Question Number 82375 by M±th+et£s last updated on 20/Feb/20
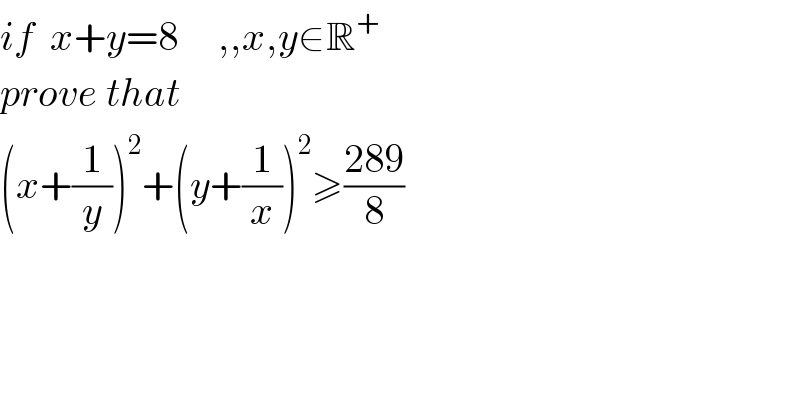
$${if}\:\:{x}+{y}=\mathrm{8}\:\:\:\:\:,,{x},{y}\in\mathbb{R}^{+} \\ $$$${prove}\:{that}\: \\ $$$$\left({x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{y}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\left({y}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \geqslant\frac{\mathrm{289}}{\mathrm{8}} \\ $$
Answered by MJS last updated on 21/Feb/20

$${f}\left({x}\right)=\left({x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8}−{x}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\left(\mathrm{8}−{x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{2}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{8}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{8}{x}+\mathrm{32}\right)}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({x}−\mathrm{8}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\mathrm{shift}\:\mathrm{4}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{left} \\ $$$${x}={t}+\mathrm{4}\:\Leftrightarrow\:{t}={x}−\mathrm{4} \\ $$$${f}\left({t}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{2}\left({t}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{17}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left({t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{16}\right)}{\left({t}−\mathrm{4}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \left({t}+\mathrm{4}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$${f}\left({t}\right)\:\mathrm{has}\:\mathrm{double}\:\mathrm{zeros}\:\mathrm{at}\:{t}=\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{17}}\:\mathrm{which}\:\mathrm{also} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{minima} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{local}\:\mathrm{minimum}\:\mathrm{at}\:{t}=\mathrm{0}\:\mathrm{with}\:{f}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{289}}{\mathrm{8}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{f}\left({x}\right)\:\mathrm{has}\:\mathrm{double}\:\mathrm{zeros}\:\mathrm{at}\:{x}=\mathrm{4}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{17}}\:\mathrm{which} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{also}\:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{minima}\:\mathrm{but}\:\mathrm{0}<{x}<\mathrm{8}\:\mathrm{so}\:\mathrm{they} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{outside}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{given}\:\mathrm{interval} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{local}\:\mathrm{minimum}\:\mathrm{at}\:{x}=\mathrm{4}\:\mathrm{with}\:{f}\left(\mathrm{4}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{289}}{\mathrm{8}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{what}'\mathrm{s}\:\mathrm{left}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{show}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{that}\:{f}\left({x}\right)\geqslant\frac{\mathrm{289}}{\mathrm{8}}\:\mathrm{at}\:\mathrm{the} \\ $$$$\mathrm{borders}:\:\mathrm{but}\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}{f}\left({x}\right)=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{8}} {\mathrm{lim}}{f}\left({x}\right)=+\infty\:\Rightarrow\: \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{proven} \\ $$
Answered by mind is power last updated on 21/Feb/20

$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{y}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\mathrm{2}\frac{{x}}{{y}}+\mathrm{2}\frac{{y}}{{x}} \\ $$$$=\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{y}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{xy}^{} }\right) \\ $$$$,{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \geqslant\frac{\left({x}+{y}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{64}}{\mathrm{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{256}}{\mathrm{8}} \\ $$$${AM}\:{GM}\Rightarrow \\ $$$${xy}\leqslant\frac{\left({x}+{y}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{4}}=\mathrm{16} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{xy}}\geqslant\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{16}}\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{xy}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)\geqslant\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{16}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{256}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{32}+\mathrm{256}}{\mathrm{256}}=\frac{\mathrm{289}}{\mathrm{256}} \\ $$$$\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{xy}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)\geqslant\frac{\mathrm{289}}{\mathrm{256}}.\frac{\mathrm{256}}{\mathrm{8}}=\frac{\mathrm{289}}{\mathrm{8}} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\left({x}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{y}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\left({y}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \geqslant\frac{\mathrm{289}}{\mathrm{8}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
