Question Number 24233 by Nayon.Sm last updated on 14/Nov/17

$${if}\:\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }={ksiny}\:{then}\:{y}=? \\ $$
Answered by ajfour last updated on 15/Nov/17

$${let}\:{y}\:\rightarrow{x}\:\:\:{and}\:{x}\rightarrow{t} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{then}\:\:\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}{{dt}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\:{k}\mathrm{sin}\:{x} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{vdv}}{{dx}}\:=\:{k}\mathrm{sin}\:{x} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{v}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:=\:−{k}\mathrm{cos}\:{x}+{C} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\:\:\:\:\:{v}\:=\:\frac{{dx}}{{dt}}\:=\:\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\left(\sqrt{{C}−{k}\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}\:\right) \\ $$$$\:\Rightarrow\:\:\int\:\frac{{dx}}{\:\sqrt{{C}−{k}\mathrm{cos}\:{x}}}\:=\:\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}{t}+{c}_{\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$${not}\:{always}\:{easily}\:{integrable}.. \\ $$
Answered by abwayh last updated on 16/Nov/17

$$\mathrm{just}\:\mathrm{try}; \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{d}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{y}}{\mathrm{dx}^{\mathrm{2}\:} }\:=\mathrm{ksin}\:\mathrm{y} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{dx}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\right)=\mathrm{ksin}\:\mathrm{y} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}=\int\mathrm{ksin}\:\mathrm{y}\:\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}=\mathrm{kxsin}\:\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{c}\left(\mathrm{y}\right)\:\:\:;\mathrm{c}\left(\mathrm{y}\right)\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{cons}.\:\mathrm{respect}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{y} \\ $$$$\mathrm{dy}=\left\{\mathrm{kxsin}\:\mathrm{y}\:+\mathrm{c}\left(\mathrm{y}\right)\right\}\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}=\int\mathrm{kxsin}\:\mathrm{y}\:\mathrm{dx}\:+\int\mathrm{c}\left(\mathrm{y}\right)\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{kx}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{c}\left(\mathrm{y}\right)\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{c1}\left(\mathrm{y}\right)……;\mathrm{c},\mathrm{c1}\:\:\mathrm{cons}. \\ $$
Commented by mrW1 last updated on 16/Nov/17
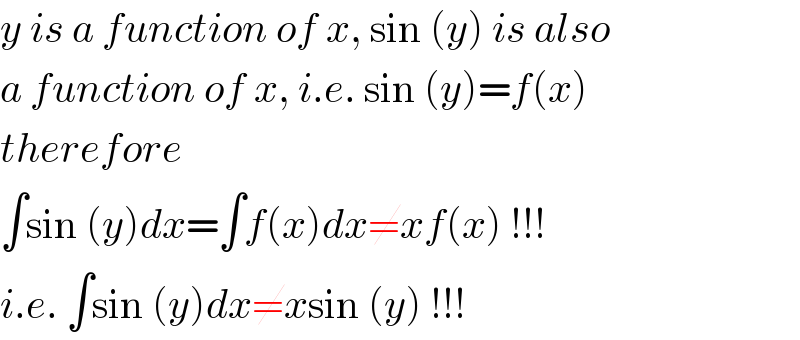
$${y}\:{is}\:{a}\:{function}\:{of}\:{x},\:\mathrm{sin}\:\left({y}\right)\:{is}\:{also} \\ $$$${a}\:{function}\:{of}\:{x},\:{i}.{e}.\:\mathrm{sin}\:\left({y}\right)={f}\left({x}\right) \\ $$$${therefore} \\ $$$$\int\mathrm{sin}\:\left({y}\right){dx}=\int{f}\left({x}\right){dx}\neq{xf}\left({x}\right)\:!!! \\ $$$${i}.{e}.\:\int\mathrm{sin}\:\left({y}\right){dx}\neq{x}\mathrm{sin}\:\left({y}\right)\:!!! \\ $$
Commented by abwayh last updated on 16/Nov/17

$$\mathrm{sorry}\:.\mathrm{sir};\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{mean}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{i}.\mathrm{e}.\mathrm{take}\:\mathrm{c}\left(\mathrm{y}\right),\mathrm{c}_{\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{y}\right)\:\mathrm{as}\:\mathrm{functions}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{y} \\ $$$$\mathrm{put}\left(\:\mathrm{c}=\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{y}\:\:\:\:;\:\:\mathrm{c}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{y}\right)\:\left(\mathrm{or}\:\mathrm{any}\:\mathrm{func}.\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{y}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{then}: \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{kx}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{xsin}\:\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{y} \\ $$$$\therefore\:\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}=\mathrm{kxsin}\:\mathrm{y}+\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{y} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{d}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{y}}{\mathrm{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\mathrm{ksin}\:\mathrm{y} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by mrW1 last updated on 17/Nov/17
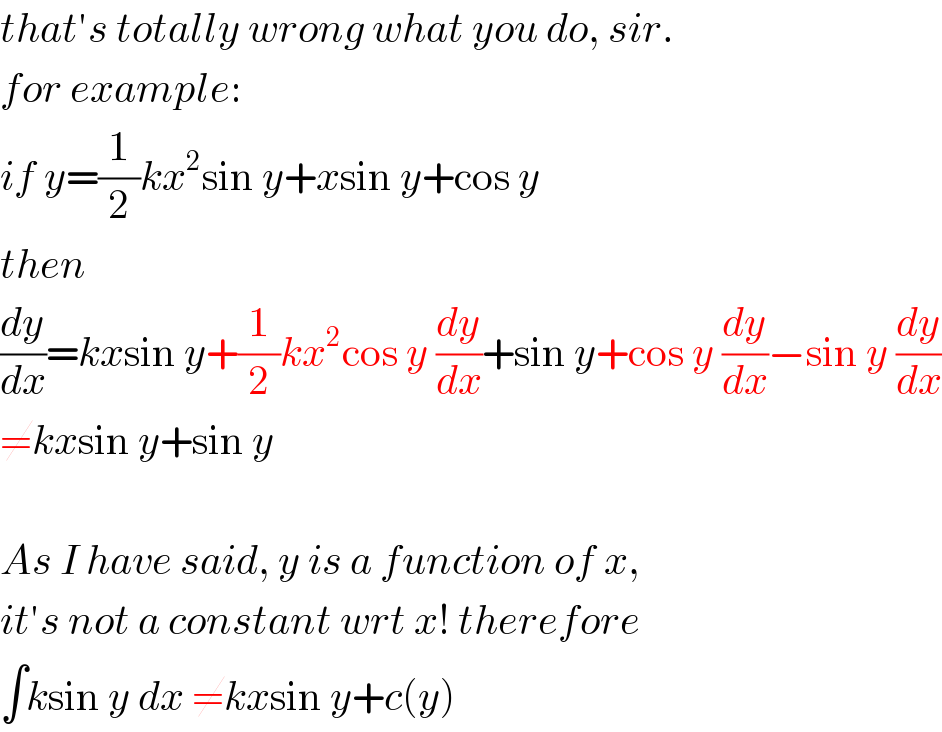
$${that}'{s}\:{totally}\:{wrong}\:{what}\:{you}\:{do},\:{sir}.\: \\ $$$${for}\:{example}: \\ $$$${if}\:{y}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{kx}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}\:{y}+{x}\mathrm{sin}\:{y}+\mathrm{cos}\:{y} \\ $$$${then} \\ $$$$\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}={kx}\mathrm{sin}\:{y}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{kx}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{cos}\:{y}\:\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}+\mathrm{sin}\:{y}+\mathrm{cos}\:{y}\:\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}−\mathrm{sin}\:{y}\:\frac{{dy}}{{dx}} \\ $$$$\neq{kx}\mathrm{sin}\:{y}+\mathrm{sin}\:{y} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${As}\:{I}\:{have}\:{said},\:{y}\:{is}\:{a}\:{function}\:{of}\:{x}, \\ $$$${it}'{s}\:{not}\:{a}\:{constant}\:{wrt}\:{x}!\:{therefore} \\ $$$$\int{k}\mathrm{sin}\:{y}\:{dx}\:\neq{kx}\mathrm{sin}\:{y}+{c}\left({y}\right) \\ $$
