Question Number 95648 by Abdulrahman last updated on 26/May/20
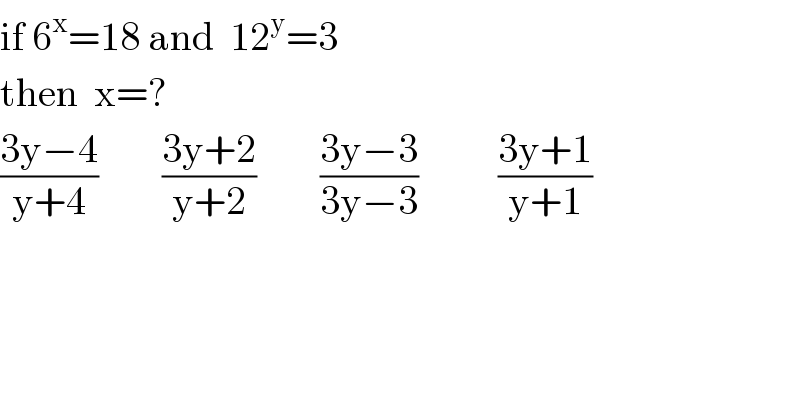
$$\mathrm{if}\:\mathrm{6}^{\mathrm{x}} =\mathrm{18}\:\mathrm{and}\:\:\mathrm{12}^{\mathrm{y}} =\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\mathrm{then}\:\:\mathrm{x}=? \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{3y}−\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{4}}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{3y}+\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{2}}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{3y}−\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{3y}−\mathrm{3}}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{3y}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$
Commented by john santu last updated on 26/May/20

$$\mathrm{12}^{\mathrm{y}} \:=\:\frac{\mathrm{18}}{\mathrm{6}}\:=\:\mathrm{6}^{\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{6}\:=\:\mathrm{y}\:\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{12} \\ $$$$\mathrm{x}\:=\:\mathrm{1}+\:\frac{\mathrm{y}\:\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{12}}{\mathrm{ln}\:\mathrm{6}}\: \\ $$
Commented by john santu last updated on 26/May/20
yes. next steps to be completed
Commented by Abdulrahman last updated on 26/May/20
$$\mathrm{but}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{these}\:\mathrm{four}\:\mathrm{answers} \\ $$
Commented by Abdulrahman last updated on 26/May/20
$$\mathrm{so}\:\mathrm{please}\:\mathrm{complete}\:\mathrm{it} \\ $$
Commented by Abdulrahman last updated on 26/May/20

$$\mathrm{please} \\ $$
Commented by Tony Lin last updated on 26/May/20
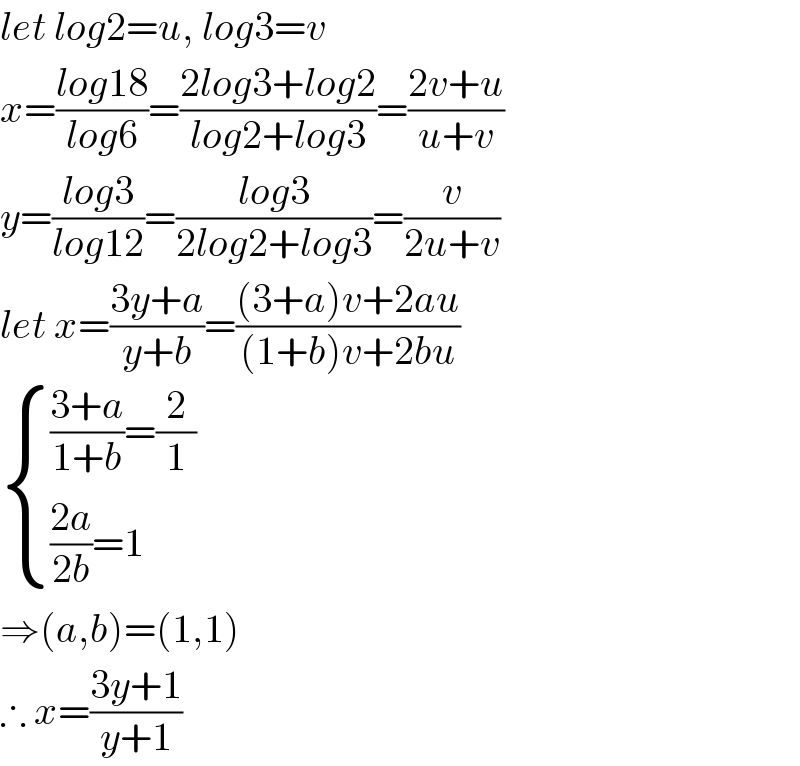
$${let}\:{log}\mathrm{2}={u},\:{log}\mathrm{3}={v} \\ $$$${x}=\frac{{log}\mathrm{18}}{{log}\mathrm{6}}=\frac{\mathrm{2}{log}\mathrm{3}+{log}\mathrm{2}}{{log}\mathrm{2}+{log}\mathrm{3}}=\frac{\mathrm{2}{v}+{u}}{{u}+{v}} \\ $$$${y}=\frac{{log}\mathrm{3}}{{log}\mathrm{12}}=\frac{{log}\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}{log}\mathrm{2}+{log}\mathrm{3}}=\frac{{v}}{\mathrm{2}{u}+{v}} \\ $$$${let}\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{3}{y}+{a}}{{y}+{b}}=\frac{\left(\mathrm{3}+{a}\right){v}+\mathrm{2}{au}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+{b}\right){v}+\mathrm{2}{bu}} \\ $$$$\begin{cases}{\frac{\mathrm{3}+{a}}{\mathrm{1}+{b}}=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{1}}}\\{\frac{\mathrm{2}{a}}{\mathrm{2}{b}}=\mathrm{1}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left({a},{b}\right)=\left(\mathrm{1},\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\therefore\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{3}{y}+\mathrm{1}}{{y}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$
Commented by Abdulrahman last updated on 27/May/20

$$\mathrm{i}\:\mathrm{didnt}\:\mathrm{know}\:\mathrm{here} \\ $$$$\mathrm{x}=\frac{\mathrm{3y}+\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{b}}\:\:\:\:\mathrm{from}\:\mathrm{where}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{find} \\ $$
Commented by Tony Lin last updated on 29/May/20
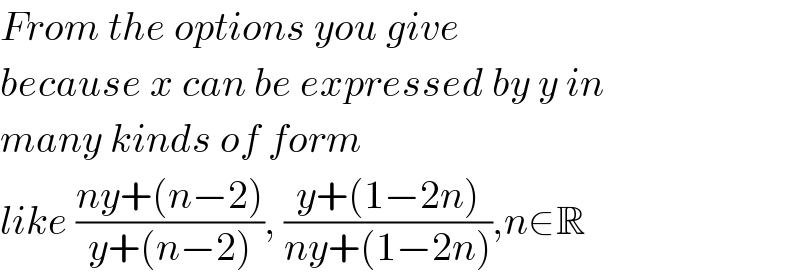
$${From}\:{the}\:{options}\:{you}\:{give} \\ $$$${because}\:{x}\:{can}\:{be}\:{expressed}\:{by}\:{y}\:{in} \\ $$$${many}\:{kinds}\:{of}\:{form} \\ $$$${like}\:\frac{{ny}+\left({n}−\mathrm{2}\right)}{{y}+\left({n}−\mathrm{2}\right)},\:\frac{{y}+\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{2}{n}\right)}{{ny}+\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{2}{n}\right)},{n}\in\mathbb{R} \\ $$
