Question Number 27182 by abdo imad last updated on 02/Jan/18
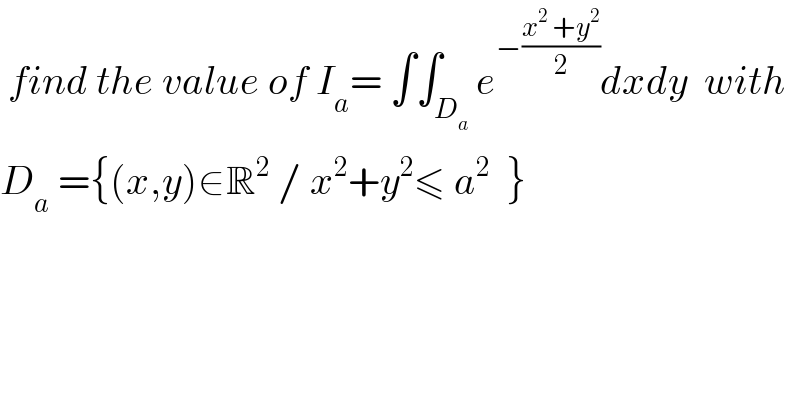
$$\:{find}\:{the}\:{value}\:{of}\:{I}_{{a}} =\:\int\int_{{D}_{{a}} } {e}^{−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+{y}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}} {dxdy}\:\:{with} \\ $$$${D}_{{a}} \:=\left\{\left({x},{y}\right)\in\mathbb{R}^{\mathrm{2}} \:/\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \leqslant\:{a}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\:\right\} \\ $$
Commented by abdo imad last updated on 05/Jan/18
![we use the polar coordinates and the diffeomorphismeψ (r,θ)−>ψ(r,θ) =(x,y)=(rcosθ,rsinθ) I_(a ) =∫∫_(o≤r≤a) e^(−(r^2 /2)) rdr dθ = ∫_0 ^(2π) ( ∫_0 ^a r e^(−(r^2 /2)) dr )dθ= 2π ∫_0 ^a r e^(−(r^2 /2)) dr = 2π[ − e^(−(r^2 /2)) ]_0 ^a =2π(1− e^(−(a^2 /2)) )](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q27378.png)
$${we}\:{use}\:{the}\:{polar}\:{coordinates}\:{and}\:{the}\:{diffeomorphisme}\psi \\ $$$$\left({r},\theta\right)−>\psi\left({r},\theta\right)\:=\left({x},{y}\right)=\left({rcos}\theta,{rsin}\theta\right) \\ $$$${I}_{{a}\:} =\int\int_{{o}\leqslant{r}\leqslant{a}} {e}^{−\frac{{r}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}} \:{rdr}\:{d}\theta \\ $$$$=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{2}\pi} \:\:\left(\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{a}} \:\:{r}\:{e}^{−\frac{{r}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}} \:{dr}\:\right){d}\theta=\:\mathrm{2}\pi\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{a}} \:{r}\:{e}^{−\frac{{r}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}} {dr} \\ $$$$=\:\mathrm{2}\pi\left[\:\:−\:{e}^{−\frac{{r}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}} \:\:\:\:\:\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{a}} =\mathrm{2}\pi\left(\mathrm{1}−\:{e}^{−\frac{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}} \:\:\:\right) \\ $$
