Question Number 15942 by Don sai last updated on 15/Jun/17

$$\mathrm{Help}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{solve}\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)\mathrm{dy}/\mathrm{dx}=\mathrm{3}−\mathrm{2y}/\mathrm{x} \\ $$
Answered by mrW1 last updated on 16/Jun/17
![(x+2)(dy/dx)+(2/x)y=3 (dy/dx)+(2/(x(x+2)))y=(3/(x+2)) (dy/dx)+p(x)y=q(x) p(x)=(2/(x(x+2))) q(x)=(3/(x+2)) P(x)=∫p(x)dx=∫(2/(x(x+2)))dx =∫((1/x)−(1/(x+2)))dx=ln (x/(x+2)) e^(−P(x)) =e^(−ln (x/(x+2))) =e^(ln ((x+2)/x)) =((x+2)/x) e^(P(x)) =e^(ln (x/(x+2))) =(x/(x+2)) let y=c(x)e^(−P(x)) =((x+2)/x)c(x) (dy/dx)=c′(x)e^(−P(x)) −c(x)e^(−P(x)) p(x) c′(x)e^(−P(x)) −c(x)e^(−P(x)) p(x)+p(x)c(x)e^(−P(x)) =q(x) c′(x)e^(−P(x)) =q(x) c′(x)=q(x)e^(P(x)) =(3/(x+2))×(x/(x+2))=((3x)/((x+2)^2 )) ⇒c(x)=∫q(x)e^(P(x)) dx=3∫(x/((x+2)^2 ))dx (x/((x+2)^2 ))=(A/(x+2))+(B/((x+2)^2 )) x=Ax+2A+B ⇒A=1 ⇒2A+B=0 ⇒B=−2 ⇒(x/((x+2)^2 ))=(1/(x+2))−(2/((x+2)^2 )) ⇒c(x)=3∫[(1/(x+2))−(2/((x+2)^2 ))]dx =3ln (x+2)+(6/(x+2))+C_1 ⇒y=c(x)e^(−P(x)) =[3ln (x+2)+(6/(x+2))+C_1 ]×((x+2)/x) y=((3(x+2))/x)[ln (x+2)+(2/(x+2))+C]](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q15944.png)
$$\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{x}}\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{x}\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)}\mathrm{y}=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}+\mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{q}\left(\mathrm{x}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{x}\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)} \\ $$$$\mathrm{q}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{P}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\int\mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{dx}=\int\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{x}\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)}\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$=\int\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}}\right)\mathrm{dx}=\mathrm{ln}\:\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{P}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)} =\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{ln}\:\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}}} =\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{ln}\:\frac{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{x}}} =\frac{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{x}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{P}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)} =\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{ln}\:\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}}} =\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{let}\:\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{c}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{P}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)} =\frac{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{x}}\mathrm{c}\left(\mathrm{x}\right) \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}=\mathrm{c}'\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{P}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)} −\mathrm{c}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{P}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)} \mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{c}'\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{P}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)} −\mathrm{c}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{P}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)} \mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)+\mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{c}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{P}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)} =\mathrm{q}\left(\mathrm{x}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{c}'\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{P}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)} =\mathrm{q}\left(\mathrm{x}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{c}'\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\mathrm{q}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{P}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)} =\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}}×\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{3x}}{\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{c}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\int\mathrm{q}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{P}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)} \mathrm{dx}=\mathrm{3}\int\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{\mathrm{A}}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{B}}{\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{Ax}+\mathrm{2A}+\mathrm{B} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{A}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{2A}+\mathrm{B}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{B}=−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{c}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\mathrm{3}\int\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\right]\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{3ln}\:\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{6}}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{c}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{P}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)} =\left[\mathrm{3ln}\:\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{6}}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{1}} \right]×\frac{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{x}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}=\frac{\mathrm{3}\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)}{\mathrm{x}}\left[\mathrm{ln}\:\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}}+\mathrm{C}\right] \\ $$
Commented by Don sai last updated on 15/Jun/17
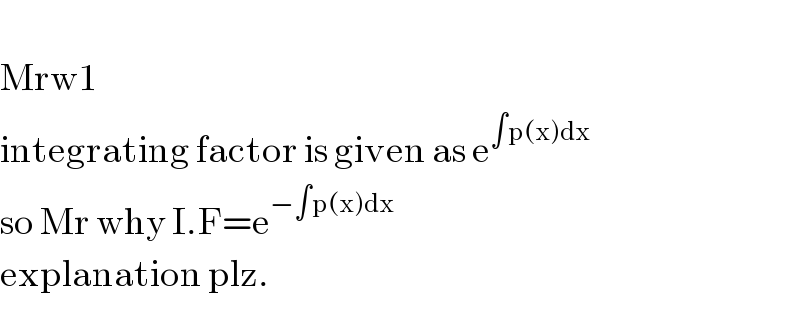
$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{Mrw1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{integrating}\:\mathrm{factor}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{given}\:\mathrm{as}\:\mathrm{e}^{\int\mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{dx}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{so}\:\mathrm{Mr}\:\mathrm{why}\:\mathrm{I}.\mathrm{F}=\mathrm{e}^{−\int\mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{dx}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{explanation}\:\mathrm{plz}. \\ $$
Commented by mrW1 last updated on 15/Jun/17
![if the equation is given as (dy/dx)+p(x)y=q(x) then y=c(x)e^(−∫p(x)dx) , since (dy/dx)=c′(x)e^(−∫p(x)dx) +c(x)e^(−∫p(x)dx) [−p(x)] and (dy/dx)+p(x)y=c′(x)e^(−∫p(x)dx) +c(x)e^(−∫p(x)dx) [−p(x)]+p(x)c(x)e^(−∫p(x)dx) =c′(x)e^(−∫p(x)dx) =q(x) ⇒c′(x)=q(x)e^(∫p(x)dx) ⇒c(x)=∫q(x)e^(∫p(x)dx) dx ⇒y=e^(−∫p(x)dx) ∫q(x)e^(∫p(x)dx) dx](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q15949.png)
$$\mathrm{if}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{equation}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{given}\:\mathrm{as} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}+\mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{q}\left(\mathrm{x}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{then}\:\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{c}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{e}^{−\int\mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{dx}} ,\:\mathrm{since} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}=\mathrm{c}'\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{e}^{−\int\mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{dx}} +\mathrm{c}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{e}^{−\int\mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{dx}} \left[−\mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\right] \\ $$$$\mathrm{and} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}+\mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{c}'\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{e}^{−\int\mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{dx}} +\mathrm{c}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{e}^{−\int\mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{dx}} \left[−\mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\right]+\mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{c}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{e}^{−\int\mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{dx}} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{c}'\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{e}^{−\int\mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{dx}} =\mathrm{q}\left(\mathrm{x}\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{c}'\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\mathrm{q}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{e}^{\int\mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{dx}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{c}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\int\mathrm{q}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{e}^{\int\mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{dx}} \mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{e}^{−\int\mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{dx}} \int\mathrm{q}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{e}^{\int\mathrm{p}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\mathrm{dx}} \mathrm{dx} \\ $$
Commented by Don sai last updated on 16/Jun/17

$$\mathrm{Thank}\:\mathrm{you} \\ $$
