Question Number 183794 by cortano1 last updated on 30/Dec/22
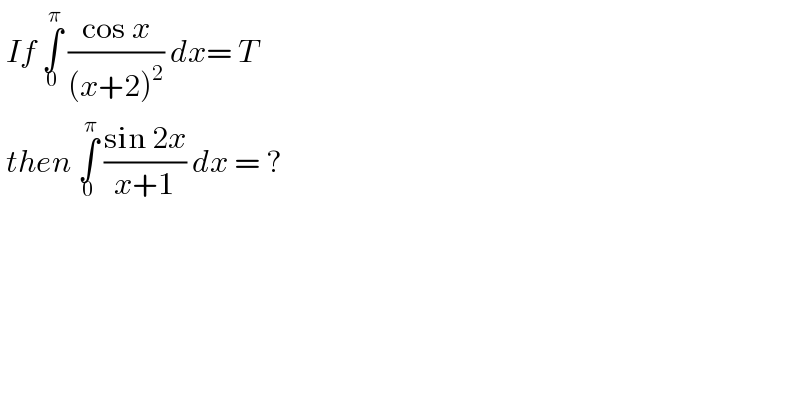
$$\:{If}\:\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\pi} {\int}}\:\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}{\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:{dx}=\:{T} \\ $$$$\:{then}\:\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\pi} {\int}}\:\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}{x}}{{x}+\mathrm{1}}\:{dx}\:=\:?\: \\ $$
Commented by Frix last updated on 30/Dec/22

$$\int\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}{\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}=\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{Ci}\:\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)\:−\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{Si}\:\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)\:−\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}\:+{C}_{\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\int\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}{x}}{{x}+\mathrm{1}}{dx}=\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{Si}\:\left(\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)\:−\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{Ci}\:\left(\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)\:+{C}_{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{don}'\mathrm{t}\:\mathrm{see}\:\mathrm{any}\:\mathrm{connection},\:\mathrm{blame}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{on}\:\mathrm{me}… \\ $$$$\mathrm{But}\:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{sure}\:\mathrm{there}'\mathrm{s}\:\mathrm{no}\:\mathrm{typo}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{your}\:\mathrm{question}? \\ $$
