Question Number 63267 by Tawa1 last updated on 01/Jul/19
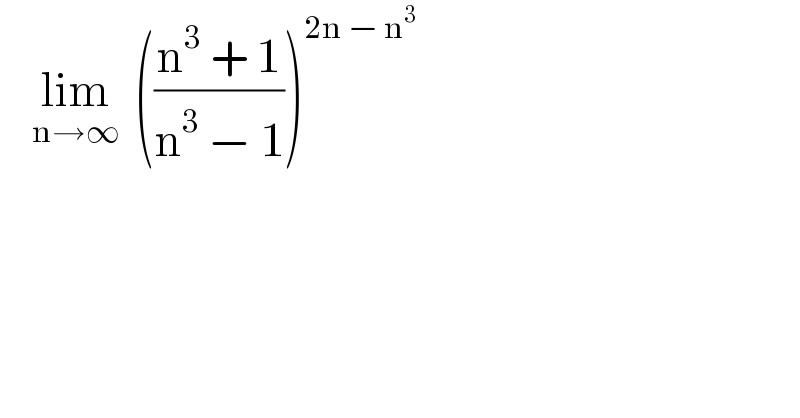
$$\:\:\:\:\underset{\mathrm{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{3}} \:+\:\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{3}} \:−\:\mathrm{1}}\right)^{\mathrm{2n}\:−\:\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{3}} } \\ $$
Commented by Tawa1 last updated on 01/Jul/19
$$\mathrm{God}\:\mathrm{bless}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{sir} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 01/Jul/19
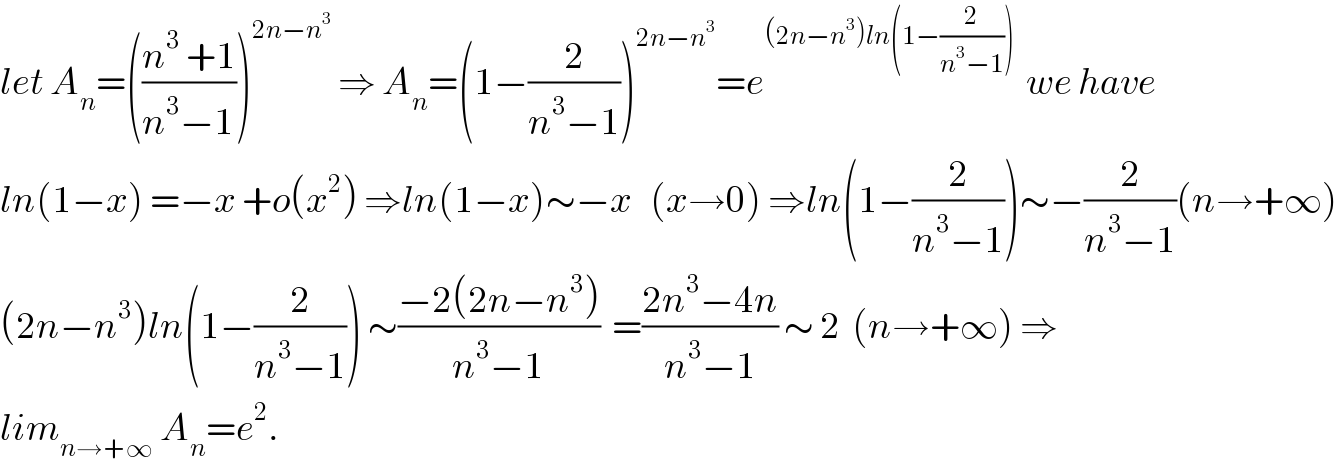
$${let}\:{A}_{{n}} =\left(\frac{{n}^{\mathrm{3}} \:+\mathrm{1}}{{n}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{1}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}{n}−{n}^{\mathrm{3}} } \:\Rightarrow\:{A}_{{n}} =\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{n}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{1}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}{n}−{n}^{\mathrm{3}} } ={e}^{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}−{n}^{\mathrm{3}} \right){ln}\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{n}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{1}}\right)} \:\:{we}\:{have} \\ $$$${ln}\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)\:=−{x}\:+{o}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\:\Rightarrow{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)\sim−{x}\:\:\:\left({x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}\right)\:\Rightarrow{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{n}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{1}}\right)\sim−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{n}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{1}}\left({n}\rightarrow+\infty\right) \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{2}{n}−{n}^{\mathrm{3}} \right){ln}\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{n}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{1}}\right)\:\sim\frac{−\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{2}{n}−{n}^{\mathrm{3}} \right)}{{n}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{1}}\:\:=\frac{\mathrm{2}{n}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{4}{n}}{{n}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{1}}\:\sim\:\mathrm{2}\:\:\left({n}\rightarrow+\infty\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} \:{A}_{{n}} ={e}^{\mathrm{2}} . \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 02/Jul/19

$${you}\:{are}\:{welcome}. \\ $$
