Question Number 26567 by abdo imad last updated on 26/Dec/17
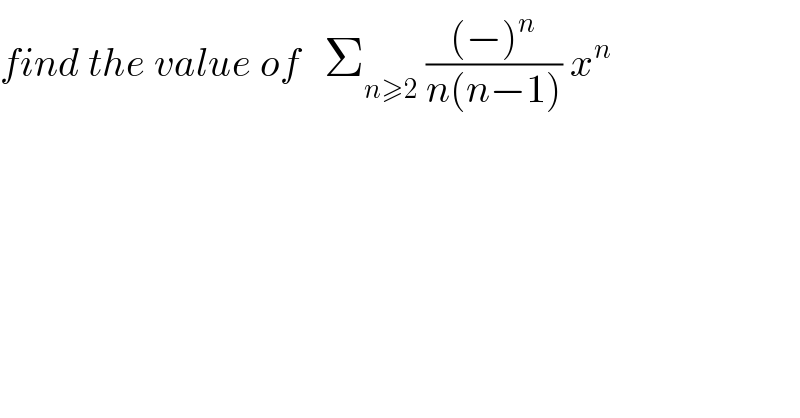
$${find}\:{the}\:{value}\:{of}\:\:\:\sum_{{n}\geqslant\mathrm{2}} \:\frac{\left(−\right)^{{n}} }{{n}\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right)}\:{x}^{{n}} \\ $$
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 27/Dec/17
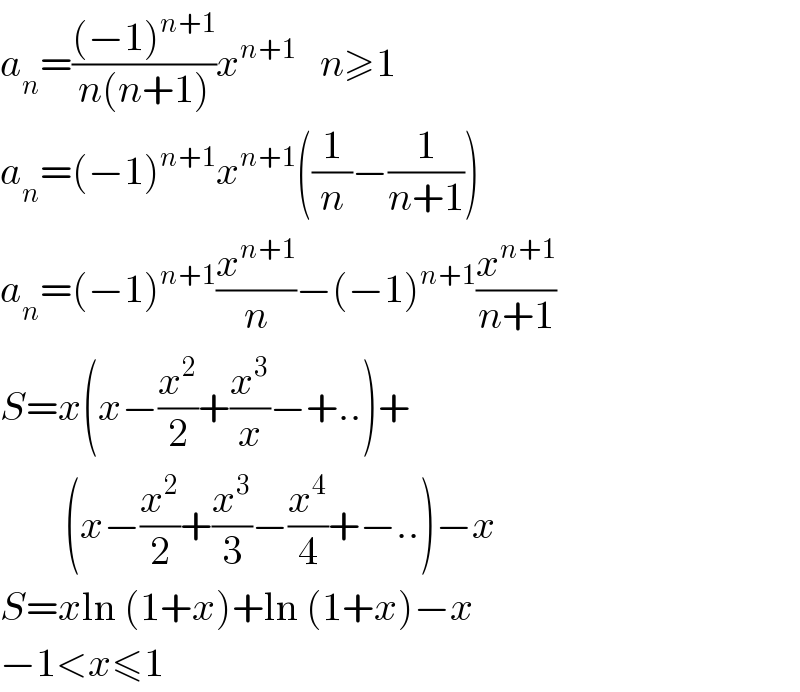
$${a}_{{n}} =\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{x}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} \:\:\:{n}\geqslant\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${a}_{{n}} =\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} {x}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} \left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}+\mathrm{1}}\right) \\ $$$${a}_{{n}} =\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} \frac{{x}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{{n}}−\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} \frac{{x}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{{n}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$${S}={x}\left({x}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{{x}}−+..\right)+ \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\left({x}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{4}}+−..\right)−{x} \\ $$$${S}={x}\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)+\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)−{x} \\ $$$$−\mathrm{1}<{x}\leqslant\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Commented by abdo imad last updated on 28/Dec/17
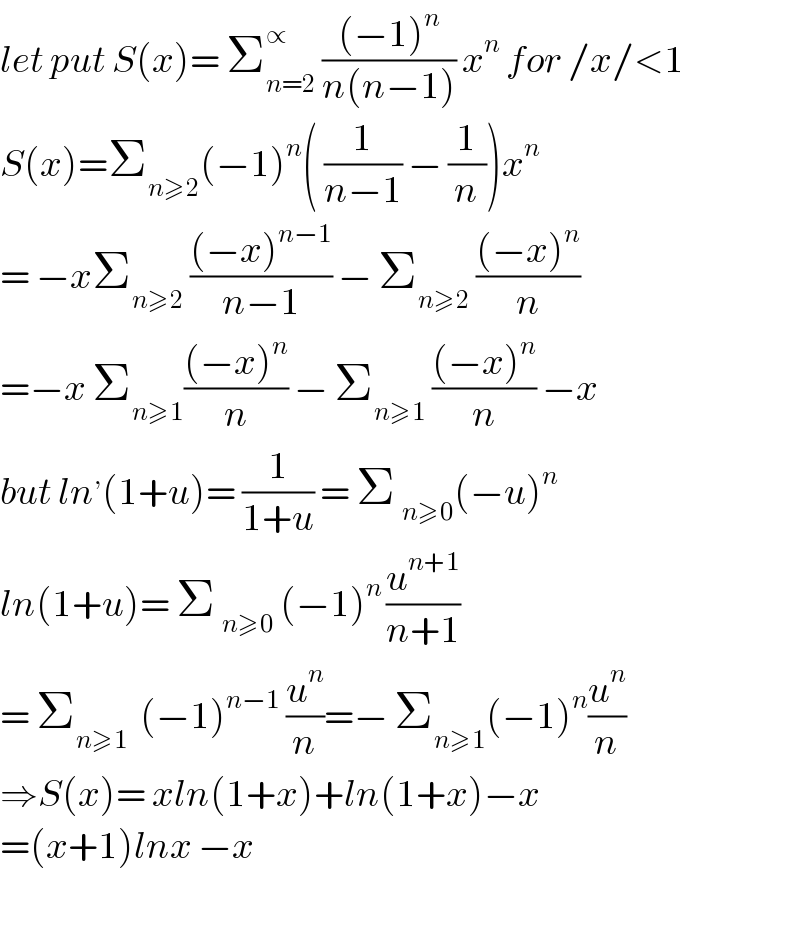
$${let}\:{put}\:{S}\left({x}\right)=\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{2}} ^{\propto} \:\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} }{{n}\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right)}\:{x}^{{n}} \:{for}\:/{x}/<\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${S}\left({x}\right)=\sum_{{n}\geqslant\mathrm{2}} \left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} \left(\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}−\mathrm{1}}\:−\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\right){x}^{{n}} \\ $$$$=\:−{x}\sum_{{n}\geqslant\mathrm{2}} \:\frac{\left(−{x}\right)^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} }{{n}−\mathrm{1}}\:−\:\sum_{{n}\geqslant\mathrm{2}} \:\frac{\left(−{x}\right)^{{n}} }{{n}} \\ $$$$=−{x}\:\sum_{{n}\geqslant\mathrm{1}} \frac{\left(−{x}\right)^{{n}} }{{n}}\:−\:\sum_{{n}\geqslant\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{\left(−{x}\right)^{{n}} }{{n}}\:−{x} \\ $$$${but}\:{ln}^{,} \left(\mathrm{1}+{u}\right)=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{u}}\:=\:\Sigma\:_{{n}\geqslant\mathrm{0}} \left(−{u}\right)^{{n}} \\ $$$${ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{u}\right)=\:\Sigma\:_{{n}\geqslant\mathrm{0}} \:\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}\:} \frac{{u}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{{n}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$=\:\sum_{{n}\geqslant\mathrm{1}} \:\:\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{{u}^{{n}} }{{n}}=−\:\sum_{{n}\geqslant\mathrm{1}} \left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} \frac{{u}^{{n}} }{{n}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{S}\left({x}\right)=\:{xln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)+{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)−{x} \\ $$$$=\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right){lnx}\:−{x} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by abdo imad last updated on 28/Dec/17
$${your}\:{answer}\:{is}\:{true}\:{prakash} \\ $$
Commented by abdo imad last updated on 28/Dec/17
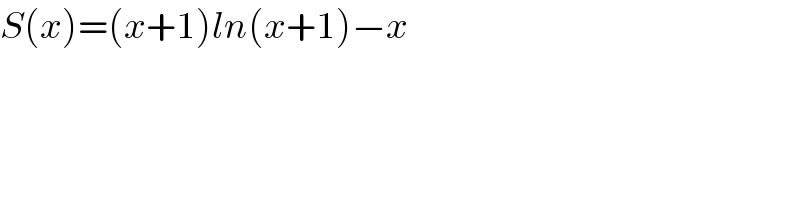
$${S}\left({x}\right)=\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right){ln}\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)−{x} \\ $$
Answered by prakash jain last updated on 28/Dec/17
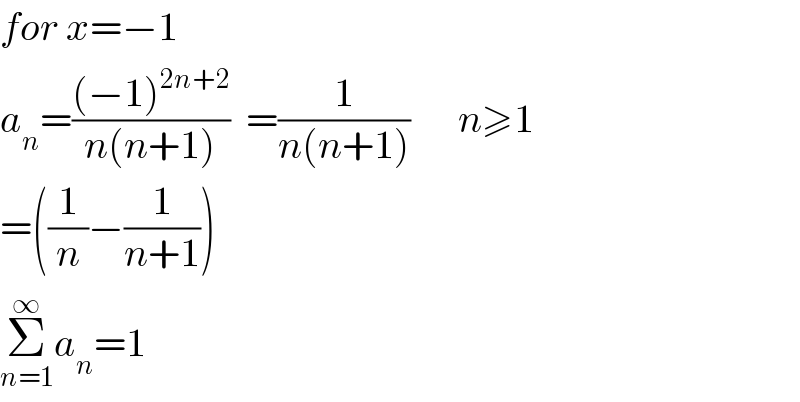
$${for}\:{x}=−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${a}_{{n}} =\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{2}} }{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}\:\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}\:\:\:\:\:\:{n}\geqslant\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$=\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}+\mathrm{1}}\right) \\ $$$$\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}{a}_{{n}} =\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 27/Dec/17
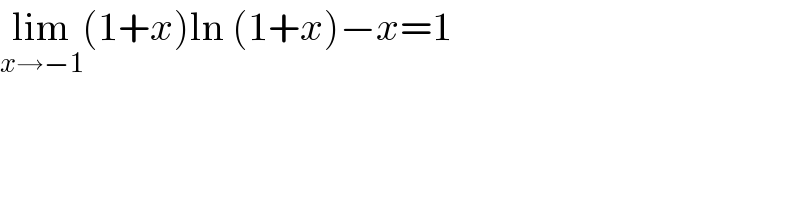
$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow−\mathrm{1}} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)−{x}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$
