Question Number 127704 by NATTAPONG4359 last updated on 01/Jan/21
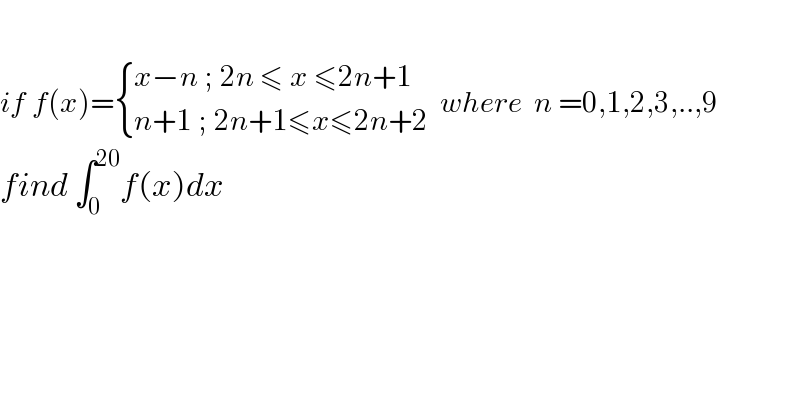
$$ \\ $$$${if}\:{f}\left({x}\right)=\begin{cases}{{x}−{n}\:;\:\mathrm{2}{n}\:\leqslant\:{x}\:\leqslant\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}}\\{{n}+\mathrm{1}\:;\:\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\leqslant{x}\leqslant\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{2}\:}\end{cases}\:{where}\:\:{n}\:=\mathrm{0},\mathrm{1},\mathrm{2},\mathrm{3},..,\mathrm{9} \\ $$$${find}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{20}} {f}\left({x}\right){dx} \\ $$
Answered by mahdipoor last updated on 01/Jan/21
![∫_(2n) ^( 2n+1) f(x)dx=∫_(2n) ^( 2n+1) (x−n)dx=[(x^2 /2)−nx]_(2n) ^(2n+1) =((((2n+1)^2 )/2)−n(2n+1))−((((2n)^2 )/2)−2(2n)) =n−(1/2) ∫_(2n+1) ^( 2n+2) f(x)dx=∫_(2n+1) ^( 2n+2) (1+n)dx=[(1+n)x]_(2n+1) ^(2n+2) =(1+n)(2n+2−(2n+1))=1+n ∫_0 ^(20) f(x)dx=(∫_0 ^1 f(x)dx+∫_2 ^( 3) f(x)dx+...+∫_(18) ^( 19) f(x)dx) +(∫_1 ^( 2) f(x)dx+∫_3 ^( 4) f(x)dx+...+∫_(19) ^( 20) f(x)dx)= Σ_(n=0) ^9 (n−(1/2))+Σ_(n=0) ^9 (1+n)=Σ_(n=0) ^9 (2n+(1/2))= 2×(((9×10)/2))+10×(1/2)=95](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q127710.png)
$$\int_{\mathrm{2}{n}} ^{\:\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} {f}\left({x}\right){dx}=\int_{\mathrm{2}{n}} ^{\:\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} \left({x}−{n}\right){dx}=\left[\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}−{nx}\right]_{\mathrm{2}{n}} ^{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$=\left(\frac{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}−{n}\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)\right)−\left(\frac{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{2}{n}\right)\right) \\ $$$$={n}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} ^{\:\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{2}} {f}\left({x}\right){dx}=\int_{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} ^{\:\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{1}+{n}\right){dx}=\left[\left(\mathrm{1}+{n}\right){x}\right]_{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$=\left(\mathrm{1}+{n}\right)\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{2}−\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)\right)=\mathrm{1}+{n} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{20}} {f}\left({x}\right){dx}=\left(\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {f}\left({x}\right){dx}+\int_{\mathrm{2}} ^{\:\mathrm{3}} {f}\left({x}\right){dx}+…+\int_{\mathrm{18}} ^{\:\mathrm{19}} {f}\left({x}\right){dx}\right) \\ $$$$\:+\left(\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\:\mathrm{2}} {f}\left({x}\right){dx}+\int_{\mathrm{3}} ^{\:\mathrm{4}} {f}\left({x}\right){dx}+…+\int_{\mathrm{19}} ^{\:\mathrm{20}} {f}\left({x}\right){dx}\right)= \\ $$$$\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{9}} {\sum}}\left({n}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)+\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{9}} {\sum}}\left(\mathrm{1}+{n}\right)=\underset{{n}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{9}} {\sum}}\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)= \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}×\left(\frac{\mathrm{9}×\mathrm{10}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)+\mathrm{10}×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{95} \\ $$
Commented by mehedi last updated on 22/Dec/21

$$\mathrm{4} \\ $$
