Question Number 95832 by M±th+et+s last updated on 28/May/20

$${find}\:{without}\:{using}\:{l}'{hopital} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} {{lim}}\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}−{x}} −\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}} \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 28/May/20
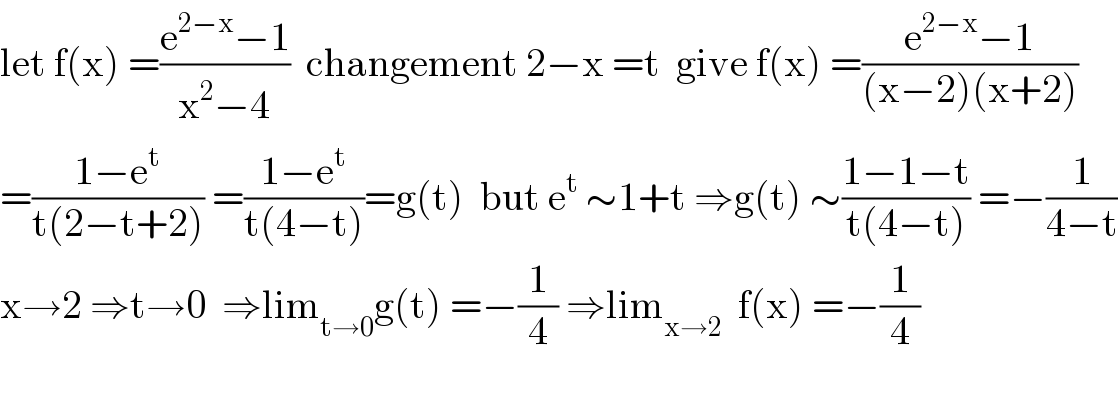
$$\mathrm{let}\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:=\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{x}} −\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}}\:\:\mathrm{changement}\:\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{x}\:=\mathrm{t}\:\:\mathrm{give}\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:=\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{x}} −\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2}\right)\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{t}} }{\mathrm{t}\left(\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{t}+\mathrm{2}\right)}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{t}} }{\mathrm{t}\left(\mathrm{4}−\mathrm{t}\right)}=\mathrm{g}\left(\mathrm{t}\right)\:\:\mathrm{but}\:\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{t}} \:\sim\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{t}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{g}\left(\mathrm{t}\right)\:\sim\frac{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{t}}{\mathrm{t}\left(\mathrm{4}−\mathrm{t}\right)}\:=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}−\mathrm{t}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}\:\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \mathrm{g}\left(\mathrm{t}\right)\:=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{lim}_{\mathrm{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} \:\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by M±th+et+s last updated on 28/May/20
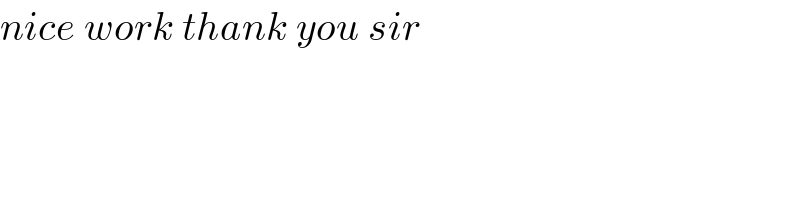
$${nice}\:{work}\:{thank}\:{you}\:{sir} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 28/May/20

$$\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{welcome}\:\mathrm{sir}. \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 21/Jun/20
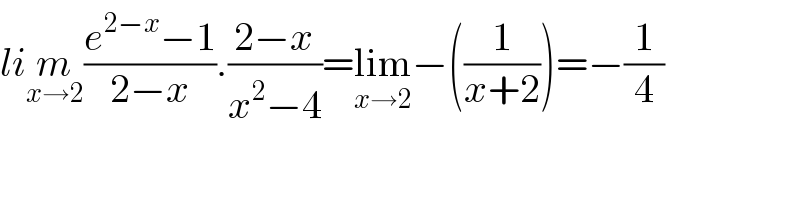
$${li}\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} {{m}}\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}−{x}} −\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}−{x}}.\frac{\mathrm{2}−{x}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{2}} {\mathrm{lim}}−\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}\right)=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$
Commented by M±th+et+s last updated on 23/Jun/20
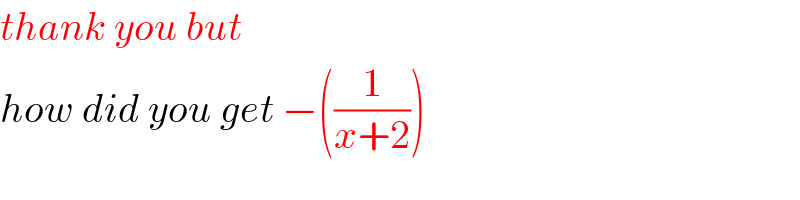
$${thank}\:{you}\:{but} \\ $$$${how}\:{did}\:{you}\:{get}\:−\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}\right) \\ $$
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 29/Jun/20

$$\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}−{x}} −\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}−{x}}=\mathrm{1}\:\: \\ $$
