Question Number 98953 by Ar Brandon last updated on 17/Jun/20
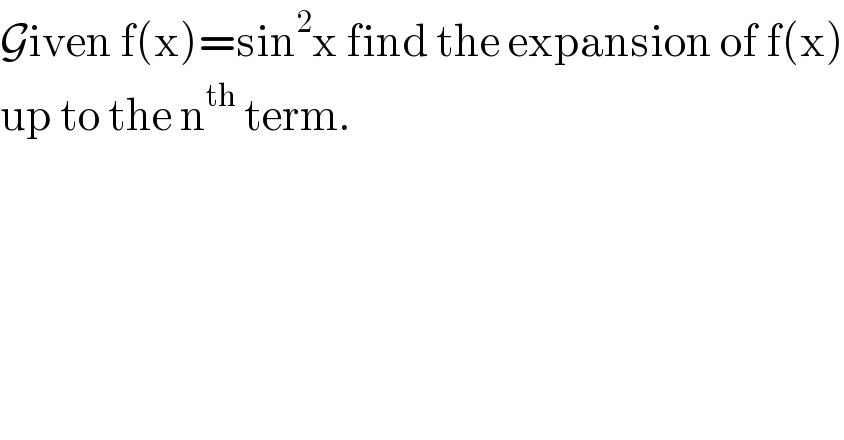
$$\mathcal{G}\mathrm{iven}\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}\:\mathrm{find}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{expansion}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{up}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{th}} \:\mathrm{term}. \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 17/Jun/20
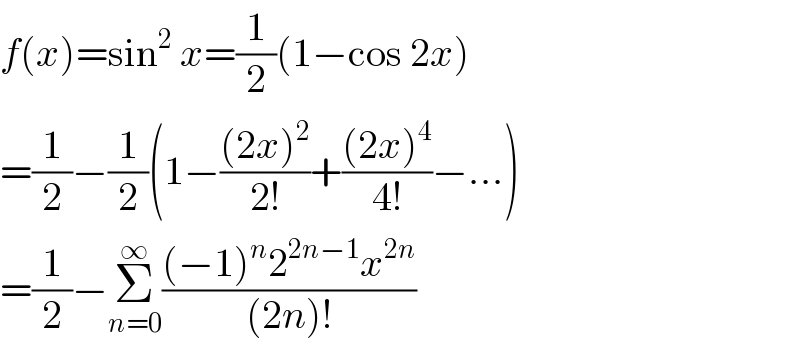
$${f}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2}{x}\right) \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}!}+\frac{\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)^{\mathrm{4}} }{\mathrm{4}!}−…\right) \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}−\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} \mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}{n}−\mathrm{1}} {x}^{\mathrm{2}{n}} }{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}\right)!} \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 17/Jun/20
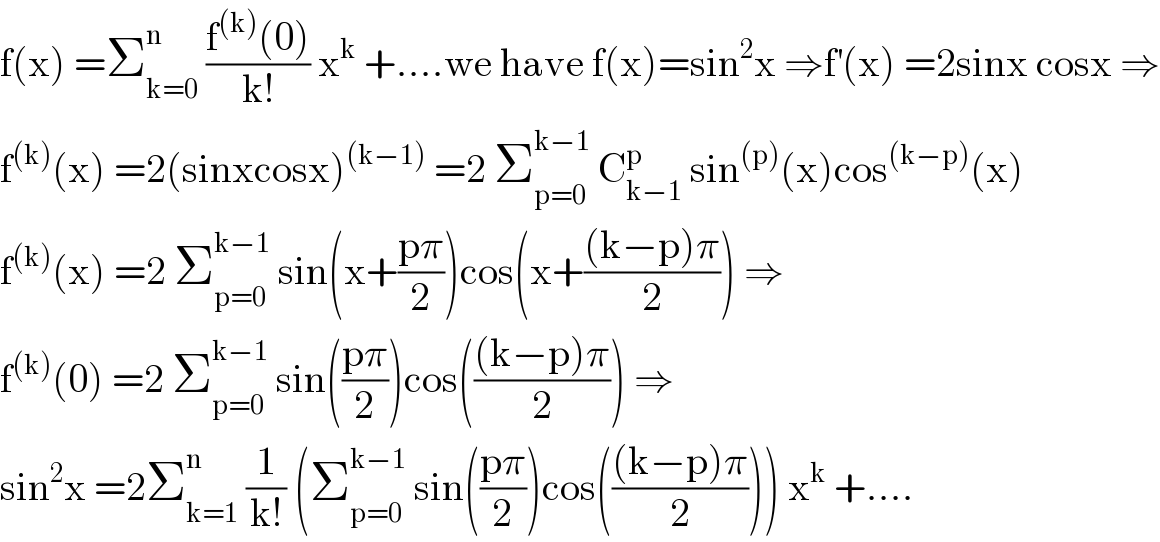
$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:=\sum_{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{n}} \:\frac{\mathrm{f}^{\left(\mathrm{k}\right)} \left(\mathrm{0}\right)}{\mathrm{k}!}\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{k}} \:+….\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{have}\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{f}^{'} \left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:=\mathrm{2sinx}\:\mathrm{cosx}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}^{\left(\mathrm{k}\right)} \left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:=\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{sinxcosx}\right)^{\left(\mathrm{k}−\mathrm{1}\right)} \:=\mathrm{2}\:\sum_{\mathrm{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{k}−\mathrm{1}} \:\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{k}−\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{p}} \:\mathrm{sin}^{\left(\mathrm{p}\right)} \left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{cos}^{\left(\mathrm{k}−\mathrm{p}\right)} \left(\mathrm{x}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}^{\left(\mathrm{k}\right)} \left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:=\mathrm{2}\:\sum_{\mathrm{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{k}−\mathrm{1}} \:\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{x}+\frac{\mathrm{p}\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\mathrm{cos}\left(\mathrm{x}+\frac{\left(\mathrm{k}−\mathrm{p}\right)\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}^{\left(\mathrm{k}\right)} \left(\mathrm{0}\right)\:=\mathrm{2}\:\sum_{\mathrm{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{k}−\mathrm{1}} \:\mathrm{sin}\left(\frac{\mathrm{p}\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\mathrm{cos}\left(\frac{\left(\mathrm{k}−\mathrm{p}\right)\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{x}\:=\mathrm{2}\sum_{\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{n}} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{k}!}\:\left(\sum_{\mathrm{p}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{k}−\mathrm{1}} \:\mathrm{sin}\left(\frac{\mathrm{p}\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\mathrm{cos}\left(\frac{\left(\mathrm{k}−\mathrm{p}\right)\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\right)\:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{k}} \:+…. \\ $$
