Question Number 117838 by snipers237 last updated on 13/Oct/20
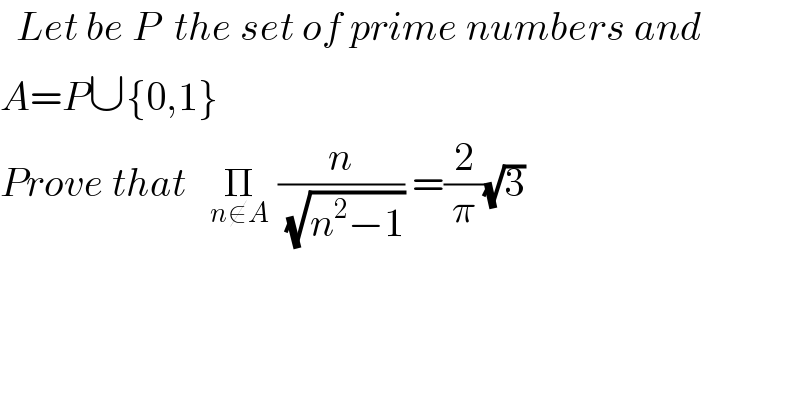
$$\:\:{Let}\:{be}\:{P}\:\:{the}\:{set}\:{of}\:{prime}\:{numbers}\:{and}\: \\ $$$${A}={P}\cup\left\{\mathrm{0},\mathrm{1}\right\} \\ $$$${Prove}\:{that}\:\:\:\underset{{n}\notin{A}} {\prod}\:\frac{{n}}{\:\sqrt{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}}\:=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\pi}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\: \\ $$
Answered by mindispower last updated on 14/Oct/20

$${let}\:\underset{{n}\geqslant\mathrm{2}} {\prod}\frac{{n}}{\:\sqrt{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}}={I} \\ $$$${I}^{\mathrm{2}} =\underset{{n}\geqslant\mathrm{2}} {\prod}\frac{{n}}{\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right)}.\frac{{n}}{\left({n}+\mathrm{1}\right)}=\frac{\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{1}.\mathrm{3}}.\frac{\mathrm{3}.\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}.\mathrm{4}}.\frac{\mathrm{4}.\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{3}.\mathrm{5}}…… \\ $$$${I}^{\mathrm{2}} =\underset{{N}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}.\underset{{n}=\mathrm{2}} {\overset{{N}} {\prod}}\left(\frac{{n}}{{n}−\mathrm{1}}.\frac{{n}}{{n}+\mathrm{1}}\right)=\underset{{N}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{2}{N}}{{N}+\mathrm{1}}\:\: \\ $$$${I}^{\mathrm{2}} \rightarrow\mathrm{2}\Rightarrow{I}\rightarrow\sqrt{\mathrm{2}},{since}\:{I}\geqslant\mathrm{0}\:{and}\:{x}\rightarrow\sqrt{{x}\:\:}\:{continus} \\ $$$${let}\:{P}\:{bee}\:{set}\:{ofrimes}\:{numbers} \\ $$$$\underset{{p}\in{P}} {\prod}\frac{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}=\underset{{p}\in{P}} {\prod}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{p}^{\mathrm{2}} }} \\ $$$$=\underset{{p}\in{P}} {\prod}\left(\underset{{s}\geqslant\mathrm{0}} {\sum}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{p}^{\mathrm{2}{s}} }\right)=\underset{{n}\geqslant\mathrm{1}} {\sum}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\zeta\left(\mathrm{2}\right)=\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{6}} \\ $$$${A}={P}\cup\left\{\mathrm{0},\mathrm{1}\right\} \\ $$$$\underset{{n}\notin{A}} {\prod}\frac{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}=\underset{{n}\geqslant\mathrm{2}} {\prod}\frac{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}/\left(\underset{{n}\in{P}} {\prod}\frac{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\frac{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{6}}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{12}}{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\underset{{n}\notin{A}} {\prod}\frac{{n}}{\:\sqrt{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}}}=\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{12}}{\pi^{\mathrm{2}} }}=\frac{\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\pi} \\ $$
