Question Number 15824 by Tinkutara last updated on 18/Jun/17
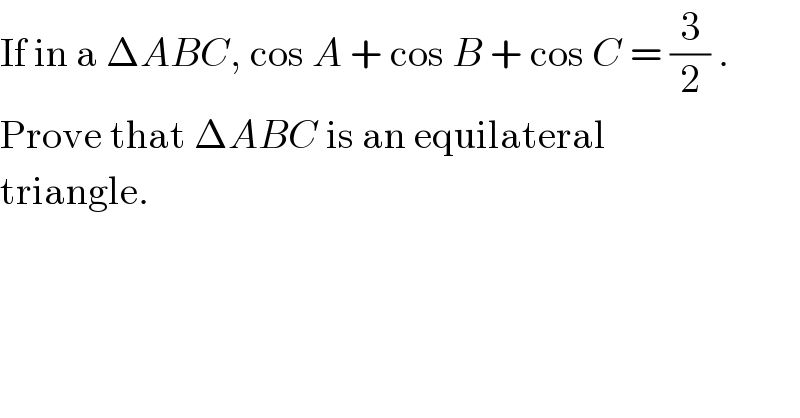
Answered by mrW1 last updated on 14/Jun/17
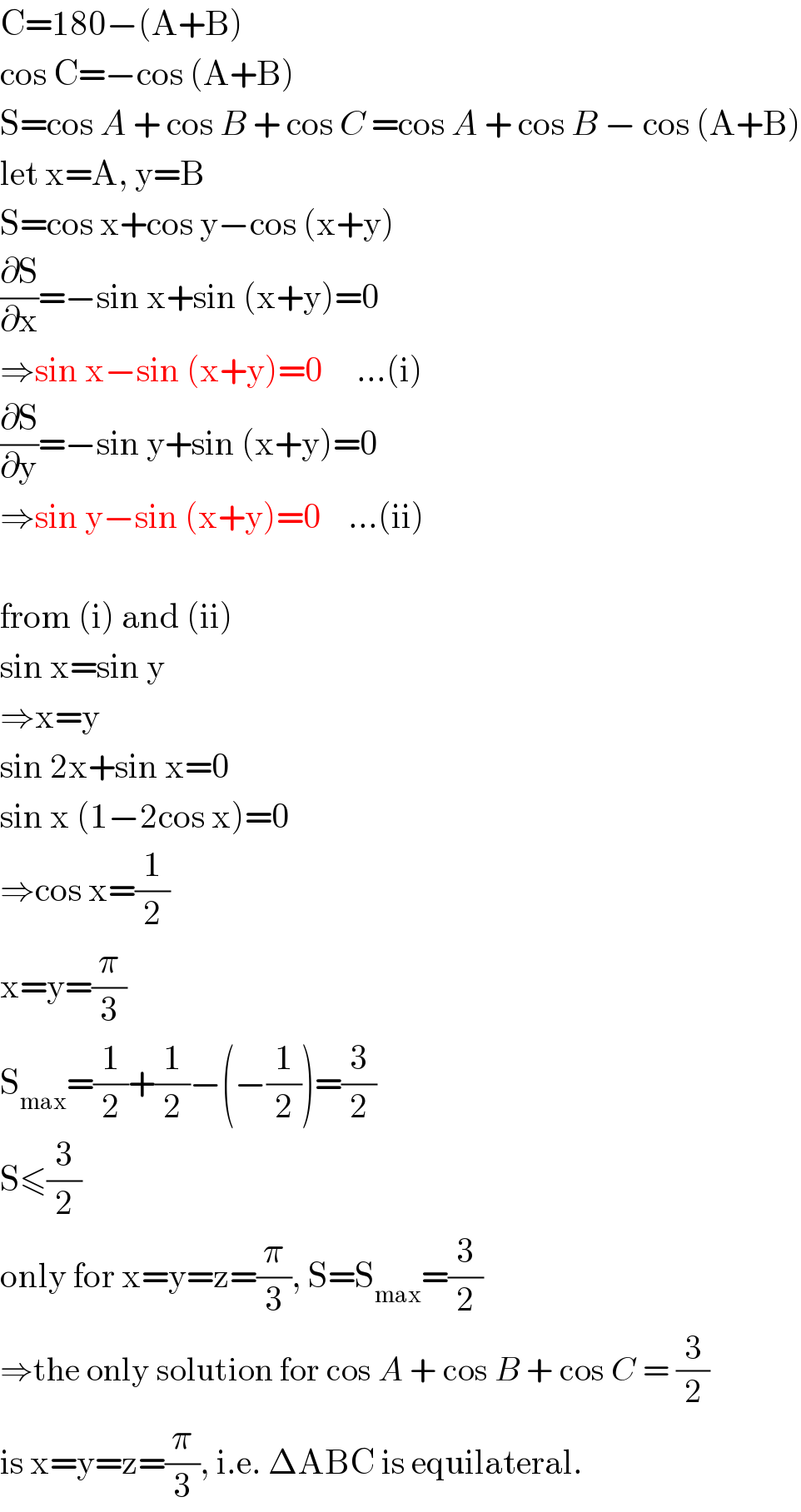
Commented by Tinkutara last updated on 14/Jun/17

Commented by mrW1 last updated on 14/Jun/17
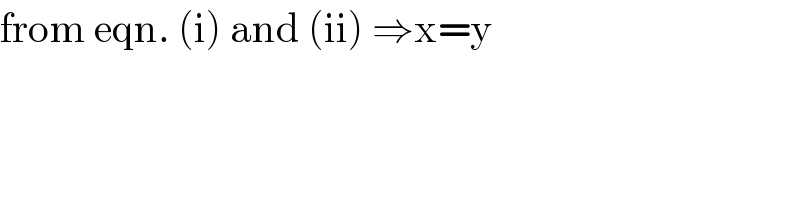
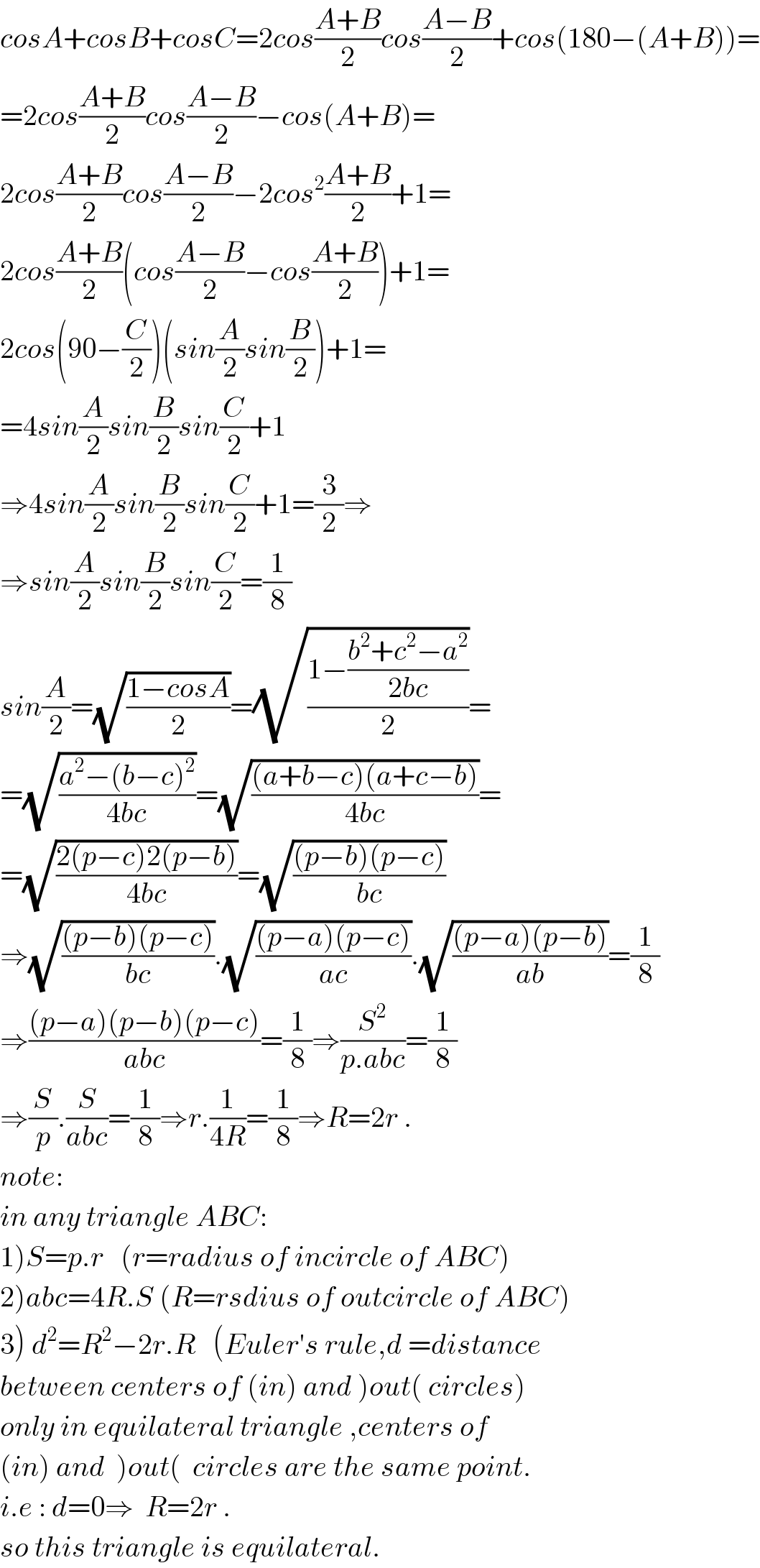
Answered by b.e.h.i.8.3.4.1.7@gmail.com last updated on 14/Jun/17
Commented by Tinkutara last updated on 15/Jun/17

