Question Number 28430 by abdo imad last updated on 25/Jan/18
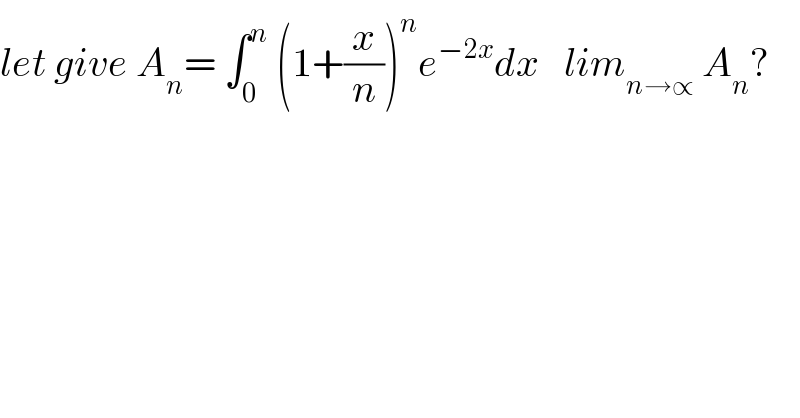
$${let}\:{give}\:{A}_{{n}} =\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{n}} \:\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{{x}}{{n}}\right)^{{n}} {e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} {dx}\:\:\:{lim}_{{n}\rightarrow\propto} \:{A}_{{n}} ? \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by abdo imad last updated on 27/Jan/18
![we have (1 +(x/n))^n =e_(n→+∞) ^(nln(1+(x/n))) →e^x so A_n = ∫_R (1+(x/n))^n e^(−2x) χ_([0,n[) (x)dx =∫_(R ) f_n (x)dx but f_n (x)→ e^(−x) on [0,+∞[ so lim_(n→+∞) A_n = ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−x) dx = [ −e^(−x) ]_0 ^(x→+∞) = 1](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q28567.png)
$${we}\:{have}\:\left(\mathrm{1}\:+\frac{{x}}{{n}}\right)^{{n}} ={e}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} ^{{nln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{{x}}{{n}}\right)} \:\rightarrow{e}^{{x}} \:\:\:{so} \\ $$$${A}_{{n}} =\:\int_{{R}} \left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{{x}}{{n}}\right)^{{n}} {e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} \chi_{\left[\mathrm{0},{n}\left[\right.\right.} \left({x}\right){dx}\:=\int_{{R}\:} {f}_{{n}} \left({x}\right){dx} \\ $$$${but}\:\:\:{f}_{{n}} \left({x}\right)\rightarrow\:{e}^{−{x}} \:\:{on}\:\left[\mathrm{0},+\infty\left[\:\:{so}\:\:{lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} {A}_{{n}} \right.\right. \\ $$$$=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:{e}^{−{x}} \:{dx}\:=\:\:\left[\:−{e}^{−{x}} \right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{x}\rightarrow+\infty} \:=\:\mathrm{1} \\ $$
