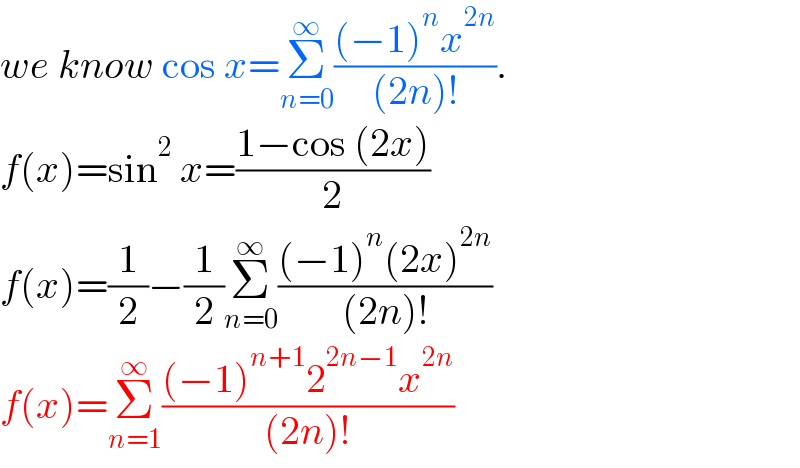Question Number 158469 by zakirullah last updated on 04/Nov/21
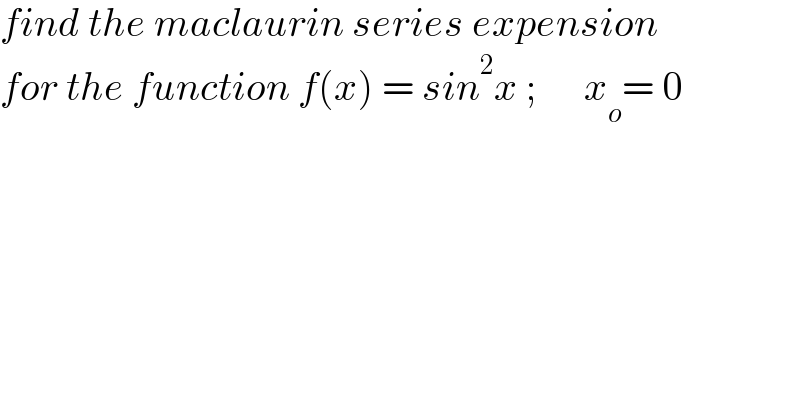
Answered by TheSupreme last updated on 04/Nov/21
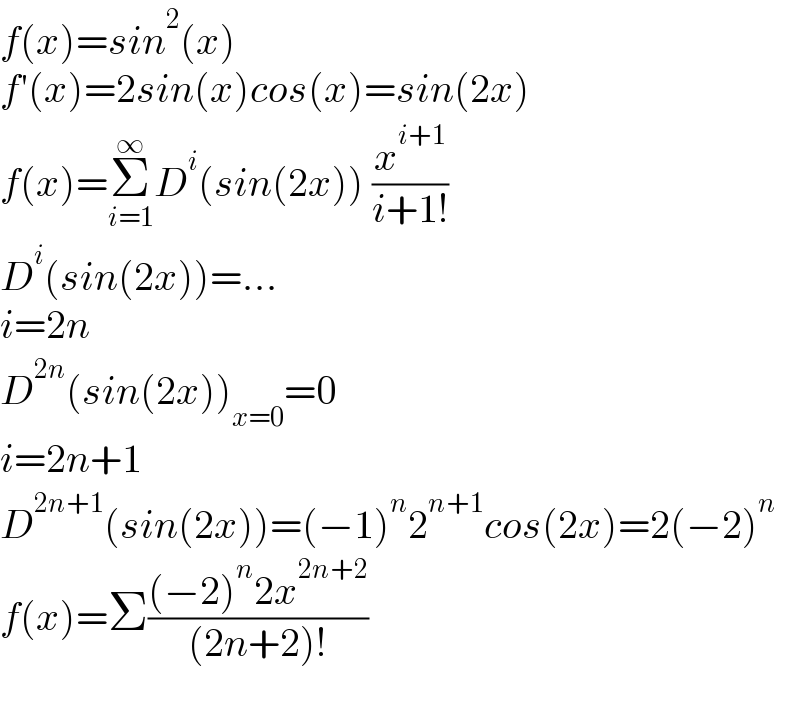
Commented by zakirullah last updated on 04/Nov/21
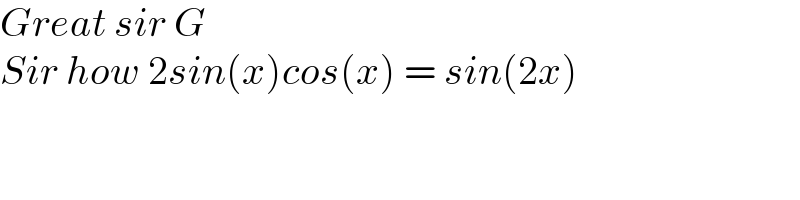
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 05/Nov/21
![2sin x cos x =2×((e^(ix) −e^(−ix) )/(2i))×((e^(ix) +e^(−ix) )/2)= [(a−b)(a+b)=a^2 +b^2 ] =((e^(2ix) −e^(−2ix) )/(2i))=sin 2x](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q158493.png)
Commented by zakirullah last updated on 05/Nov/21
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 05/Nov/21
Answered by mr W last updated on 04/Nov/21