Question Number 109119 by 1777 last updated on 21/Aug/20
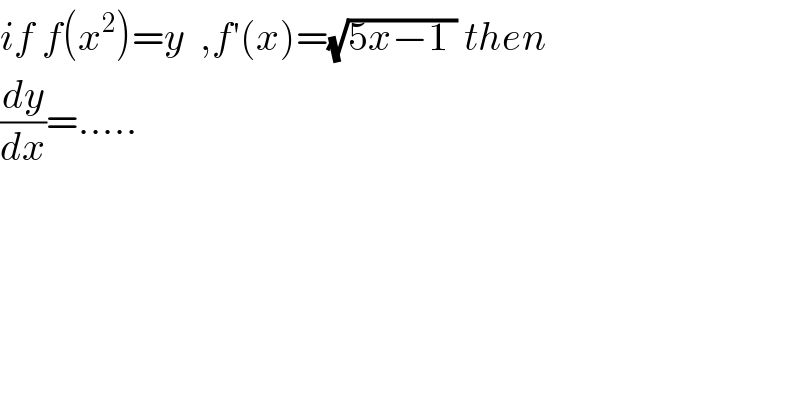
$${if}\:{f}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)={y}\:\:,{f}'\left({x}\right)=\sqrt{\mathrm{5}{x}−\mathrm{1}\:}\:{then}\: \\ $$$$\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}=….. \\ $$
Answered by bemath last updated on 21/Aug/20
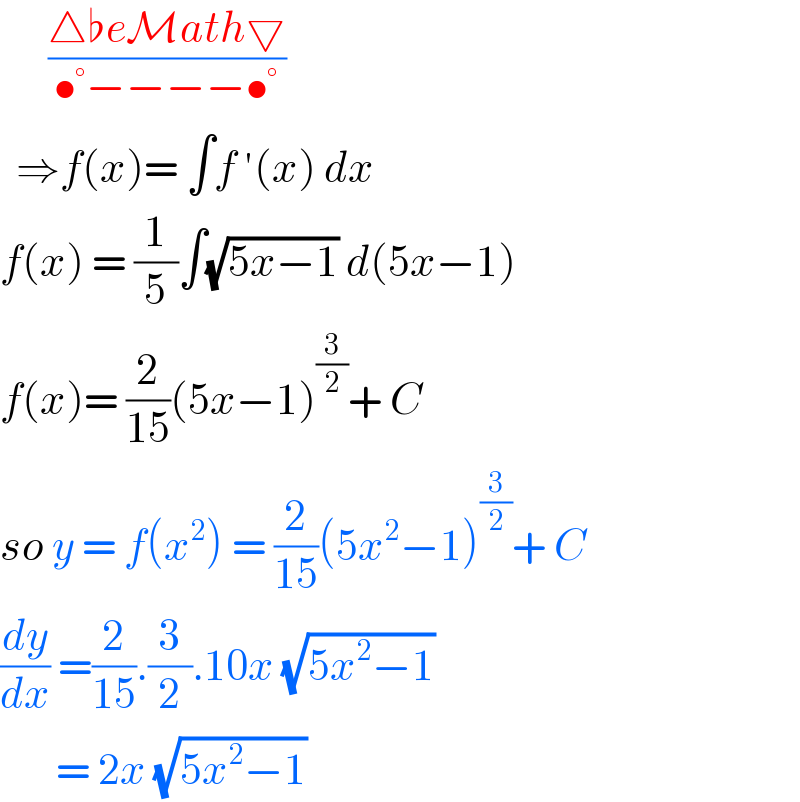
$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{\bigtriangleup\flat{e}\mathcal{M}{ath}\bigtriangledown}{\bullet°−−−−\bullet°} \\ $$$$\:\:\Rightarrow{f}\left({x}\right)=\:\int{f}\:'\left({x}\right)\:{dx} \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}\int\sqrt{\mathrm{5}{x}−\mathrm{1}}\:{d}\left(\mathrm{5}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{15}}\left(\mathrm{5}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} +\:{C} \\ $$$${so}\:{y}\:=\:{f}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{15}}\left(\mathrm{5}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}\right)^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} +\:{C} \\ $$$$\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\:=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{15}}.\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}.\mathrm{10}{x}\:\sqrt{\mathrm{5}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\:\mathrm{2}{x}\:\sqrt{\mathrm{5}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}\: \\ $$
Answered by 1549442205PVT last updated on 21/Aug/20
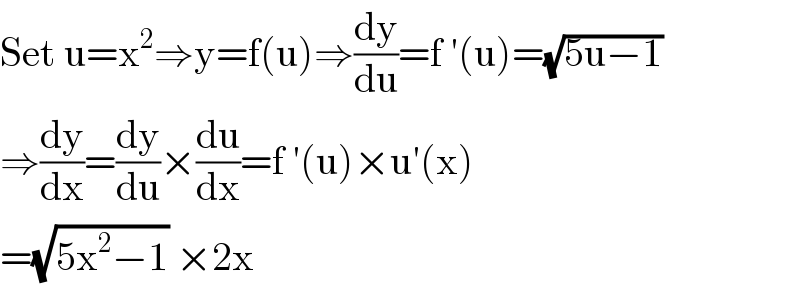
$$\mathrm{Set}\:\mathrm{u}=\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \Rightarrow\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{u}\right)\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{du}}=\mathrm{f}\:'\left(\mathrm{u}\right)=\sqrt{\mathrm{5u}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}=\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{du}}×\frac{\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{dx}}=\mathrm{f}\:'\left(\mathrm{u}\right)×\mathrm{u}'\left(\mathrm{x}\right) \\ $$$$=\sqrt{\mathrm{5x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}\:×\mathrm{2x} \\ $$
