Question Number 32008 by gunawan last updated on 18/Mar/18
![lim_(n→∞) [((1/n))^n +((2/n))^n +..+((n/n))^n ]=...](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q32008.png)
$$\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\left[\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\right)^{{n}} +\left(\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{n}}\right)^{{n}} +..+\left(\frac{{n}}{{n}}\right)^{{n}} \right]=… \\ $$
Commented by JDamian last updated on 18/Mar/18
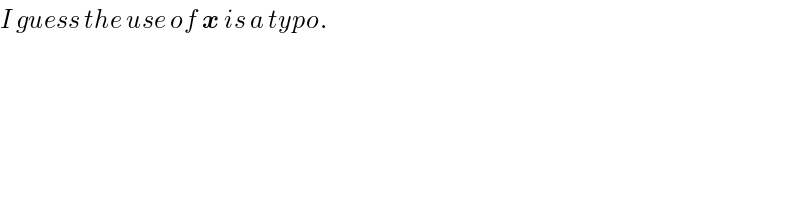
$${I}\:{guess}\:{the}\:{use}\:{of}\:\boldsymbol{{x}}\:{is}\:{a}\:{typo}. \\ $$
Commented by gunawan last updated on 18/Mar/18

$$\mathrm{oh}\:\mathrm{i}'\mathrm{m}\:\mathrm{sorry} \\ $$
Commented by gunawan last updated on 18/Mar/18
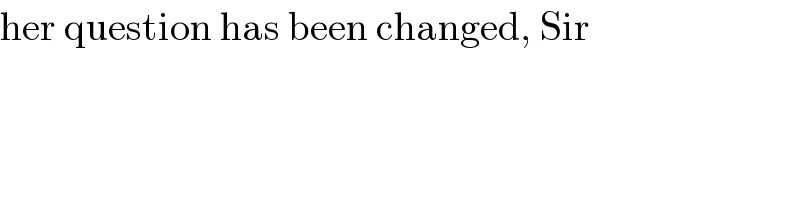
$$\mathrm{her}\:\mathrm{question}\:\mathrm{has}\:\mathrm{been}\:\mathrm{changed},\:\mathrm{Sir} \\ $$
Answered by ajfour last updated on 18/Mar/18
![=lim_(n→0) n[(1/n)Σ_(r=1) ^n ((r/n))^n ] =lim_(n→0) n∫_0 ^( 1) x^n dx = lim_(n→0) (n/(n+1)) = 1 .](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q32016.png)
$$=\underset{{n}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:{n}\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}\underset{{r}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\left(\frac{{r}}{{n}}\right)^{{n}} \right] \\ $$$$=\underset{{n}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:{n}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\:\mathrm{1}} {x}^{{n}} {dx}\:=\:\underset{{n}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{{n}}{{n}+\mathrm{1}}\:=\:\mathrm{1}\:\:. \\ $$
Commented by gunawan last updated on 18/Mar/18

$$\mathrm{wow} \\ $$$$\mathrm{thank}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{very}\:\mathrm{much}\:\mathrm{sir} \\ $$
Commented by gunawan last updated on 18/Mar/18

$$\mathrm{sorry}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{touch} \\ $$
