Question Number 25684 by NECx last updated on 13/Dec/17

$${For}\:{a}\:{geosynchronous}\:{satellite}\:{of} \\ $$$${mass}\:{m}\:{moving}\:{in}\:{a}\:{circular} \\ $$$${orbit}\:{around}\:{the}\:{earth}\:{at}\:{a}\:{constant} \\ $$$${speed}\:{v}\:{and}\:{an}\:{altitude}\:{h}\:{above} \\ $$$${the}\:{earth}\:{surface}.{Show}\:{the} \\ $$$${velocity}\:{v}=\left(\frac{{GM}_{{e}} }{{R}_{{e}} +{h}}\right)^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} . \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${If}\:{the}\:{satellite}\:{above}\:{is}\:{synchronous} \\ $$$${how}\:{fast}\:{is}\:{it}\:{moving}\:{through} \\ $$$${space},{taking}\:{the}\:{period}\:{to}\:{be}\:\mathrm{24}{hrs} \\ $$$${and}\:{M}_{{e}} ={mass}\:{of}\:{the}\:{satellite}\:{and} \\ $$$${is}\:{equal}\:{to}\:\mathrm{5}.\mathrm{98}×\mathrm{10}^{\mathrm{24}} {kg} \\ $$
Answered by jota@ last updated on 13/Dec/17
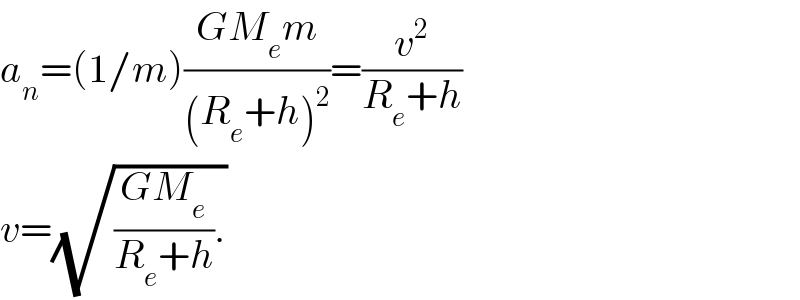
$${a}_{{n}} =\left(\mathrm{1}/{m}\right)\frac{{GM}_{{e}} {m}}{\left({R}_{{e}} +{h}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{{v}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{R}_{{e}} +{h}} \\ $$$${v}=\sqrt{\frac{{GM}_{{e}} }{{R}_{{e}} +{h}}.} \\ $$
Commented by NECx last updated on 13/Dec/17

$${thanks}\:{boss} \\ $$
