Question Number 130442 by greg_ed last updated on 25/Jan/21
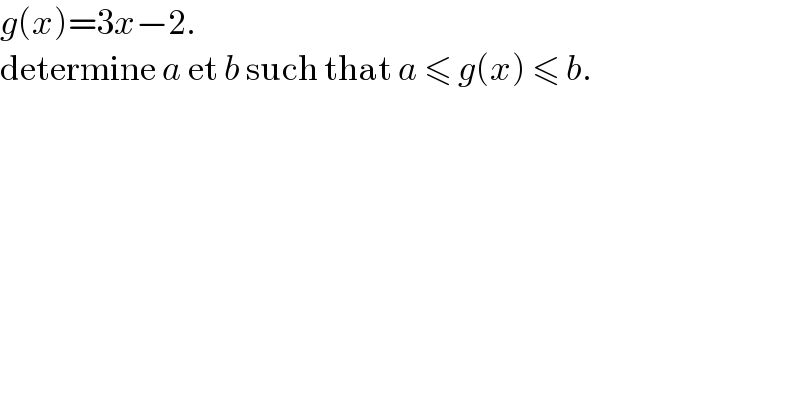
$${g}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{3}{x}−\mathrm{2}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{determine}\:{a}\:\mathrm{et}\:{b}\:\mathrm{such}\:\mathrm{that}\:{a}\:\leqslant\:{g}\left({x}\right)\:\leqslant\:{b}. \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 25/Jan/21
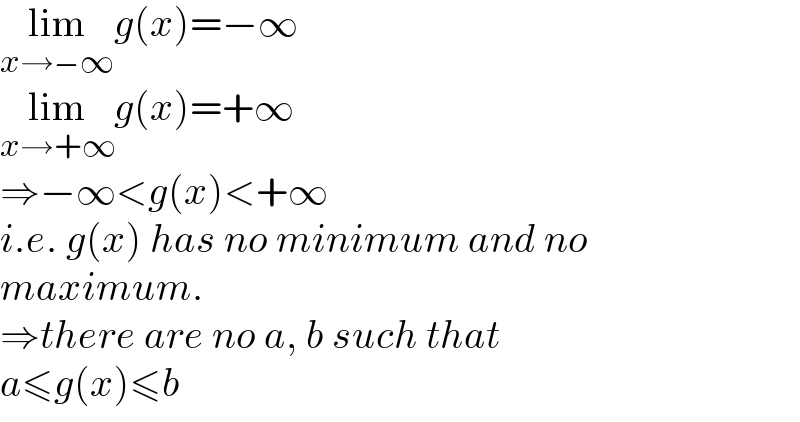
$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow−\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}{g}\left({x}\right)=−\infty \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow+\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}{g}\left({x}\right)=+\infty \\ $$$$\Rightarrow−\infty<{g}\left({x}\right)<+\infty \\ $$$${i}.{e}.\:{g}\left({x}\right)\:{has}\:{no}\:{minimum}\:{and}\:{no} \\ $$$${maximum}. \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{there}\:{are}\:{no}\:{a},\:{b}\:{such}\:{that} \\ $$$${a}\leqslant{g}\left({x}\right)\leqslant{b} \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 25/Jan/21

$$\mathrm{c}\:\mathrm{est}\:\mathrm{lequation}\:\mathrm{dune}\:\mathrm{droite}\:\mathrm{donc}\:\mathrm{g}\:\mathrm{nest}\:\mathrm{pas}\:\mathrm{bornee}… \\ $$
