Question Number 27094 by abdo imad last updated on 02/Jan/18
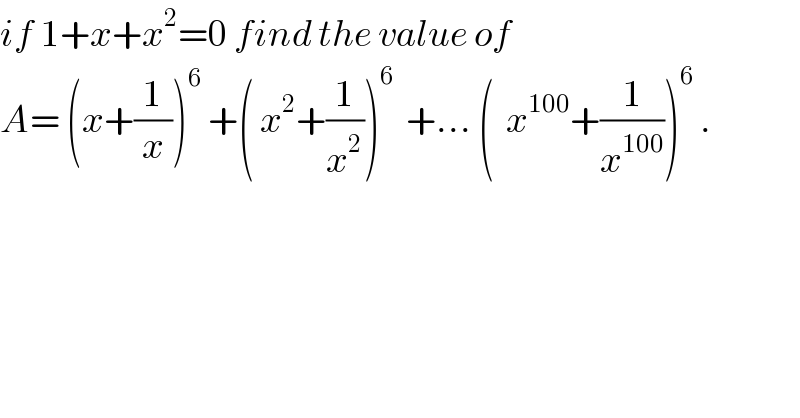
$${if}\:\mathrm{1}+{x}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{0}\:{find}\:{the}\:{value}\:{of}\: \\ $$$${A}=\:\left({x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right)^{\mathrm{6}} \:+\left(\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)^{\mathrm{6}} \:\:+…\:\left(\:\:{x}^{\mathrm{100}} +\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{100}} }\right)^{\mathrm{6}} \:. \\ $$
Commented by AHSoomro last updated on 02/Jan/18

$$\mathrm{Question}\:\mathrm{same}\:\mathrm{as}\:\mathrm{Q}#\mathrm{27002} \\ $$
Commented by abdo imad last updated on 08/Jan/18
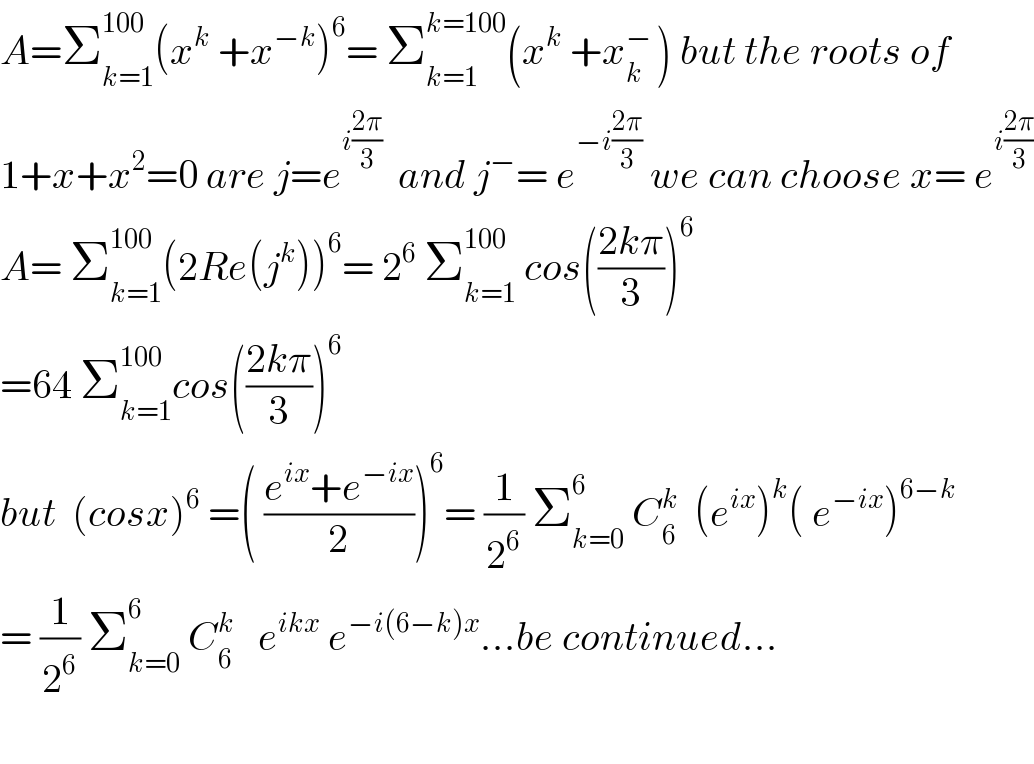
$${A}=\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{100}} \left({x}^{{k}} \:+{x}^{−{k}} \right)^{\mathrm{6}} =\:\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{k}=\mathrm{100}} \left({x}^{{k}} \:+{x}_{{k}} ^{−\:} \right)\:{but}\:{the}\:{roots}\:{of}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}+{x}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{0}\:{are}\:{j}={e}^{{i}\frac{\mathrm{2}\pi}{\mathrm{3}}} \:\:{and}\:{j}^{−} =\:{e}^{−{i}\frac{\mathrm{2}\pi}{\mathrm{3}}} \:{we}\:{can}\:{choose}\:{x}=\:{e}^{{i}\frac{\mathrm{2}\pi}{\mathrm{3}}} \\ $$$${A}=\:\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{100}} \left(\mathrm{2}{Re}\left({j}^{{k}} \right)\right)^{\mathrm{6}} =\:\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{6}} \:\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{100}} \:{cos}\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}{k}\pi}{\mathrm{3}}\right)^{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{64}\:\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{100}} {cos}\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}{k}\pi}{\mathrm{3}}\right)^{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$$${but}\:\:\left({cosx}\right)^{\mathrm{6}} \:=\left(\:\frac{{e}^{{ix}} +{e}^{−{ix}} }{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{6}} =\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{6}} }\:\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{6}} \:{C}_{\mathrm{6}} ^{{k}} \:\:\left({e}^{{ix}} \right)^{{k}} \left(\:{e}^{−{ix}} \right)^{\mathrm{6}−{k}} \\ $$$$=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{6}} }\:\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{6}\:} \:{C}_{\mathrm{6}} ^{{k}} \:\:\:{e}^{{ikx}} \:{e}^{−{i}\left(\mathrm{6}−{k}\right){x}} …{be}\:{continued}… \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by bsayani309@gmail.com last updated on 05/Jan/18
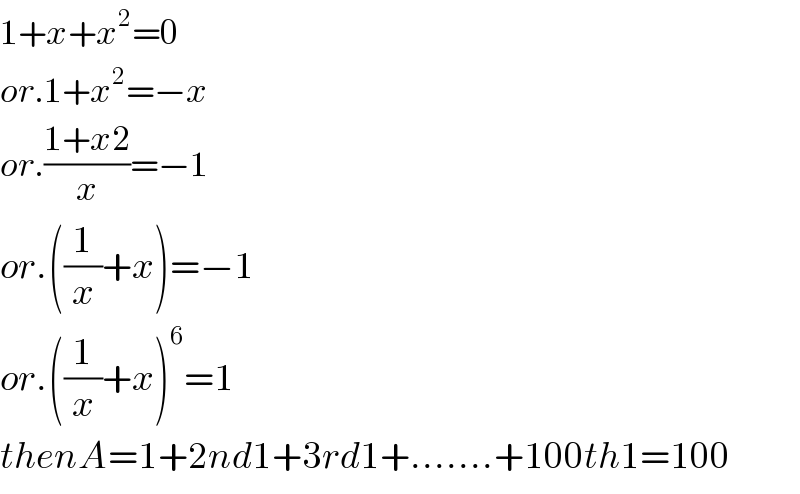
$$\mathrm{1}+{x}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${or}.\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} =−{x} \\ $$$${or}.\frac{\mathrm{1}+{x}\mathrm{2}}{{x}}=−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${or}.\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}+{x}\right)=−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${or}.\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}+{x}\right)^{\mathrm{6}} =\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${thenA}=\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}{nd}\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{3}{rd}\mathrm{1}+…….+\mathrm{100}{th}\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{100} \\ $$
