up}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{different}\:\mathrm{window}.\:\mathrm{try} \\ $$$$−\mathrm{4}\leqslant{x}\leqslant\mathrm{4}\:\mathrm{and}\:−\mathrm{100}\leqslant{y}\leqslant\mathrm{300} \\ $$
Commented by bemath last updated on 25/Nov/20

$${yes}\:{sir}.\: \\ $$
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 25/Nov/20
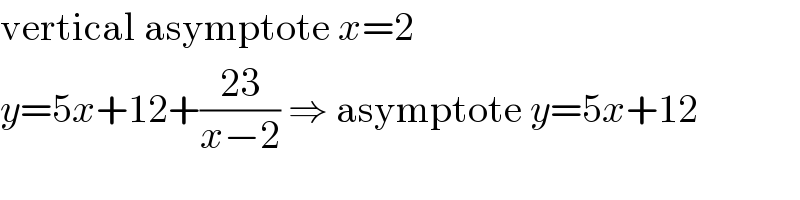
$$\mathrm{vertical}\:\mathrm{asymptote}\:{x}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${y}=\mathrm{5}{x}+\mathrm{12}+\frac{\mathrm{23}}{{x}−\mathrm{2}}\:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{asymptote}\:{y}=\mathrm{5}{x}+\mathrm{12} \\ $$
