Question Number 146063 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 10/Jul/21
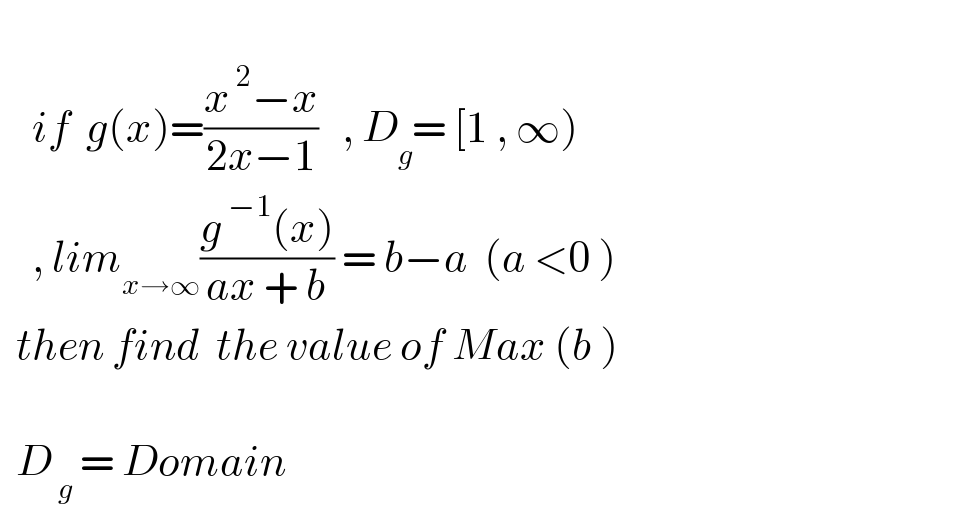
$$ \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:{if}\:\:{g}\left({x}\right)=\frac{{x}^{\:\mathrm{2}} −{x}}{\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{1}}\:\:\:,\:{D}_{{g}} =\:\left[\mathrm{1}\:,\:\infty\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:,\:{lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\infty} \frac{{g}^{\:−\mathrm{1}} \left({x}\right)}{{ax}\:+\:{b}}\:=\:{b}−{a}\:\:\left({a}\:<\mathrm{0}\:\right) \\ $$$$\:\:{then}\:{find}\:\:{the}\:{value}\:{of}\:{Max}\:\left({b}\:\right) \\ $$$$\:\: \\ $$$$\:\:{D}_{\:{g}} \:=\:{Domain}\: \\ $$
Answered by gsk2684 last updated on 10/Jul/21

$${g}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({x}\right)={y}\Rightarrow{x}={g}\left({y}\right)=\frac{{y}^{\mathrm{2}} −{y}}{\mathrm{2}{y}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{y}=\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{4}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${then}\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{4}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}}}{\mathrm{2}\left({ax}+{b}\right)}={b}−{a} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{1}+{x}\sqrt{\mathrm{4}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}}{\mathrm{2}\left({ax}+{b}\right)}={b}−{a} \\ $$$$\underset{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{2}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{4}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}}{\mathrm{2}\left({a}+\frac{{b}}{{x}}\right)}={b}−{a} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{2}+\sqrt{\mathrm{4}}}{\mathrm{2}{a}}={b}−{a} \\ $$$${b}={a}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{a}}\leqslant−\mathrm{2}\sqrt{{a}.\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{a}}}\left(\because{a}<\mathrm{0}\right) \\ $$$${b}\leqslant−\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${max}\:{of}\:{b}\:{is}\:−\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 10/Jul/21
$$\:{very}\:{nice}\:{mr}\:{g}.{s}.{k}\:{thank}\:{you}.. \\ $$
Commented by gsk2684 last updated on 10/Jul/21

$${welcome} \\ $$
