Question Number 35689 by prof Abdo imad last updated on 22/May/18

$${let}\:{S}_{{n}} =\:\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{n}} \:\:\:\frac{{k}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \sqrt{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+{k}^{\mathrm{2}} }} \\ $$$${find}\:{lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} \:\:{S}_{{n}} \\ $$
Commented by prof Abdo imad last updated on 22/May/18
![we have S_n = Σ_(k=1) ^n (k^2 /(n^3 (√(1+(k^2 /n^2 ))))) = (1/n) Σ_(k=1) ^n ((k^2 /n^2 )/( (√(1+(k^2 /n^2 ))))) so S_n is a Rieman sum and lim_(n→+∞) S_n = ∫_0 ^1 (x^2 /( (√(1+x^2 ))))dx =I changement x =sht give t=argsh(x) and I = ∫_0 ^(ln(1+(√2))) ((sh^2 t)/(cht)) ch tdt = ∫_0 ^(ln(1+(√2))) sh^2 t dt =(1/2) ∫_0 ^(ln(1+(√2))) (ch(2t)−1)dt =(1/2) ∫_0 ^(ln(1+(√2))) ch(2t) dt −((ln(1+(√2)))/2) =(1/4)[ sh(2t)]_0 ^(ln(1+(√2))) − ((ln(1+(√2)))/2) =(1/4)sh(2ln(1+(√2))) −((ln(1+(√2)))/2) sh(2x)= ((e^(2x) −e^(−2x) )/2) ⇒ sh(2x)=(((1+(√2))^4 +(1/((1+(√2))^2 )))/2) I = (1/8){ (1+(√2))^4 −(1+(√2))^(−4) } −((ln(1+(√2)})/2)](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q35721.png)
$${we}\:{have}\:{S}_{{n}} \:=\:\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{n}} \:\:\:\frac{{k}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{n}^{\mathrm{3}} \sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\frac{{k}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }}} \\ $$$$=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\:\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{n}} \:\:\frac{\frac{{k}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\frac{{k}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }}}\:{so}\:{S}_{{n}} \:{is}\:{a}\:{Rieman}\:{sum} \\ $$$${and}\:{lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} \:\:{S}_{{n}} \:\:=\:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{dx}\:={I} \\ $$$${changement}\:\:{x}\:={sht}\:{give}\:{t}={argsh}\left({x}\right)\:{and} \\ $$$${I}\:\:=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)} \:\:\frac{{sh}^{\mathrm{2}} {t}}{{cht}}\:{ch}\:{tdt}\:=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)} \:{sh}^{\mathrm{2}} {t}\:{dt} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)} \:\:\left({ch}\left(\mathrm{2}{t}\right)−\mathrm{1}\right){dt} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)} {ch}\left(\mathrm{2}{t}\right)\:{dt}\:\:\:−\frac{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\left[\:{sh}\left(\mathrm{2}{t}\right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)} \:−\:\frac{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}{sh}\left(\mathrm{2}{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)\right)\:−\frac{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${sh}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)=\:\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \:−{e}^{−\mathrm{2}{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:\Rightarrow\:{sh}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)=\frac{\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{4}} \:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${I}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8}}\left\{\:\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{4}} \:−\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{−\mathrm{4}} \right\}\:−\frac{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right\}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by prof Abdo imad last updated on 22/May/18
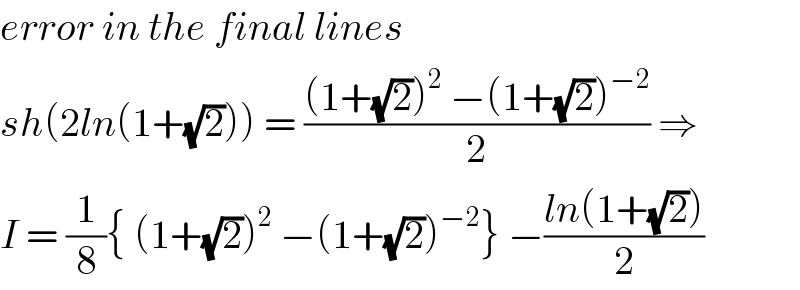
$${error}\:{in}\:{the}\:{final}\:{lines} \\ $$$${sh}\left(\mathrm{2}{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)\right)\:=\:\frac{\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \:−\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{−\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${I}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8}}\left\{\:\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} \:−\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{−\mathrm{2}} \right\}\:−\frac{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\right)}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 22/May/18

$$=\frac{{lim}}{{n}\rightarrow\infty}×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}×\frac{\left(\frac{{k}}{{n}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\left(\frac{{k}}{{n}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }} \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:}{dx} \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\:\:{dx}−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \frac{{dx}}{\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }} \\ $$$${now}\:{use}\:{formula} \\ $$
