Question Number 168576 by cortano1 last updated on 13/Apr/22
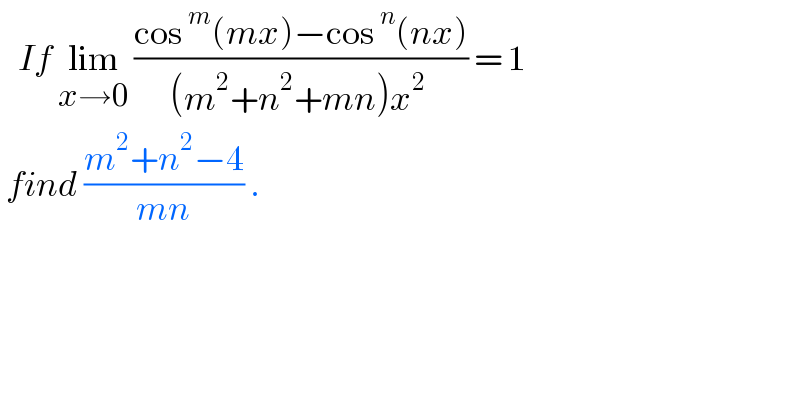
$$\:\:\:{If}\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:^{{m}} \left({mx}\right)−\mathrm{cos}\:^{{n}} \left({nx}\right)}{\left({m}^{\mathrm{2}} +{n}^{\mathrm{2}} +{mn}\right){x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:}\:=\:\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\:{find}\:\frac{{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +{n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}}{{mn}}\:. \\ $$
Commented by blackmamba last updated on 17/Apr/22
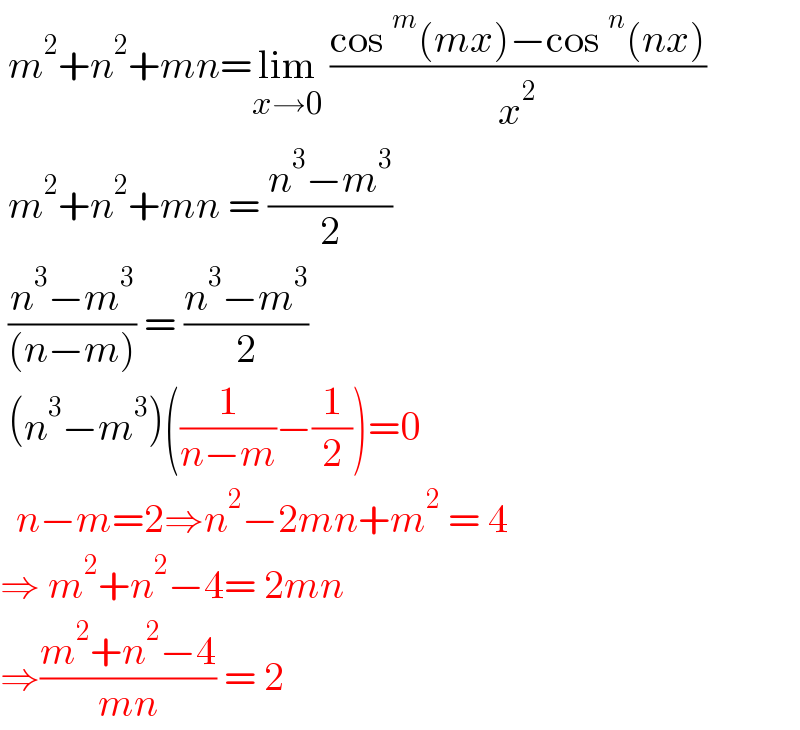
$$\:{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +{n}^{\mathrm{2}} +{mn}=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{cos}\:^{{m}} \left({mx}\right)−\mathrm{cos}\:^{{n}} \left({nx}\right)}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\:{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +{n}^{\mathrm{2}} +{mn}\:=\:\frac{{n}^{\mathrm{3}} −{m}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\frac{{n}^{\mathrm{3}} −{m}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\left({n}−{m}\right)}\:=\:\frac{{n}^{\mathrm{3}} −{m}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\:\left({n}^{\mathrm{3}} −{m}^{\mathrm{3}} \right)\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}−{m}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\:{n}−{m}=\mathrm{2}\Rightarrow{n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{mn}+{m}^{\mathrm{2}} \:=\:\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +{n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}=\:\mathrm{2}{mn} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{{m}^{\mathrm{2}} +{n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}}{{mn}}\:=\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$
