Question Number 118511 by ZiYangLee last updated on 18/Oct/20
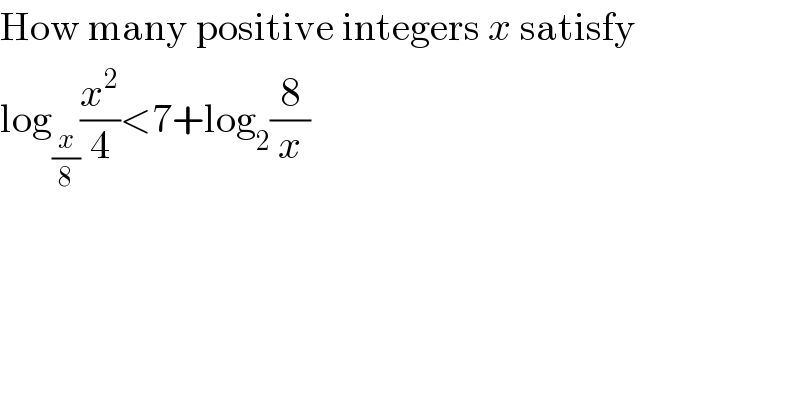
Answered by mr W last updated on 18/Oct/20
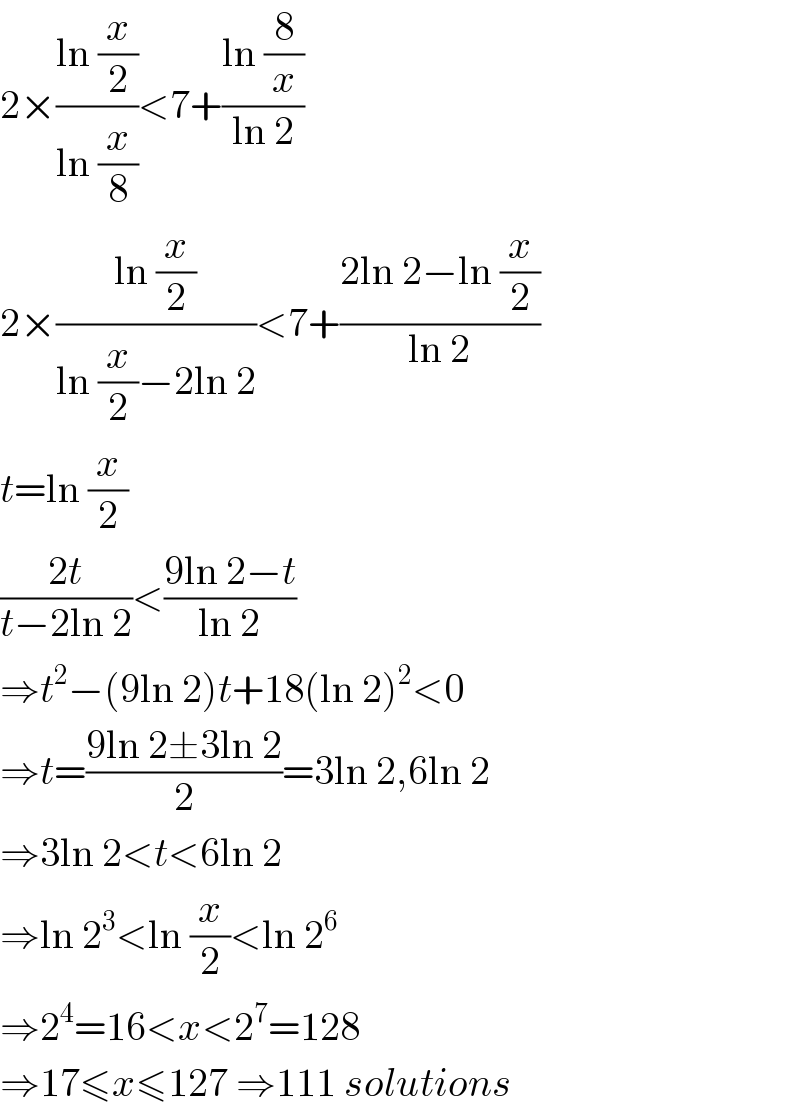
Answered by Lordose last updated on 18/Oct/20
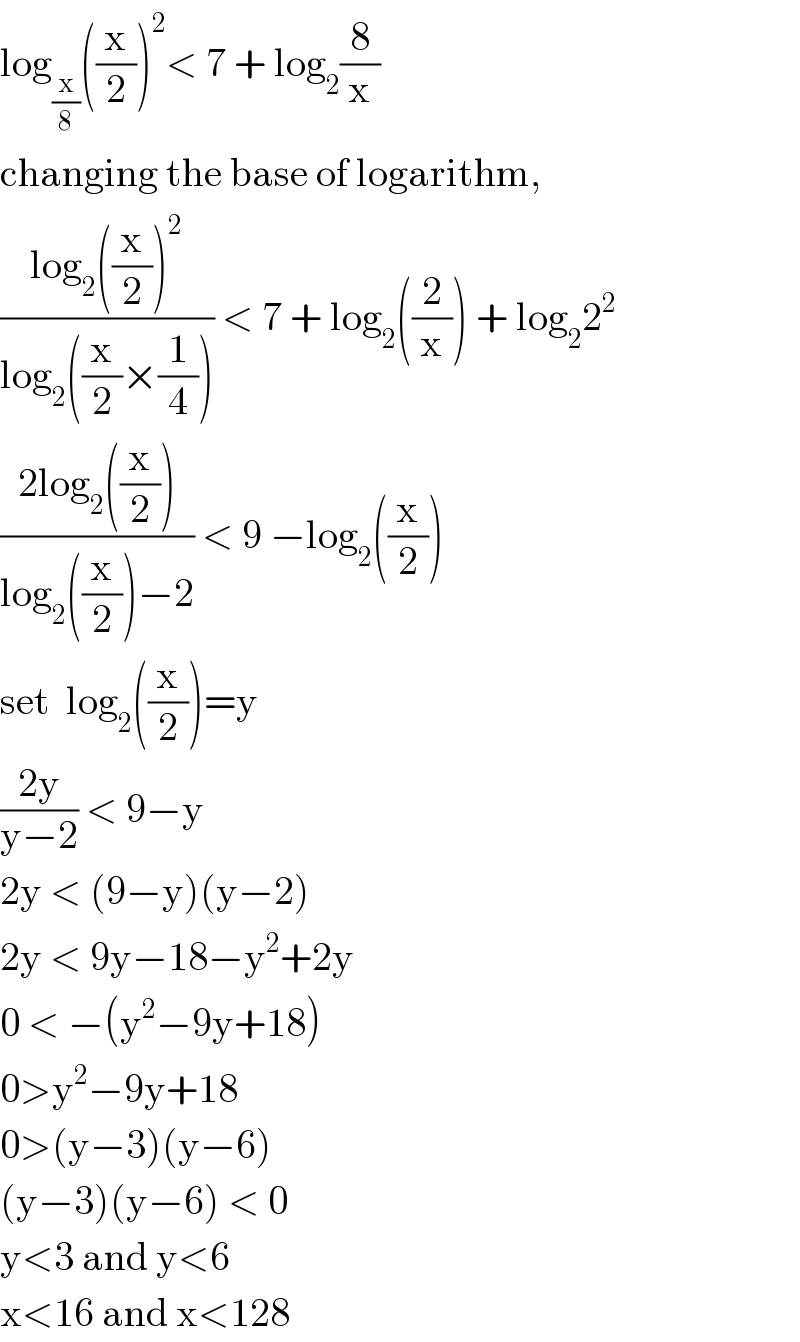
Answered by 1549442205PVT last updated on 18/Oct/20
![We need the condition x>0,x≠8 log_(x/8) (x^2 /4)<7+log_2 (8/x)⇔log_(x/8) [((x/8))^2 .16] <7+log_2 8−log_2 x⇔log_(x/8) ((x/8))^2 +log_(x/8) 16 <7+3−log_2 x⇔2+4log_(x/8) 2<10−log_2 x ⇔(4/(log_2 (x/8)))<8−log_2 x⇔(4/(log_2 x−3))<8−log_2 x ⇔(4/(log_2 x−3))+log_2 x−8<0.Put log_2 x=t ⇔(4/(t−3))+t−8<0⇔((t^2 −11t+28)/(t−3))<0 ⇔(((t−4)(t−7))/(t−3))<0 ⇔t∈(−∞,3)∪(4,7) i)log_2 x<3⇔0<x<8 ii)4<log_2 x<7⇔2^4 <x<2^7 ⇔16<x<128 Thus,the roots of given inequality are: x∈(0,8)∪(16,128) Since x∈N^∗ ,x∈{1,2,...,7}∪{17,...,127} hence all there are 11 positive integers satisfying the given inequality](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q118536.png)
Commented by mr W last updated on 18/Oct/20

Commented by 1549442205PVT last updated on 18/Oct/20

Commented by ZiYangLee last updated on 19/Oct/20

