Question Number 60946 by Tawa1 last updated on 27/May/19
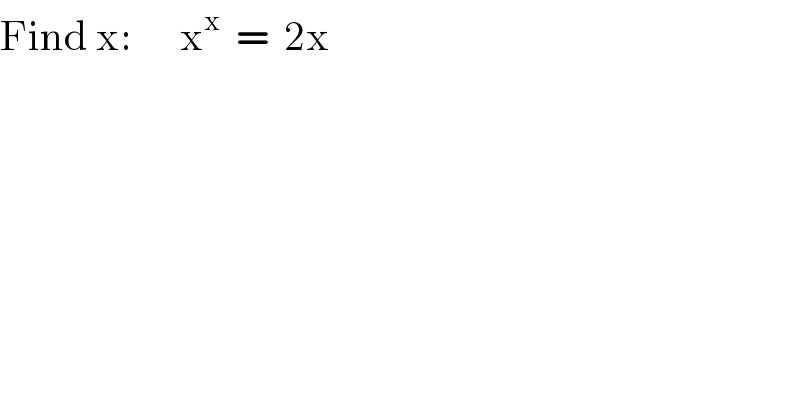
$$\mathrm{Find}\:\mathrm{x}:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{x}} \:\:=\:\:\mathrm{2x} \\ $$
Commented by Prithwish sen last updated on 27/May/19

$$\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 28/May/19
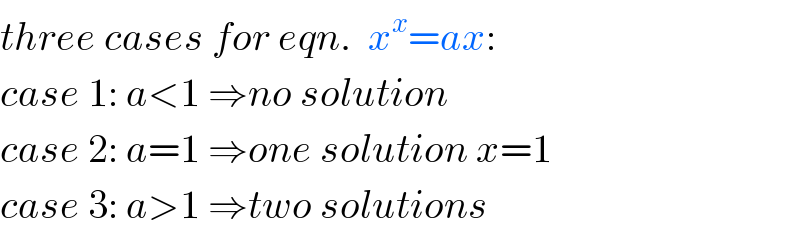
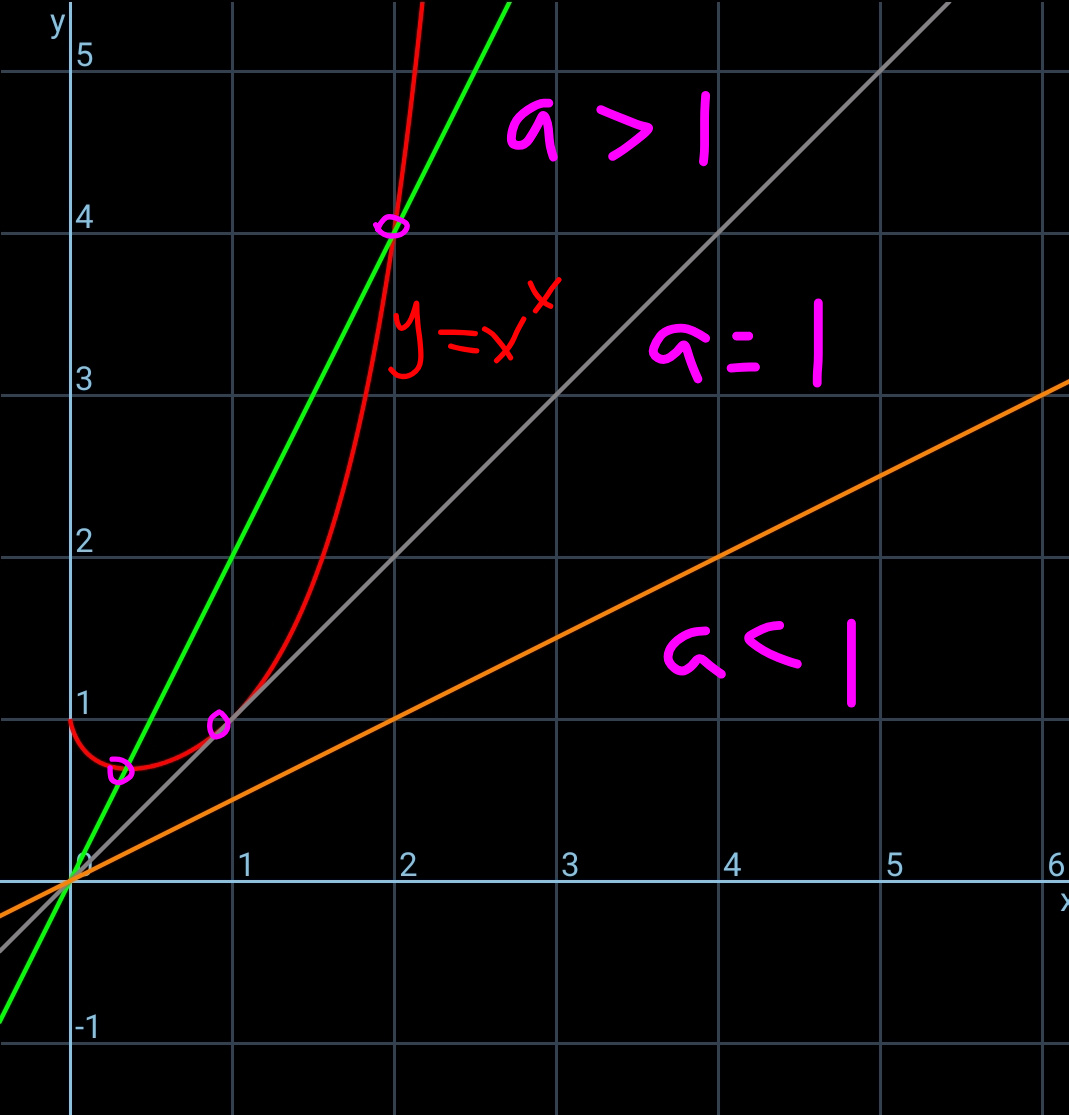
$${three}\:{cases}\:{for}\:{eqn}.\:\:{x}^{{x}} ={ax}: \\ $$$${case}\:\mathrm{1}:\:{a}<\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow{no}\:{solution} \\ $$$${case}\:\mathrm{2}:\:{a}=\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow{one}\:{solution}\:{x}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${case}\:\mathrm{3}:\:{a}>\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow{two}\:{solutions} \\ $$
Commented by Tawa1 last updated on 28/May/19
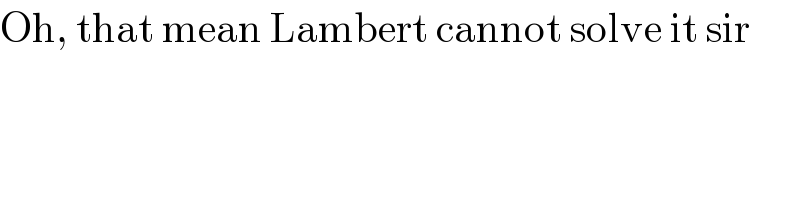
$$\mathrm{Oh},\:\mathrm{that}\:\mathrm{mean}\:\mathrm{Lambert}\:\mathrm{cannot}\:\mathrm{solve}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{sir} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 28/May/19
Answered by meme last updated on 27/May/19

$$\Rightarrow{e}^{{xln}\left({x}\right)} ={e}^{\mathrm{2}{ln}\left({x}\right)} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{xln}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{2}{ln}\left({x}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 27/May/19
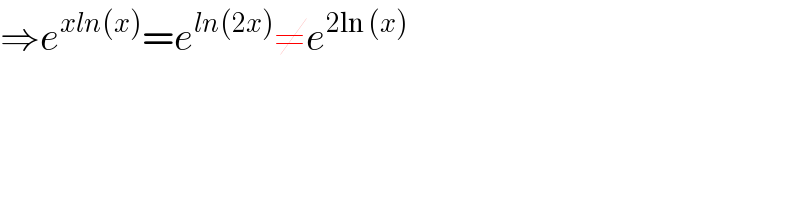
$$\Rightarrow{e}^{{xln}\left({x}\right)} ={e}^{{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)} \neq{e}^{\mathrm{2ln}\:\left({x}\right)} \\ $$
Commented by Tawa1 last updated on 28/May/19
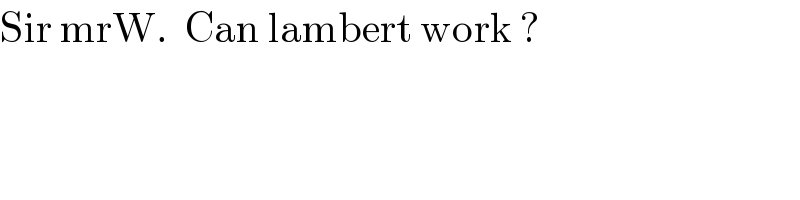
$$\mathrm{Sir}\:\mathrm{mrW}.\:\:\mathrm{Can}\:\mathrm{lambert}\:\mathrm{work}\:? \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 28/May/19

$${no},\:{i}'{m}\:{afraid}. \\ $$
Commented by kaivan.ahmadi last updated on 28/May/19
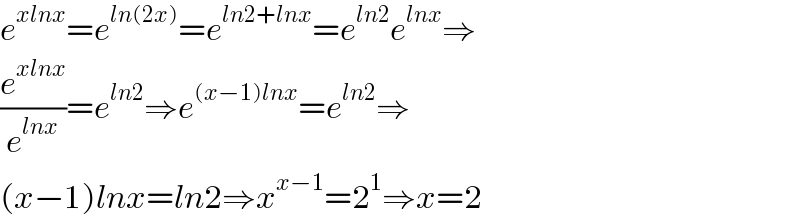
$${e}^{{xlnx}} ={e}^{{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)} ={e}^{{ln}\mathrm{2}+{lnx}} ={e}^{{ln}\mathrm{2}} {e}^{{lnx}} \Rightarrow \\ $$$$\frac{{e}^{{xlnx}} }{{e}^{{lnx}} }={e}^{{ln}\mathrm{2}} \Rightarrow{e}^{\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right){lnx}} ={e}^{{ln}\mathrm{2}} \Rightarrow \\ $$$$\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right){lnx}={ln}\mathrm{2}\Rightarrow{x}^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{1}} \Rightarrow{x}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 29/May/19
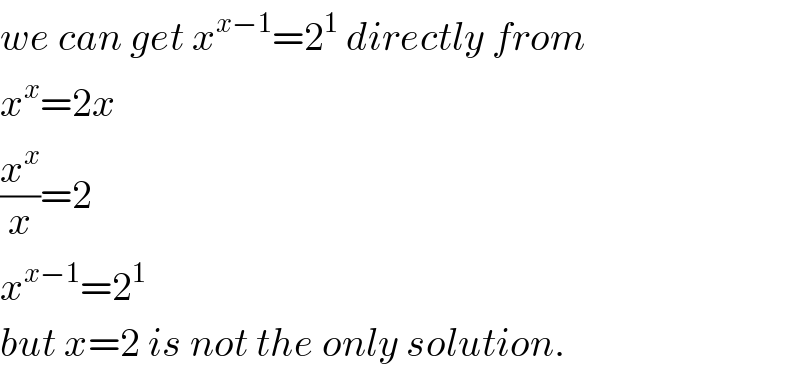
$${we}\:{can}\:{get}\:{x}^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{1}} \:{directly}\:{from} \\ $$$${x}^{{x}} =\mathrm{2}{x} \\ $$$$\frac{{x}^{{x}} }{{x}}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${x}^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$${but}\:{x}=\mathrm{2}\:{is}\:{not}\:{the}\:{only}\:{solution}. \\ $$
Answered by meme last updated on 27/May/19
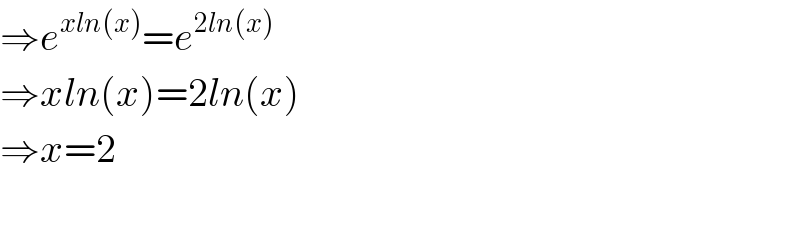
$$\Rightarrow{e}^{{xln}\left({x}\right)} ={e}^{\mathrm{2}{ln}\left({x}\right)} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{xln}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{2}{ln}\left({x}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by JDamian last updated on 27/May/19

$${e}^{\mathrm{2}{ln}\left({x}\right)} \neq\mathrm{2}{x} \\ $$$${e}^{\mathrm{2}{ln}\left({x}\right)} ={x}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Answered by MJS last updated on 27/May/19
![f(x)=x^x −2x f(0)=1 [because lim_(x→0) f(x)=1] f(1)=−1 f(2)=0 f(3)=21 ⇒ there must be a zero in [0; 1], approximating we find x≈.346323 and of course x=2 is the other solution](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q60970.png)
$${f}\left({x}\right)={x}^{{x}} −\mathrm{2}{x} \\ $$$${f}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\mathrm{1}\:\:\:\:\:\left[\mathrm{because}\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}{f}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{1}\right] \\ $$$${f}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)=−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${f}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${f}\left(\mathrm{3}\right)=\mathrm{21} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{there}\:\mathrm{must}\:\mathrm{be}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{zero}\:\mathrm{in}\:\left[\mathrm{0};\:\mathrm{1}\right],\:\mathrm{approximating} \\ $$$$\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{find} \\ $$$${x}\approx.\mathrm{346323} \\ $$$$\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{course}\:{x}=\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{other}\:\mathrm{solution} \\ $$
Commented by Tawa1 last updated on 28/May/19

$$\mathrm{God}\:\mathrm{bless}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{sir} \\ $$
