Question Number 174883 by infinityaction last updated on 13/Aug/22
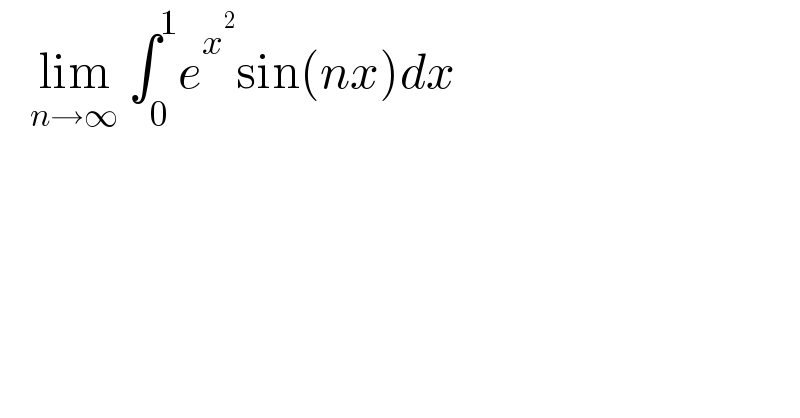
$$\:\:\:\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {e}^{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \mathrm{sin}\left({nx}\right){dx}\: \\ $$
Answered by Mathspace last updated on 14/Aug/22
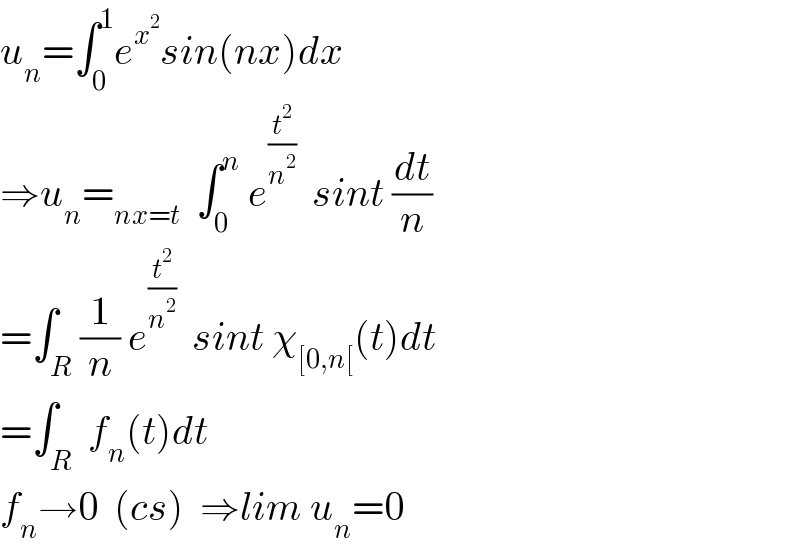
$${u}_{{n}} =\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {e}^{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } {sin}\left({nx}\right){dx} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{u}_{{n}} =_{{nx}={t}} \:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{{n}} \:{e}^{\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }} \:\:{sint}\:\frac{{dt}}{{n}} \\ $$$$=\int_{{R}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\:{e}^{\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{n}^{\mathrm{2}} }} \:\:{sint}\:\chi_{\left[\mathrm{0},{n}\left[\right.\right.} \left({t}\right){dt} \\ $$$$=\int_{{R}} \:{f}_{{n}} \left({t}\right){dt} \\ $$$${f}_{{n}} \rightarrow\mathrm{0}\:\:\left({cs}\right)\:\:\Rightarrow{lim}\:{u}_{{n}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Answered by Mathspace last updated on 14/Aug/22
![another way by ρarts u_n =[−(1/n)cos(nx)e^x^2 ]_0 ^1 +(1/n)∫_0 ^1 e^x^2 cos(nx)dx (1/n)−e((cosn)/n) +(1/n)∫_0 ^1 e^x^2 cos(nx)dx ∣u_n ∣≤(1/n)+(e/n) +(1/n)∫_0 ^1 e^x^2 dx→0(n→+∞) ⇒lim u_n =0](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q174913.png)
$${another}\:{way} \\ $$$${by}\:\:\rho{arts}\: \\ $$$${u}_{{n}} =\left[−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}{cos}\left({nx}\right){e}^{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:{e}^{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } {cos}\left({nx}\right){dx} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}−{e}\frac{{cosn}}{{n}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {e}^{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } {cos}\left({nx}\right){dx} \\ $$$$\mid{u}_{{n}} \mid\leqslant\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}+\frac{{e}}{{n}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {e}^{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } {dx}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}\left({n}\rightarrow+\infty\right) \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{lim}\:{u}_{{n}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by infinityaction last updated on 14/Aug/22

$${thank}\:{you}\:{sir} \\ $$
