Question Number 63232 by mathmax by abdo last updated on 01/Jul/19
![let B(x,y) =∫_0 ^1 (1−t)^(x−1) t^(y−1) dt 1) study the convergence of B(x,y) 1) prove that B(x,y)=B(y,x) prove that B(x,y) =∫_0 ^∞ (t^(x−1) /((1+t)^(x+y) )) dt 2) prove that B(x,y) =((Γ(x).Γ(y))/(Γ(x+y))) 3) prove that Γ(x).Γ(1−x) =(π/(sin(πx))) for allx ∈]0,1[](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q63232.png)
$${let}\:{B}\left({x},{y}\right)\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{1}−{t}\right)^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} {t}^{{y}−\mathrm{1}} \:{dt} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right)\:{study}\:{the}\:{convergence}\:{of}\:{B}\left({x},{y}\right) \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right)\:{prove}\:{that}\:{B}\left({x},{y}\right)={B}\left({y},{x}\right) \\ $$$${prove}\:{that}\:{B}\left({x},{y}\right)\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\frac{{t}^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} }{\left(\mathrm{1}+{t}\right)^{{x}+{y}} }\:{dt} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right)\:{prove}\:{that}\:{B}\left({x},{y}\right)\:=\frac{\Gamma\left({x}\right).\Gamma\left({y}\right)}{\Gamma\left({x}+{y}\right)} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{3}\left.\right)\:{prove}\:{that}\:\Gamma\left({x}\right).\Gamma\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)\:=\frac{\pi}{{sin}\left(\pi{x}\right)}\:\:\:{for}\:{allx}\:\in\right]\mathrm{0},\mathrm{1}\left[\right. \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 03/Jul/19
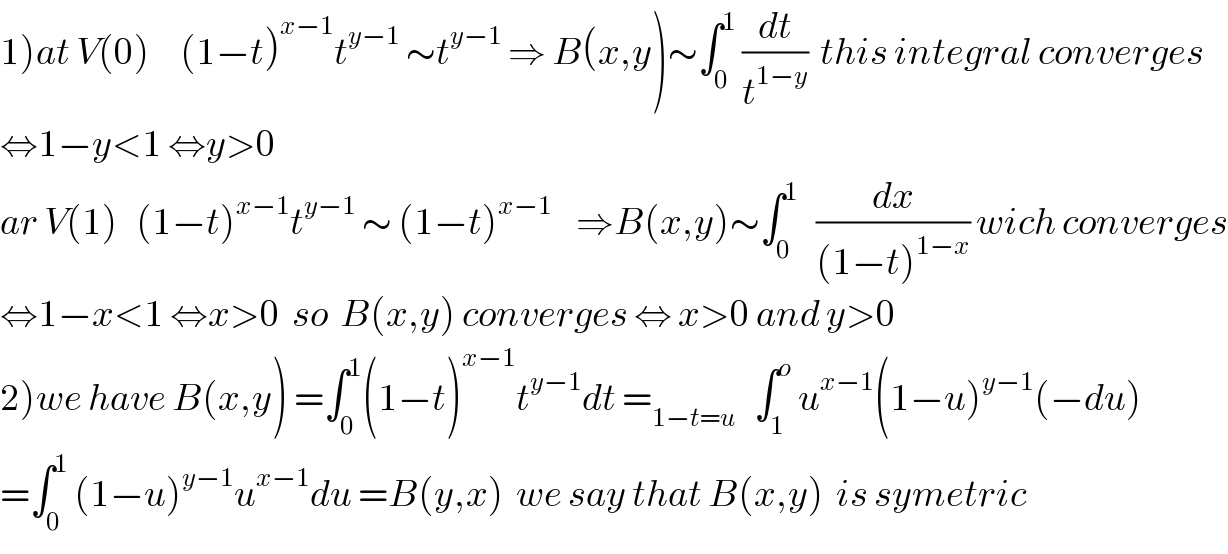
$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right){at}\:{V}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)\:\:\:\:\:\left(\mathrm{1}−{t}\right)^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} {t}^{{y}−\mathrm{1}} \:\sim{t}^{{y}−\mathrm{1}} \:\Rightarrow\:{B}\left({x},{y}\right)\sim\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{{dt}}{{t}^{\mathrm{1}−{y}} }\:\:{this}\:{integral}\:{converges} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\mathrm{1}−{y}<\mathrm{1}\:\Leftrightarrow{y}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${ar}\:{V}\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:\:\:\left(\mathrm{1}−{t}\right)^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} {t}^{{y}−\mathrm{1}} \:\sim\:\left(\mathrm{1}−{t}\right)^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} \:\:\:\:\Rightarrow{B}\left({x},{y}\right)\sim\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\:\frac{{dx}}{\left(\mathrm{1}−{t}\right)^{\mathrm{1}−{x}} }\:{wich}\:{converges} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\mathrm{1}−{x}<\mathrm{1}\:\Leftrightarrow{x}>\mathrm{0}\:\:{so}\:\:{B}\left({x},{y}\right)\:{converges}\:\Leftrightarrow\:{x}>\mathrm{0}\:{and}\:{y}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right){we}\:{have}\:{B}\left({x},{y}\right)\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{1}−{t}\right)^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} {t}^{{y}−\mathrm{1}} {dt}\:=_{\mathrm{1}−{t}={u}} \:\:\:\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{{o}} \:{u}^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{1}−{u}\right)^{{y}−\mathrm{1}} \left(−{du}\right) \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\left(\mathrm{1}−{u}\right)^{{y}−\mathrm{1}} {u}^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} {du}\:={B}\left({y},{x}\right)\:\:{we}\:{say}\:{that}\:{B}\left({x},{y}\right)\:\:{is}\:{symetric} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 04/Jul/19
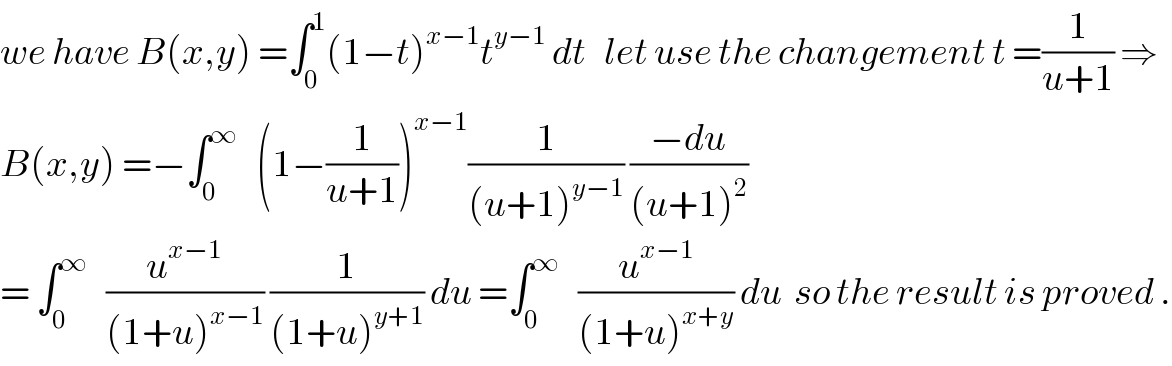
$${we}\:{have}\:{B}\left({x},{y}\right)\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{1}−{t}\right)^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} {t}^{{y}−\mathrm{1}} \:{dt}\:\:\:{let}\:{use}\:{the}\:{changement}\:{t}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{u}+\mathrm{1}}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${B}\left({x},{y}\right)\:=−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\:\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{u}+\mathrm{1}}\right)^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left({u}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{{y}−\mathrm{1}} }\:\frac{−{du}}{\left({u}+\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\:\frac{{u}^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} }{\left(\mathrm{1}+{u}\right)^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} }\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+{u}\right)^{{y}+\mathrm{1}} }\:{du}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\:\:\frac{{u}^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} }{\left(\mathrm{1}+{u}\right)^{{x}+{y}} }\:{du}\:\:{so}\:{the}\:{result}\:{is}\:{proved}\:. \\ $$
