Question Number 165021 by mathlove last updated on 25/Jan/22
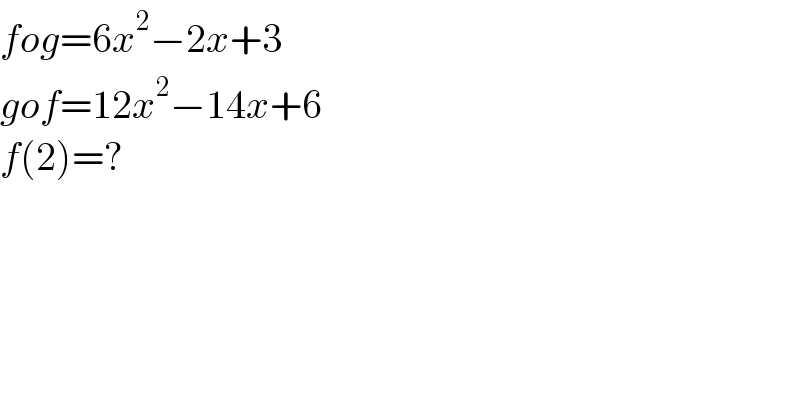
$${fog}=\mathrm{6}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{3} \\ $$$${gof}=\mathrm{12}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{14}{x}+\mathrm{6} \\ $$$${f}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)=? \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 25/Jan/22
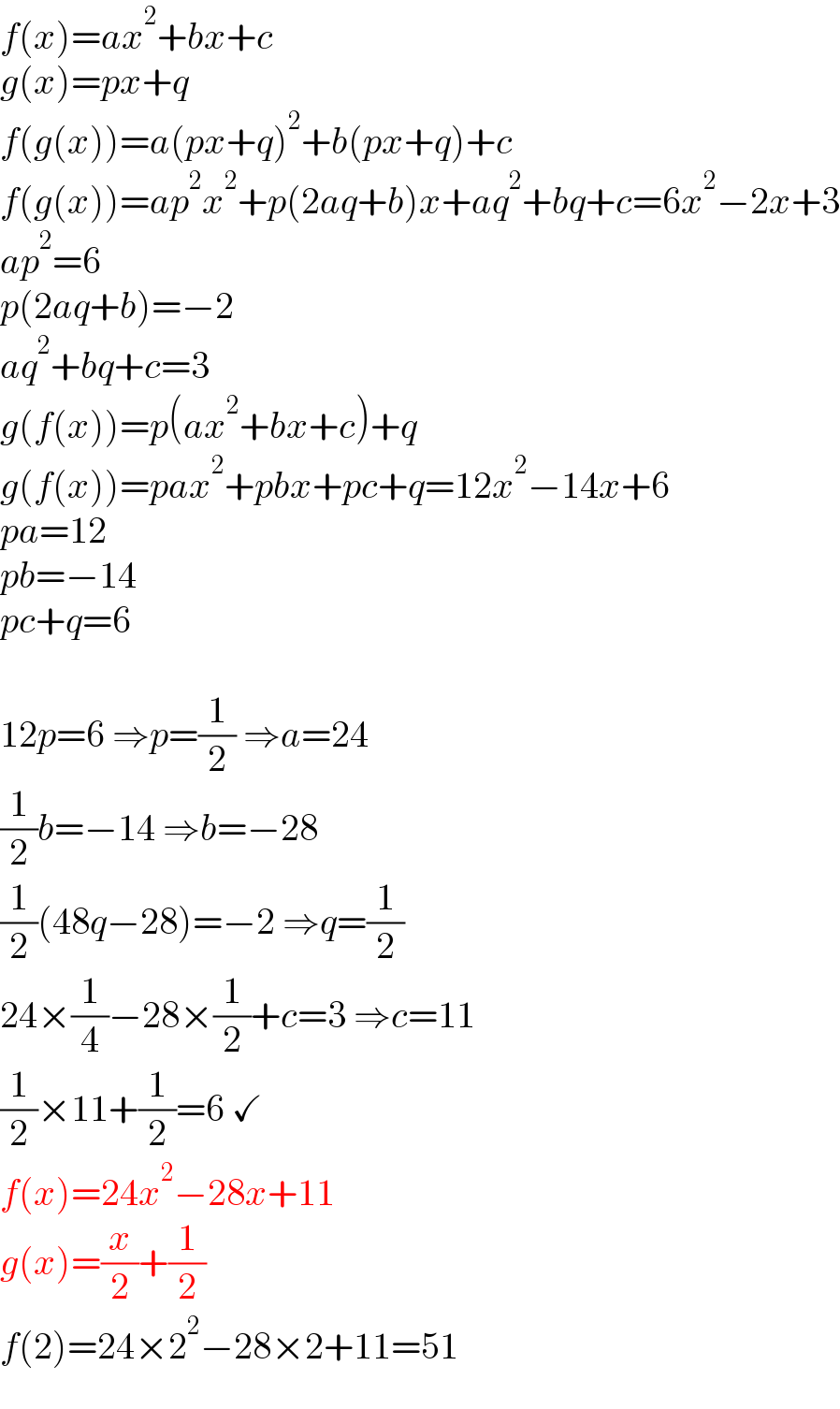
$${f}\left({x}\right)={ax}^{\mathrm{2}} +{bx}+{c} \\ $$$${g}\left({x}\right)={px}+{q} \\ $$$${f}\left({g}\left({x}\right)\right)={a}\left({px}+{q}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +{b}\left({px}+{q}\right)+{c} \\ $$$${f}\left({g}\left({x}\right)\right)={ap}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{p}\left(\mathrm{2}{aq}+{b}\right){x}+{aq}^{\mathrm{2}} +{bq}+{c}=\mathrm{6}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{3} \\ $$$${ap}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{6} \\ $$$${p}\left(\mathrm{2}{aq}+{b}\right)=−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${aq}^{\mathrm{2}} +{bq}+{c}=\mathrm{3} \\ $$$${g}\left({f}\left({x}\right)\right)={p}\left({ax}^{\mathrm{2}} +{bx}+{c}\right)+{q} \\ $$$${g}\left({f}\left({x}\right)\right)={pax}^{\mathrm{2}} +{pbx}+{pc}+{q}=\mathrm{12}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{14}{x}+\mathrm{6} \\ $$$${pa}=\mathrm{12} \\ $$$${pb}=−\mathrm{14} \\ $$$${pc}+{q}=\mathrm{6} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{12}{p}=\mathrm{6}\:\Rightarrow{p}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\Rightarrow{a}=\mathrm{24} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{b}=−\mathrm{14}\:\Rightarrow{b}=−\mathrm{28} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{48}{q}−\mathrm{28}\right)=−\mathrm{2}\:\Rightarrow{q}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{24}×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}−\mathrm{28}×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}+{c}=\mathrm{3}\:\Rightarrow{c}=\mathrm{11} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}×\mathrm{11}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{6}\:\checkmark \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{24}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{28}{x}+\mathrm{11} \\ $$$${g}\left({x}\right)=\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${f}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)=\mathrm{24}×\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{28}×\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{11}=\mathrm{51} \\ $$
Commented by aleks041103 last updated on 25/Jan/22
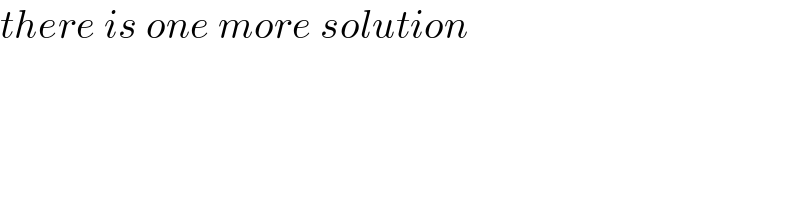
$${there}\:{is}\:{one}\:{more}\:{solution} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 25/Jan/22
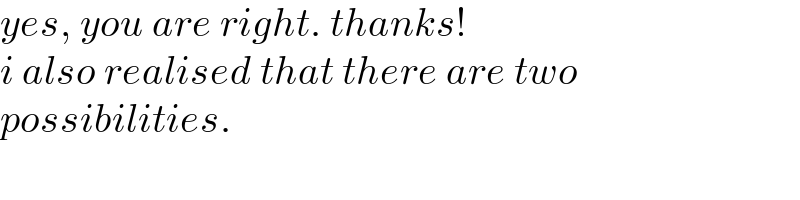
$${yes},\:{you}\:{are}\:{right}.\:{thanks}! \\ $$$${i}\:{also}\:{realised}\:{that}\:{there}\:{are}\:{two}\: \\ $$$${possibilities}. \\ $$
Commented by Tawa11 last updated on 25/Jan/22

$$\mathrm{Weldone}\:\mathrm{sirs} \\ $$
Answered by aleks041103 last updated on 25/Jan/22
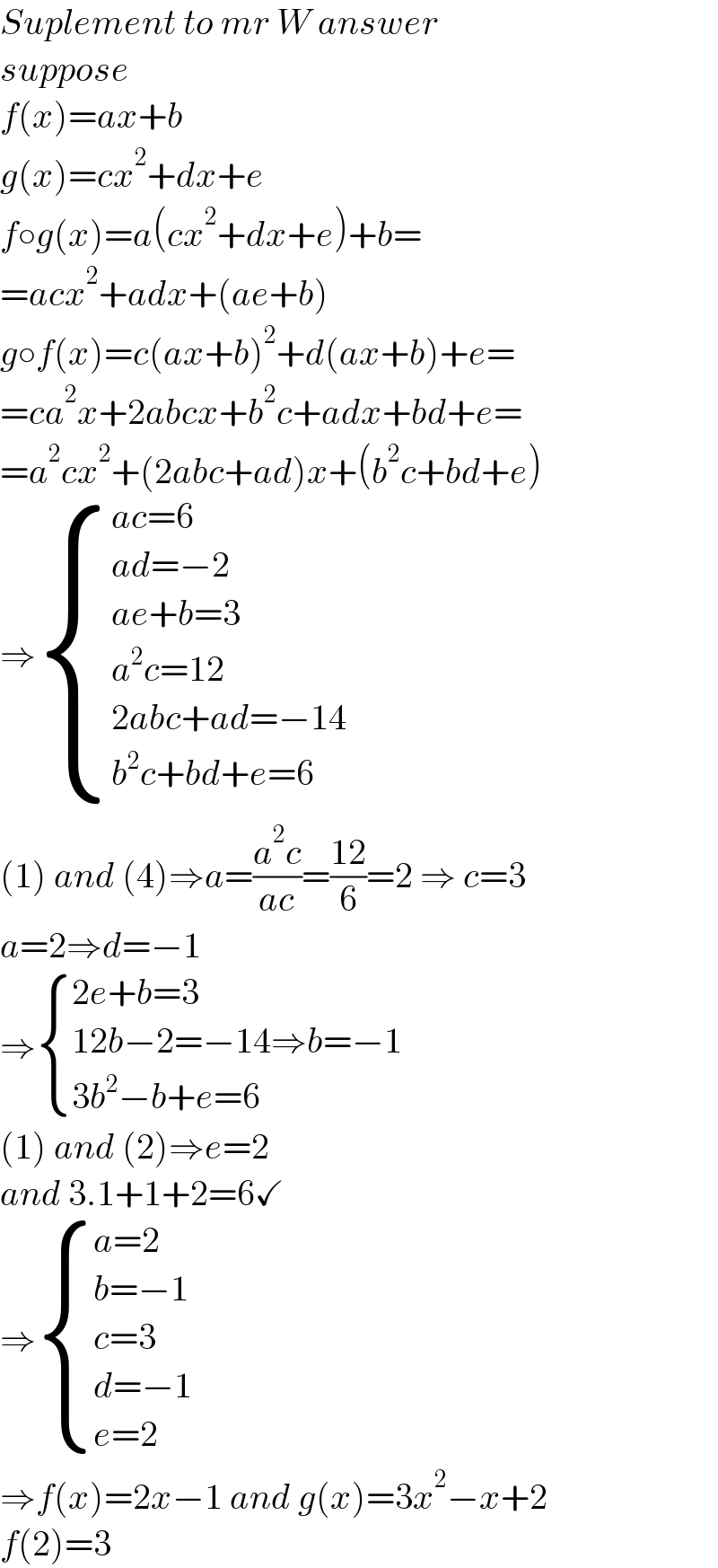
$${Suplement}\:{to}\:{mr}\:{W}\:{answer} \\ $$$${suppose} \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)={ax}+{b} \\ $$$${g}\left({x}\right)={cx}^{\mathrm{2}} +{dx}+{e} \\ $$$${f}\circ{g}\left({x}\right)={a}\left({cx}^{\mathrm{2}} +{dx}+{e}\right)+{b}= \\ $$$$={acx}^{\mathrm{2}} +{adx}+\left({ae}+{b}\right) \\ $$$${g}\circ{f}\left({x}\right)={c}\left({ax}+{b}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +{d}\left({ax}+{b}\right)+{e}= \\ $$$$={ca}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}+\mathrm{2}{abcx}+{b}^{\mathrm{2}} {c}+{adx}+{bd}+{e}= \\ $$$$={a}^{\mathrm{2}} {cx}^{\mathrm{2}} +\left(\mathrm{2}{abc}+{ad}\right){x}+\left({b}^{\mathrm{2}} {c}+{bd}+{e}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\begin{cases}{{ac}=\mathrm{6}}\\{{ad}=−\mathrm{2}}\\{{ae}+{b}=\mathrm{3}}\\{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} {c}=\mathrm{12}}\\{\mathrm{2}{abc}+{ad}=−\mathrm{14}}\\{{b}^{\mathrm{2}} {c}+{bd}+{e}=\mathrm{6}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:{and}\:\left(\mathrm{4}\right)\Rightarrow{a}=\frac{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} {c}}{{ac}}=\frac{\mathrm{12}}{\mathrm{6}}=\mathrm{2}\:\Rightarrow\:{c}=\mathrm{3} \\ $$$${a}=\mathrm{2}\Rightarrow{d}=−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\begin{cases}{\mathrm{2}{e}+{b}=\mathrm{3}}\\{\mathrm{12}{b}−\mathrm{2}=−\mathrm{14}\Rightarrow{b}=−\mathrm{1}}\\{\mathrm{3}{b}^{\mathrm{2}} −{b}+{e}=\mathrm{6}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:{and}\:\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\Rightarrow{e}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${and}\:\mathrm{3}.\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{6}\checkmark \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\begin{cases}{{a}=\mathrm{2}}\\{{b}=−\mathrm{1}}\\{{c}=\mathrm{3}}\\{{d}=−\mathrm{1}}\\{{e}=\mathrm{2}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{f}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}\:{and}\:{g}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{3}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}+\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${f}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)=\mathrm{3} \\ $$
